Abstract
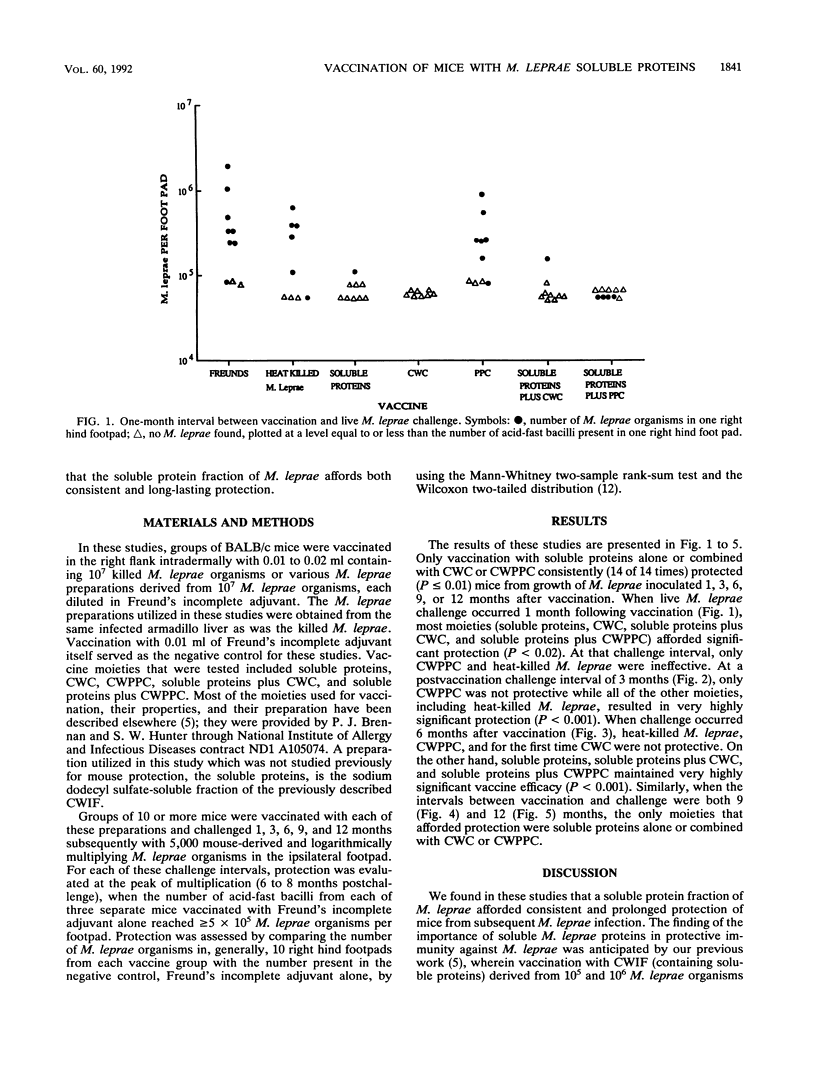
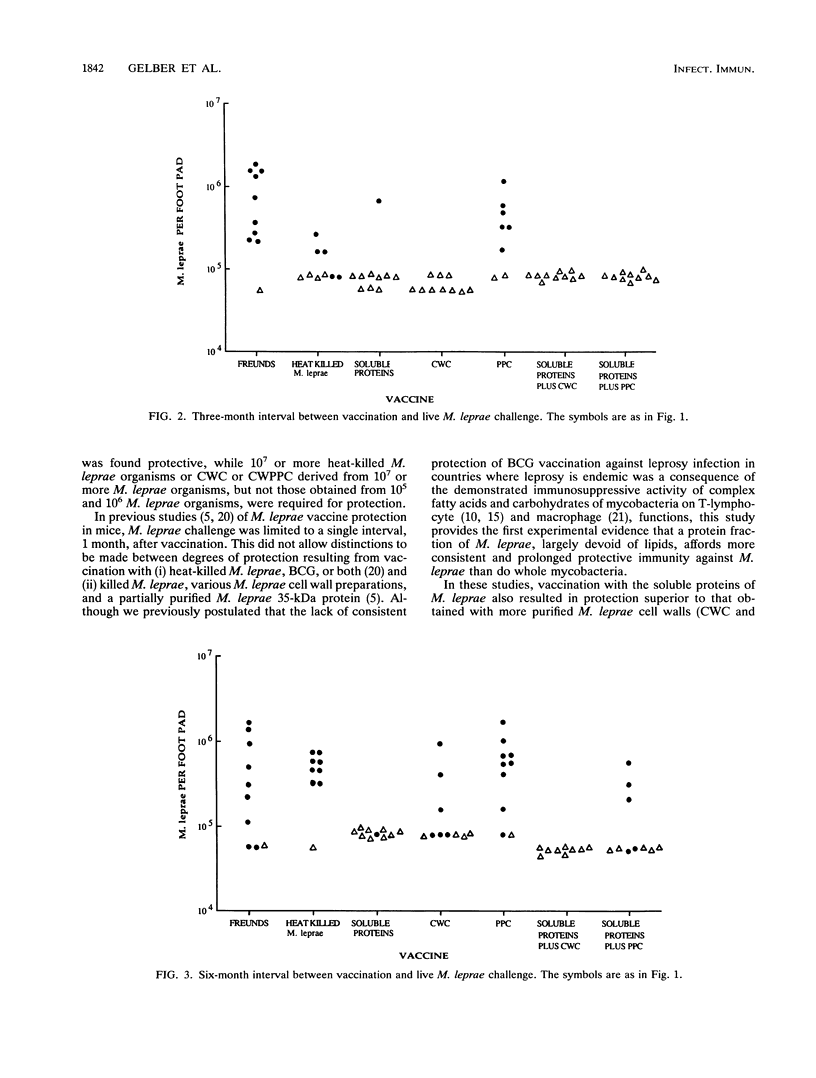
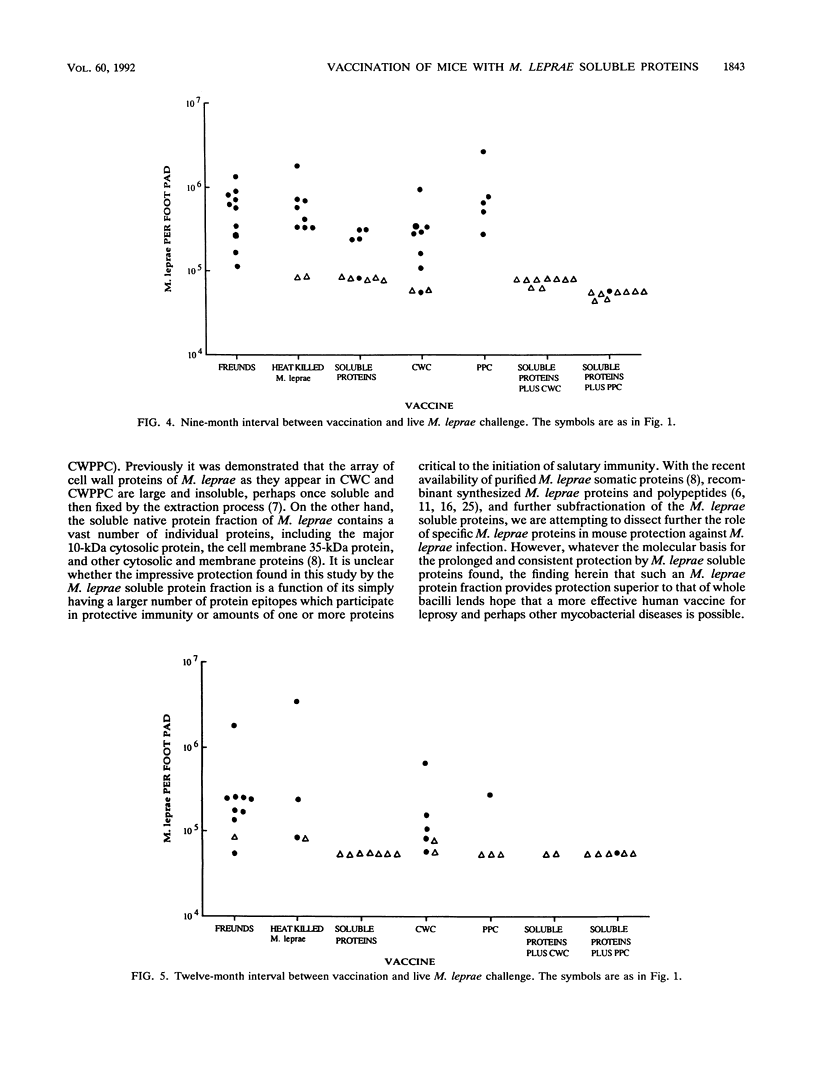
Groups of BALB/c mice were vaccinated intradermally with either Freund's incomplete adjuvant (FIA) alone, 10(7) heat-killed Mycobacterium leprae organisms in FIA, or a number of fractions of M. leprae containing soluble and/or cell wall components. At 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months later, vaccinated mice were challenged in the right hind footpad with 5,000 live M. leprae organisms, and vaccine protection was assessed 6 to 8 months later, at the peak of M. leprae multiplication in the negative control (FIA alone), by the two-sample rank-sum test. In these studies, a cell wall fraction rich in peptidoglycan was consistently ineffective. Both heat-killed M. leprae and a fraction containing cell wall and fixed proteins generally protected when the interval between vaccination and challenge was 1 or 3 months but not subsequently. On the other hand, soluble proteins of M. leprae alone or in combination (with cell wall fractions) consistently (14 of 14 instances) afforded highly significant protection (P less than or equal to 0.01) at all challenge intervals up to 1 year after vaccination. These results suggest that the soluble protein fraction of M. leprae offers promise for a vaccine against leprosy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom B. R., Godal T. Selective primary health care: strategies for control of disease in the developing world. V. Leprosy. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):765–780. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock G. W., Palmer C. E. Long-term results of BCG vaccination in the southern United States. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966 Feb;93(2):171–183. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1966.93.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock G. W., Webster R. G. Tuberculosis studies in Muscogee County, Georgia. VII. A twenty-year evaluation of BCG vaccination in a school population. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Dec;100(6):839–845. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.100.6.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frimodt-Möller J., Acharyulu G. S., Pillai K. K. Observation concernant l'effet protecteur de la vaccination BCG parmi une population rurale du sud de l'Inde: quatrième rapport. Bull Int Union Tuberc. 