Abstract
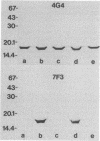
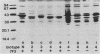
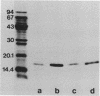
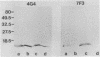
The P6 outer membrane protein is a highly conserved molecule which is present on the surface of all strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Sixty strains of nontypeable H. influenzae which caused invasive disease or colonized the female urogenital tract were studied with monoclonal antibodies 7F3 and 4G4, which recognize different surface-exposed epitopes on the P6 molecule. All 60 strains expressed the epitope recognized by 4G4, whereas 47 of 60 strains expressed the epitope recognized by antibody 7F3. The 7F3-nonreactive strains were all biotype 4 and were recovered from the blood of neonates or postpartum women or from the female urogenital tract. The P6 genes from two 7F3-nonreactive strains were cloned, and the nucleotide sequences were determined. Analysis of amino acid sequences, immunoassays with synthetic peptides, and site-directed mutation of the P6 gene indicate that the epitope recognized by antibody 7F3 is conformational and that the sequence Asp-Ile-Thr is critical in maintaining the conformation of the epitope. We conclude that the unusually virulent clone family of biotype 4 strains of nontypeable H. influenzae express a variant P6 molecule which has an alteration in a highly conserved surface-exposed epitope.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Back A. E., Oberhofer T. R. Use of the Minitek system for biotyping Haemophilus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Mar;7(3):312–313. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.3.312-313.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branefors P., Elgefors B., Olegård R. Intrauterine infection by non-capsulated Haemophilus influenzae in a case of maternal immunodeficiency. Scand J Infect Dis. 1980;12(1):70–73. doi: 10.3109/inf.1980.12.issue-1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campognone P., Singer D. B. Neonatal sepsis due to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Am J Dis Child. 1986 Feb;140(2):117–121. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1986.02140160035025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverdale C. H., Temple G. S. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of non-serotypable strains of Haemophilus influenzae. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Apr;42(4):409–413. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deich R. A., Metcalf B. J., Finn C. W., Farley J. E., Green B. A. Cloning of genes encoding a 15,000-dalton peptidoglycan-associated outer membrane lipoprotein and an antigenically related 15,000-dalton protein from Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):489–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.489-498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Shahidi A. Postpartum bacteremia due to Haemophilus influenzae. Report of two cases. Obstet Gynecol. 1969 Sep;34(3):403–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Corrado M. L., Cleri D., Sierra M. F. Non-type b Haemophilus influenzae infections in adults with reference to biotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):669–671. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.669-671.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenbach D. A., Buchanan T. M., Pollock H. M., Forsyth P. S., Alexander E. R., Lin J. S., Wang S. P., Wentworth B. B., MacCormack W. M., Holmes K. K. Polymicrobial etiology of acute pelvic inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 24;293(4):166–171. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507242930403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H. Meningitis caused by nontypable Haemophilus influenzae in a four-month-old infant. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Mar;10(3):254–255. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199103000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrand R. J. Haemophilus influenzae infections of the genital tract. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Aug;4(3):357–358. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen C. A., Cho C. T. Characteristic features of neonatal sepsis due to Haemophilus influenzae. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):777–780. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Metcalf B. J., Quinn-Dey T., Kirkley D. H., Quataert S. A., Deich R. A. A recombinant non-fatty acylated form of the Hi-PAL (P6) protein of Haemophilus influenzae elicits biologically active antibody against both nontypeable and type b H. influenzae. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3272–3278. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3272-3278.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld K., van Alphen L., van Ketel R. J., Geelen-van den Broek L., Eijk P. P., Zanen H. C. Nonculture detection of Haemophilus influenzae in sputum with monoclonal antibodies specific for outer membrane lipoprotein P6. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2263–2267. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2263-2267.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Antigenic heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae is a basis for a serotyping system. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.15-21.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Campagnari A. A., Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A. Antigenic characterization of the P6 protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.774-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Rice P. A., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Apicella M. A. Identification of a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein on nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a target for human serum bactericidal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. Identification of a specific epitope of Haemophilus influenzae on a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Selander R. K. Genetic relationships of serologically nontypable and serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):183–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.183-191.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A., Murphy T. F., Vankeulen H., Spotila L. D., Rekosh D. Cloning and sequencing of Haemophilus influenzae outer membrane protein P6. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):128–134. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.128-134.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. B., Munson R. S., Jr, Apicella M. A., Sikkema D. J., Molleston J. P., Murphy T. F. Molecular conservation of the P6 outer membrane protein among strains of Haemophilus influenzae: analysis of antigenic determinants, gene sequences, and restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2658–2663. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2658-2663.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris K., Norris F., Christiansen L., Fiil N. Efficient site-directed mutagenesis by simultaneous use of two primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5103–5112. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhofer T. R., Back A. E. Biotypes of Haemophilus encountered in clinical laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):168–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.168-174.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quentin R., Goudeau A., Wallace R. J., Jr, Smith A. L., Selander R. K., Musser J. M. Urogenital, maternal and neonatal isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: identification of unusually virulent serologically non-typable clone families and evidence for a new Haemophilus species. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jul;136(7):1203–1209. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-7-1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quentin R., Musser J. M., Mellouet M., Sizaret P. Y., Selander R. K., Goudeau A. Typing of urogenital, maternal, and neonatal isolates of Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae in correlation with clinical source of isolation and evidence for a genital specificity of H. influenzae biotype IV. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2286–2294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2286-2294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. L., Mills J., Hadley K. W., Blumenstock E., Schachter J., Robbie M. O., Draper D. L. Use of laparoscopy to determine the microbiologic etiology of acute salpingitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1979 May 1;134(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(79)90798-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:329–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]