Abstract
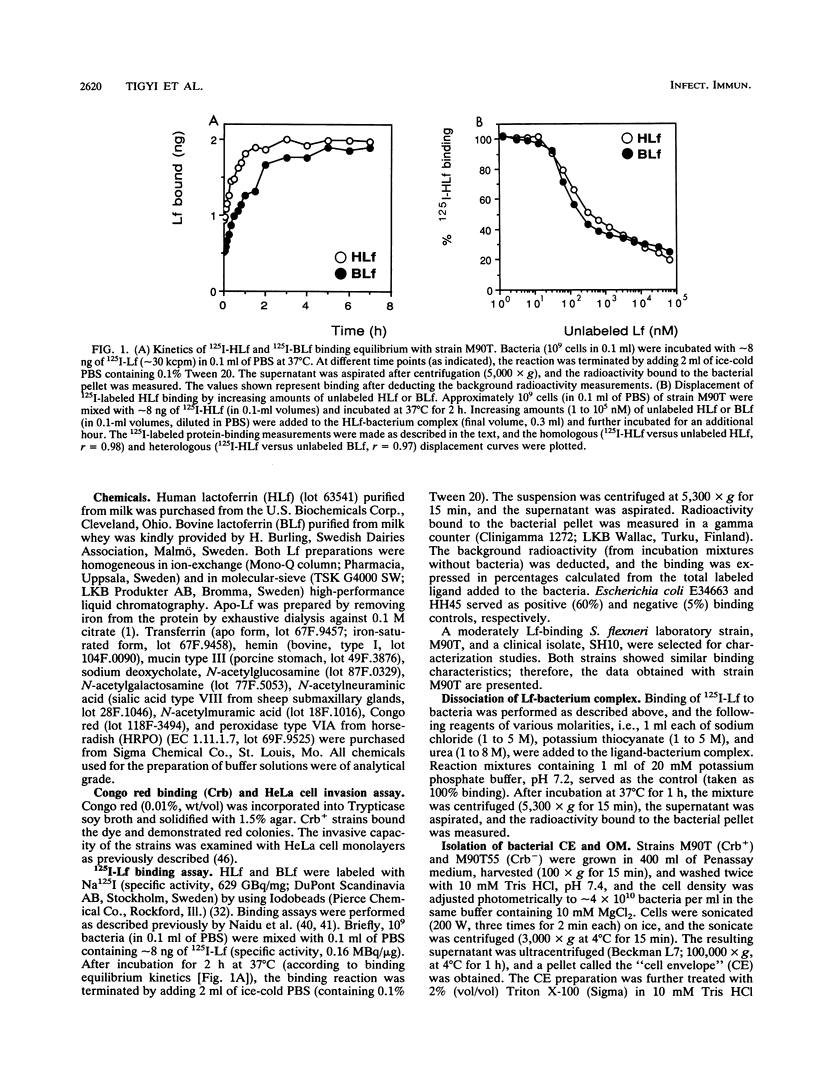