1973 Jun;48(0):40–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelber R. H., Brennan P. J., Hunter S. W., Munn M. W., Monson J. M., Murray L. P., Siu P., Tsang M., Engleman E. G., Mohagheghpour N. Effective vaccination of mice against leprosy bacilli with subunits of Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):711–718. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.711-718.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. P., Bäckström B. T., Booth R. J., Love S. G., Harding D. R., Watson J. D. The mapping of epitopes of the 18-kDa protein of Mycobacterium leprae recognized by murine T cells in a proliferation assay. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):2006–2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., McNeil M., Modlin R. L., Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Brennan P. J. Isolation and characterization of the highly immunogenic cell wall-associated protein of Mycobacterium leprae. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2864–2872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Gandhi R. R., Weinstein D. E., Levis W. R., Patarroyo M. E., Brennan P. J., Cohn Z. A. Mycobacterium leprae antigen-induced suppression of T cell proliferation in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):3028–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb F. I., Kingston A. E., Estrada I., Colston M. J. Heterologous expression of the 65-kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium leprae and murine T-cell responses to the gene product. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1237–1241. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1237-1241.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lwin K., Sundaresan T., Gyi M. M., Bechelli L. M., Tamondong C., Garbajosa P. G., Sansarricq H., Noordeen S. K. BCG vaccination of children against leprosy: fourteen-year findings of the trial in Burma. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(6):1069–1078. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Bajardi A. C., Grisso C. L., Sieling P. A., Alland D., Convit J., Fan X. D., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. A major T cell antigen of Mycobacterium leprae is a 10-kD heat-shock cognate protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):275–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Brennan P. J., Rada E., Convit J., Bloom B. R. Lymphocyte suppression in leprosy induced by unique M. leprae glycolipid. