Abstract
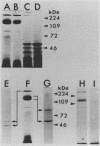
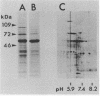
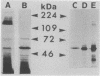
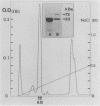
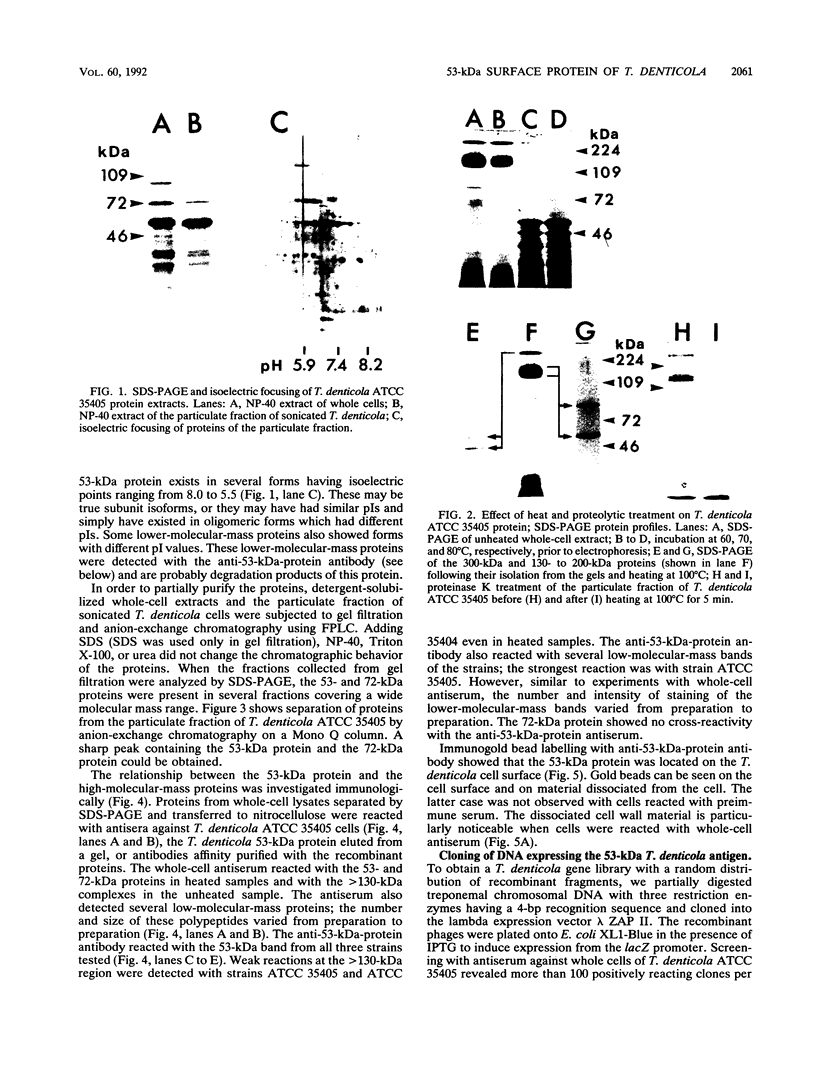
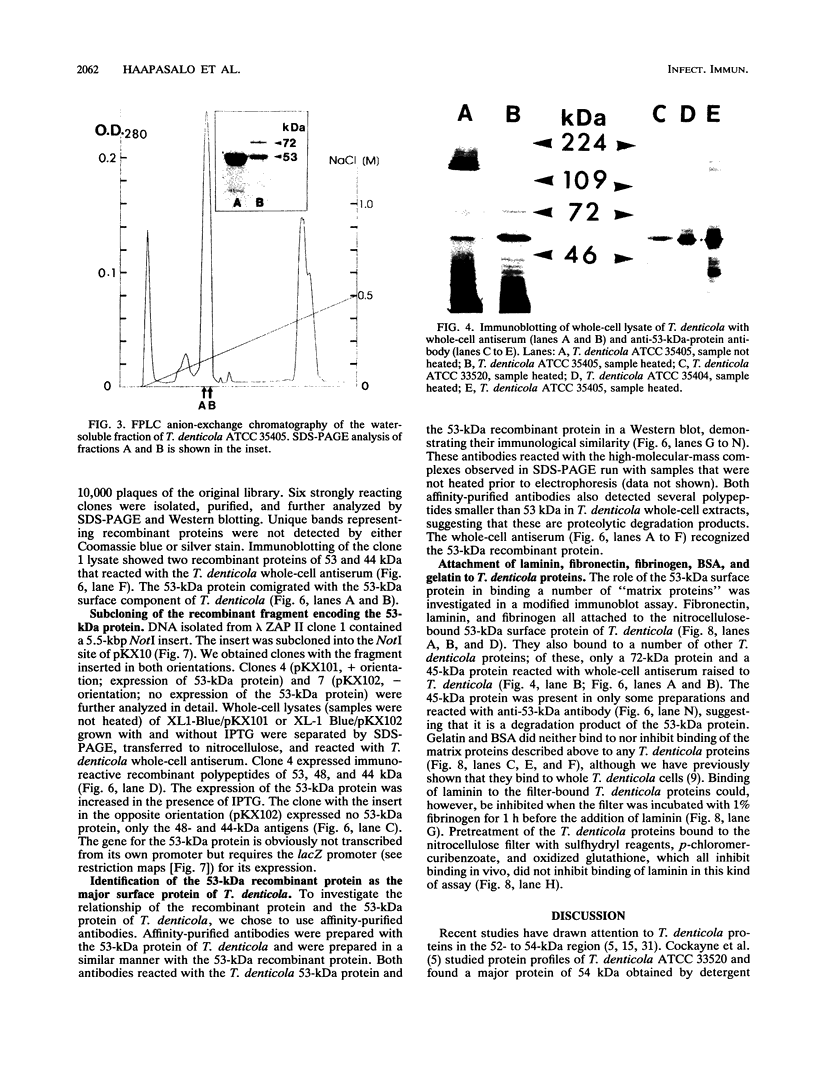
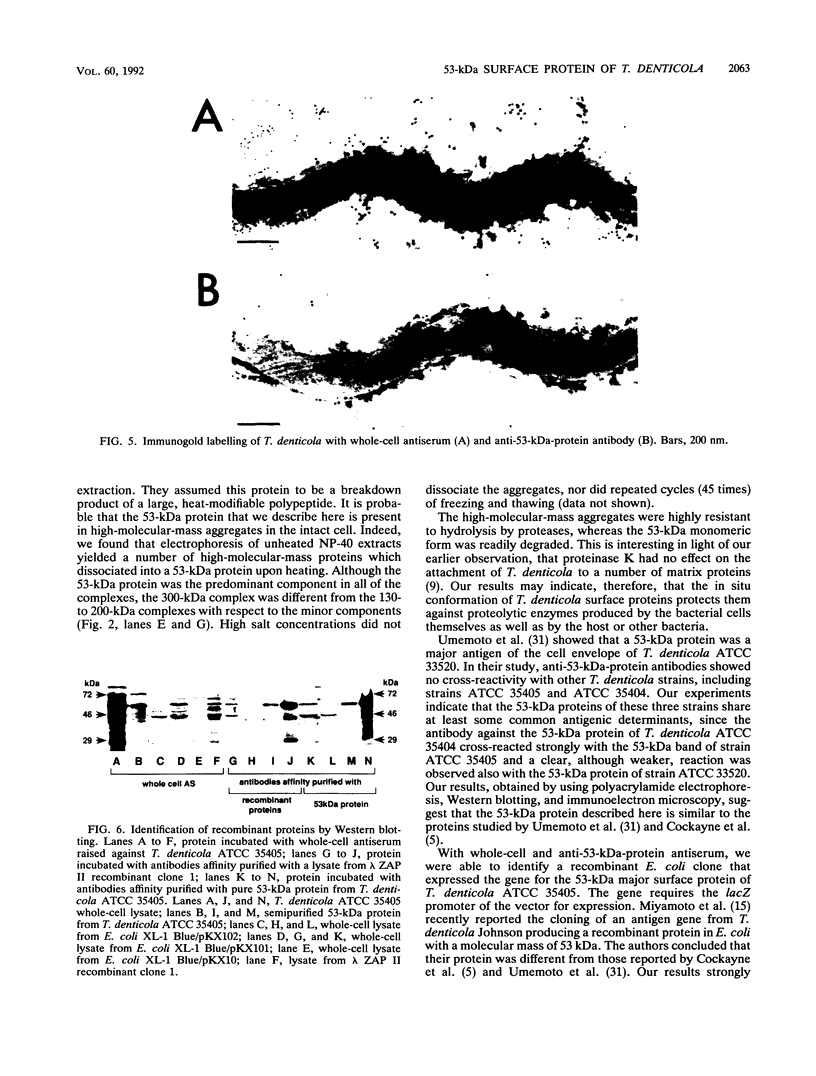
Treponema denticola surface proteins were studied for their biochemical and biological characteristics. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis of detergent extracts of whole cells revealed a major protein of 53 kDa and a number of minor proteins. Antiserum raised against whole cells of T. denticola ATCC 35405 reacted with the 53-kDa protein and a 72-kDa protein but not with the other proteins. Immunoelectron microscopy with anti-53-kDa-protein antibodies showed that the 53-kDa protein is located on the surface of the cell. SDS-PAGE analysis of unheated samples indicated that the 53-kDa protein is the major component of oligomers with molecular masses ranging from 130 to 300 kDa. Western blot (immunoblot) analysis showed that the high-molecular-mass oligomers reacted with whole-cell antiserum and anti-53-kDa-protein antibody. The aggregates dissociated into their subunits after heating to 70 degrees C. Isoelectric focusing followed by SDS-PAGE indicated that the 53-kDa protein was separated into several forms with apparent pI values ranging from 8.0 to 5.5. The oligomeric forms were highly resistant to proteolysis by trypsin and proteinase K, whereas the monomeric proteins were readily digested. A clone expressing a 53-kDa antigen in Escherichia coli was isolated from a lambda ZAP II DNA library of T. denticola ATCC 35405. The recombinant protein had exactly the same molecular mass as the major 53-kDa T. denticola surface protein and reacted with antisera raised against this protein. The role of T. denticola ATCC 35405 surface proteins in attachment to laminin, fibronectin, gelatin, fibrinogen, and bovine serum albumin (BSA) was studied by a modified Western blot binding assay. Fibronectin, laminin, and fibrinogen attached to the 53-kDa surface protein of T. denticola as well as to a 72-kDa protein, whereas no attachment to gelatin or BSA was observed. Attachment could be inhibited by pretreating the blots with fibrinogen but not with gelatin or BSA. Our results suggest that the 53-kDa major surface protein of T. denticola may play a role in the attachment to host proteins and may thus be an important virulence determinant of this species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage G. C., Dickinson W. R., Jenderseck R. S., Levine S. M., Chambers D. W. Relationship between the percentage of subgingival spirochetes and the severity of periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1982 Sep;53(9):550–556. doi: 10.1902/jop.1982.53.9.