Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Obesity is a highly burdensome public health issue associated with premature death, multiple comorbid disabilities and staggering healthcare costs. Between 1980-2000, the prevalence of obesity among children and adolescents nearly tripled. Obesity subjects youth to social stigmatization and discrimination. These economic and personal burdens mandate targeted prevention and detection educational programs for all individuals at risk. The most cost-effective method of approaching this obesity epidemic is through education of health professionals. METHODS: As part of an "Obesity Prevention in Pediatrics" curriculum, postgraduate-year (PGY)-2 residents first observed and then participated in the dietary evaluation and counseling of pediatric patients and their families. Attitudinal questionnaires, multiple-choice knowledge examinations and a pre-established checklist of desired skills and behaviors provided evaluation of the curriculum's effect on the participants' ability and willingness to manage actually obese or at-risk pediatric patients and their families. RESULTS: Attitudinal survey and knowledge test scores from control PGY-3 residents generally confirmed that their knowledge and counseling skills on obesity prevention and management were well below expectation. Following participation in the curriculum, study residents' knowledge tended to improve, as did their level of comfort in counseling obese and at-risk children, adolescents and their parents. CONCLUSION: Implementation of an "Obesity Prevention in Pediatrics" curriculum appears to improve participants' knowledge base as well as their skills and level of personal comfort in the recognition, evaluation and management, including counseling, of both obese and at-risk pediatric patients and their families.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birch L. L., Fisher J. O. Development of eating behaviors among children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 1998 Mar;101(3 Pt 2):539–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison K. K., Birch L. L. Weight status, parent reaction, and self-concept in five-year-old girls. Pediatrics. 2001 Jan;107(1):46–53. doi: 10.1542/peds.107.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. H., Myers M. D., Raynor H. A., Saelens B. E. Treatment of pediatric obesity. Pediatrics. 1998 Mar;101(3 Pt 2):554–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. M., Newton R. W., Ruta D. A., MacDonald T. M., Morris A. D. Socio-economic status, obesity and prevalence of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2000 Jun;17(6):478–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn Kevin, Johannsen Neil, Specker Bonny. Factors associated with physical activity in preschool children. J Pediatr. 