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):194–196. doi: 10.1038/308194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomaguchi H., Matsuoka M., Kohsaka K., Nakata A., Ito T. Overproduction, affinity purification and characterization of 65-kDa protein of Mycobacterium leprae in Escherichia coli. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1989 Dec;57(4):817–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENTHAL S. R., LOEWINSOHNE, GRAHAM M. L., LIVERIGHT D., THORNE G., JOHNSON V. BCG vaccination against tuberculosis in Chicago. A twenty-year study statistically analyzed. Pediatrics. 1961 Oct;28:622–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN S. C., ARONSON J. D. The occurrence of pulmonary lesions in BCG-vaccinated and unvaccinated persons. Am Rev Tuberc. 1953 Nov;68(5):695–712. doi: 10.1164/art.1953.68.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., van Landingham R. M., Walker L. L., Ye S. Z. Comparison of the immunogenicity of vaccines prepared from viable Mycobacterium bovis BCG, heat-killed Mycobacterium leprae, and a mixture of the two for normal and M. leprae-tolerant mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1096–1103. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1096-1103.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J., Krahenbuhl J. L. Mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan inhibits gamma interferon-mediated activation of macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1232–1236. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1232-1236.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley S. J., Howland C., Stone M. M., Sutherland I. BCG vaccination of children against leprosy in Uganda: final results. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Oct;87(2):233–248. doi: 10.1017/s002217240006945x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thangaraj H. S., Lamb F. I., Davis E. O., Jenner P. J., Jeyakumar L. H., Colston M. J. Identification, sequencing, and expression of Mycobacterium leprae superoxide dismutase, a major antigen. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1937–1942. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1937-1942.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