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehringer H., Berthold P. H., Taichman N. S. Studies on the interaction of human neutrophils with plaque spirochetes. J Periodontal Res. 1986 May;21(3):195–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1986.tb01452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimasoni G., McBride B. C. Adherence of Treponema denticola to modified hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res. 1987 Dec;66(12):1727–1729. doi: 10.1177/00220345870660120601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockayne A., Sanger R., Ivic A., Strugnell R. A., MacDougall J. H., Russell R. R., Penn C. W. Antigenic and structural analysis of Treponema denticola. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3209–3218. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. R., Ellen R. P. Tip-oriented adherence of Treponema denticola to fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3924–3928. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3924-3928.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiehn N. E. Enzyme activities from eight small-sized oral spirochetes. Scand J Dent Res. 1986 Apr;94(2):132–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1986.tb01377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier D., Uitto V. J., McBride B. C. Cellular location of a Treponema denticola chymotrypsinlike protease and importance of the protease in migration through the basement membrane. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):347–351. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.347-351.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapasalo M., Singh U., McBride B. C., Uitto V. J. Sulfhydryl-dependent attachment of Treponema denticola to laminin and other proteins. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4230–4237. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4230-4237.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listgarten M. A., Levin S. Positive correlation between the proportions of subgingival spirochetes and motile bacteria and susceptibility of human subjects to periodontal deterioration. J Clin Periodontol. 1981 Apr;8(2):122–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1981.tb02352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Syed S. A., Schmidt E., Morrison E. C. Bacterial profiles of subgingival plaques in periodontitis. J Periodontol. 1985 Aug;56(8):447–456. doi: 10.1902/jop.1985.56.8.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Noji S., Kokeguchi S., Kato K., Kurihara H., Murayama Y., Taniguchi S. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of antigen gene tdpA of Treponema denticola. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1941–1947. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1941-1947.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Hash D. E., Burmeister J. A., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of severe periodontitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1137–1148. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1137-1148.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta K., Makinen K. K., Loesche W. J. Purification and characterization of an enzyme produced by Treponema denticola capable of hydrolyzing synthetic trypsin substrates. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):213–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.213-220.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen I. Attachment of Treponema denticola to cultured human epithelial cells. Scand J Dent Res. 1984 Feb;92(1):55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1984.tb00860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijntjens F. M., Mikx F. H., Wolters-Lutgerhorst J. M., Maltha J. C. Adherence of oral treponemes and their effect on morphological damage and detachment of epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):642–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.642-647.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saglie F. R., Carranza F. A., Jr, Newman M. G., Cheng L., Lewin K. J. Identification of tissue-invading bacteria in human periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Sep;17(5):452–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saglie R., Newman M. G., Carranza F. A., Jr, Pattison G. L. Bacterial invasion of gingiva in advanced periodontitis in humans. J Periodontol. 1982 Apr;53(4):217–222. doi: 10.1902/jop.1982.53.4.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela M. N., Weinberg A., Borinsky R., Holt S. C., Dishon T. Inhibition of superoxide production in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by oral treponemal factors. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):589–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.589-594.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson L. G., Goodman C. H., Bial J. J., Morton H. E. Quantitative relationship of Treponema denticola to severity of periodontal disease. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):726–728. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.726-728.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson L. G., Goodman C. H., Morton H. E. Quantitative immunoassay of Treponema denticola serovar C in adult periodontitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1493–1496. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1493-1496.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto V. J., Grenier D., Chan E. C., McBride B. C. Isolation of a chymotrypsinlike enzyme from Treponema denticola. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2717–2722. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2717-2722.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemoto T., Namikawa I., Suido H., Asai S. A major antigen on the outer envelope of a human oral spirochete, Treponema denticola. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2470–2474. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2470-2474.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg A., Holt S. C. Interaction of Treponema denticola TD-4, GM-1, and MS25 with human gingival fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1720–1729. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1720-1729.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]