2002 Jan;140(1):81–85. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2002.120693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman D. S., Khan L. K., Dietz W. H., Srinivasan S. R., Berenson G. S. Relationship of childhood obesity to coronary heart disease risk factors in adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 2001 Sep;108(3):712–718. doi: 10.1542/peds.108.3.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galuska D. A., Will J. C., Serdula M. K., Ford E. S. Are health care professionals advising obese patients to lose weight? JAMA. 1999 Oct 27;282(16):1576–1578. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.16.1576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
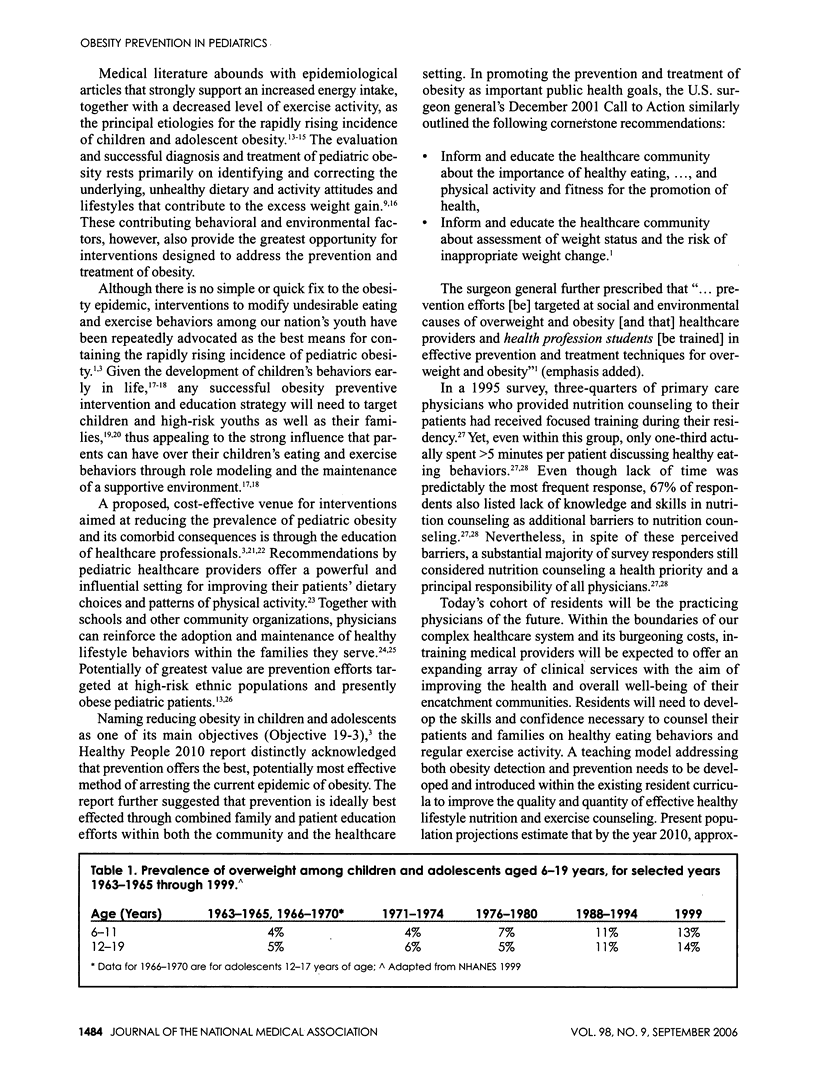
- Gortmaker S. L., Must A., Perrin J. M., Sobol A. M., Dietz W. H. Social and economic consequences of overweight in adolescence and young adulthood. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 30;329(14):1008–1012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309303291406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gortmaker S. L., Peterson K., Wiecha J., Sobol A. M., Dixit S., Fox M. K., Laird N. Reducing obesity via a school-based interdisciplinary intervention among youth: Planet Health. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999 Apr;153(4):409–418. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.153.4.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. O., Peters J. C. Environmental contributions to the obesity epidemic. Science. 1998 May 29;280(5368):1371–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5368.1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner R. F. Barriers to providing nutrition counseling by physicians: a survey of primary care practitioners. Prev Med. 1995 Nov;24(6):546–552. doi: 10.1006/pmed.1995.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner R. F., McGaghie W. C., Pendarvis L. Medical residency training in the management of obesity. Acad Med. 2000 May;75(5):550–550. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200005000-00080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisacano J. C., Lichter H., Ritter J., Siegal A. P. An attempt at prevention of obesity in infancy. Pediatrics. 1978 Mar;61(3):360–364. doi: 10.1542/peds.61.3.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. N., Chang J. Y., Haydel K. F., Killen J. D. Overweight concerns and body dissatisfaction among third-grade children: the impacts of ethnicity and socioeconomic status. J Pediatr. 2001 Feb;138(2):181–187. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2001.110526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
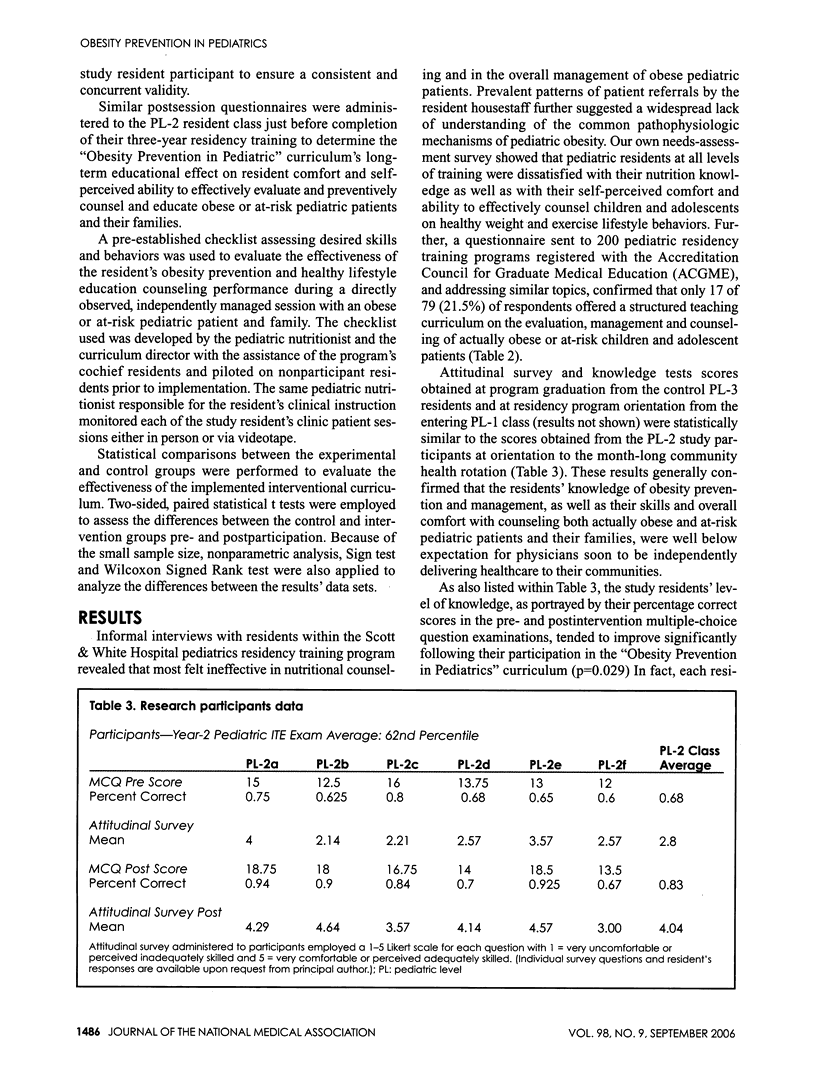
- Story Mary T., Neumark-Stzainer Dianne R., Sherwood Nancy E., Holt Katrina, Sofka Denise, Trowbridge Frederick L., Barlow Sarah E. Management of child and adolescent obesity: attitudes, barriers, skills, and training needs among health care professionals. Pediatrics. 2002 Jul;110(1 Pt 2):210–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss R. S., Pollack H. A. Epidemic increase in childhood overweight, 1986-1998. JAMA. 2001 Dec 12;286(22):2845–2848. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.22.2845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss R. S., Rodzilsky D., Burack G., Colin M. Psychosocial correlates of physical activity in healthy children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001 Aug;155(8):897–902. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.155.8.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm Roland. The effects of obesity, smoking, and drinking on medical problems and costs. Health Aff (Millwood) 2002 Mar-Apr;21(2):245–253. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.21.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treviño R. P., Marshall R. M., Jr, Hale D. E., Rodriguez R., Baker G., Gomez J. Diabetes risk factors in low-income Mexican-American children. Diabetes Care. 1999 Feb;22(2):202–207. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.2.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troiano R. P., Flegal K. M. Overweight children and adolescents: description, epidemiology, and demographics. Pediatrics. 1998 Mar;101(3 Pt 2):497–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomilehto J., Lindström J., Eriksson J. G., Valle T. T., Hämäläinen H., Ilanne-Parikka P., Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S., Laakso M., Louheranta A., Rastas M. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001 May 3;344(18):1343–1350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200105033441801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker R. C., Wright J. A., Pepe M. S., Seidel K. D., Dietz W. H. Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. N Engl J Med. 1997 Sep 25;337(13):869–873. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199709253371301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf A. M., Colditz G. A. Current estimates of the economic cost of obesity in the United States. Obes Res. 1998 Mar;6(2):97–106. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1998.tb00322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Writing Group for the Activity Counseling Trial Research Group Effects of physical activity counseling in primary care: the Activity Counseling Trial: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2001 Aug 8;286(6):677–687. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.6.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