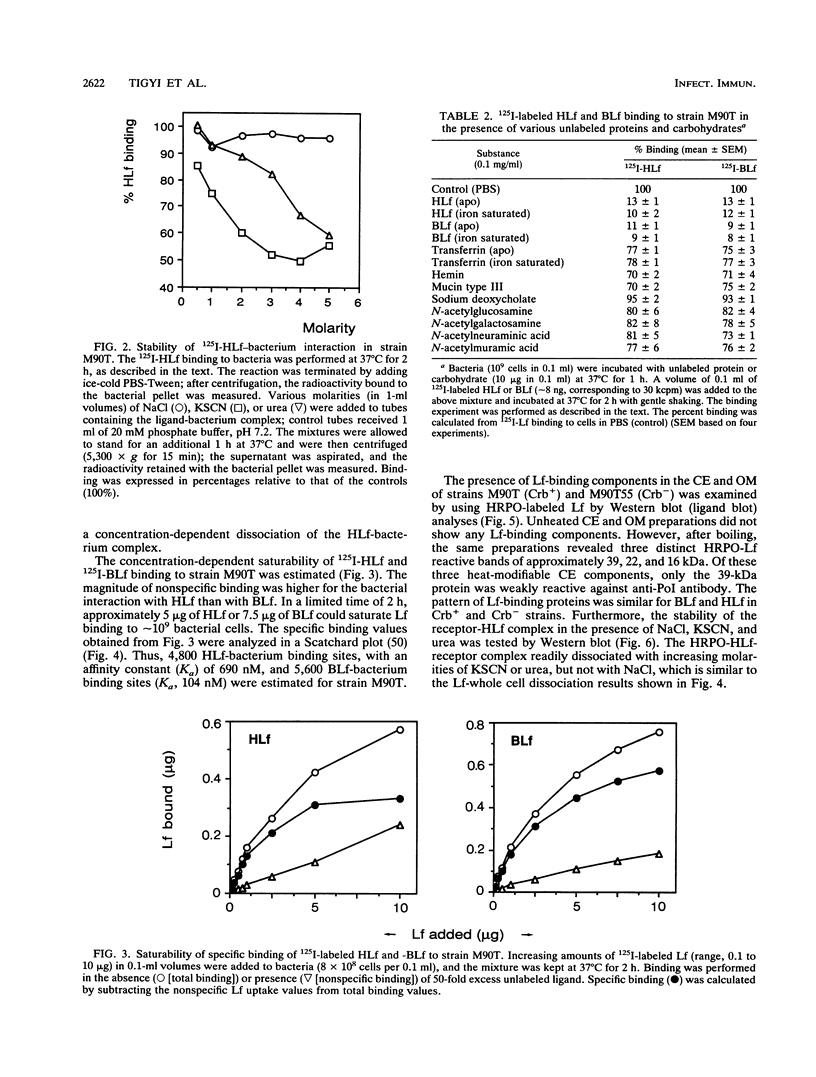
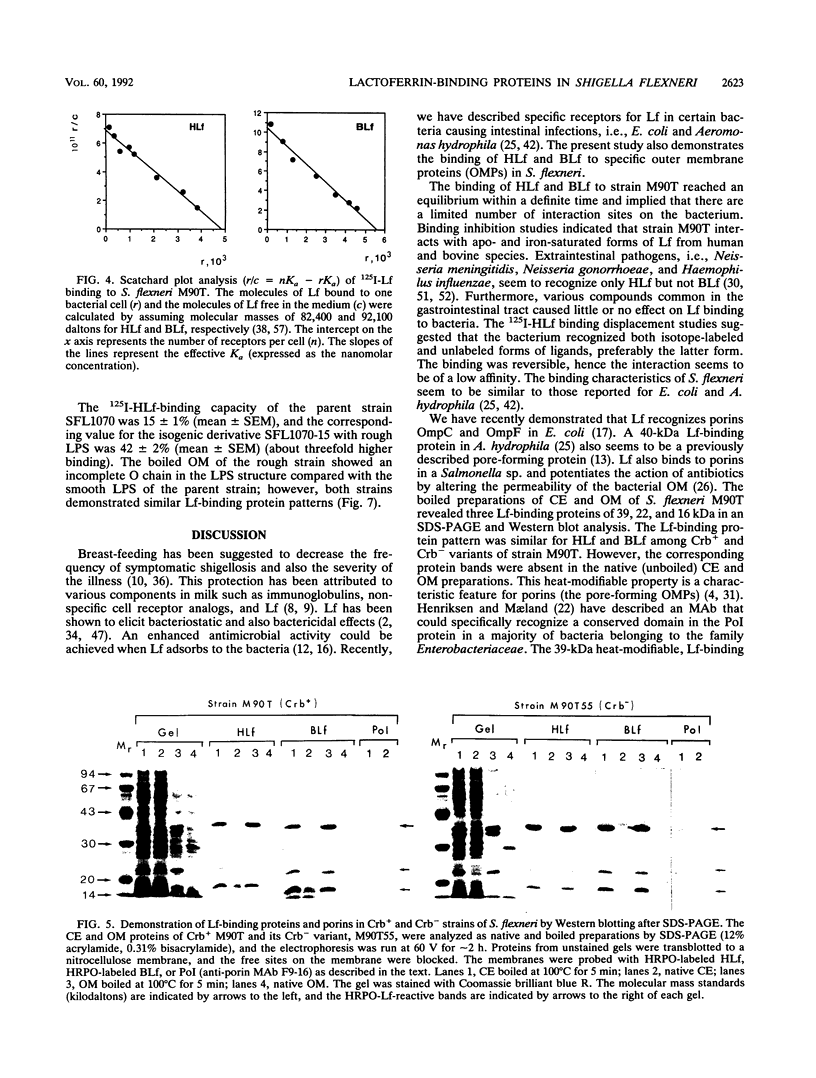
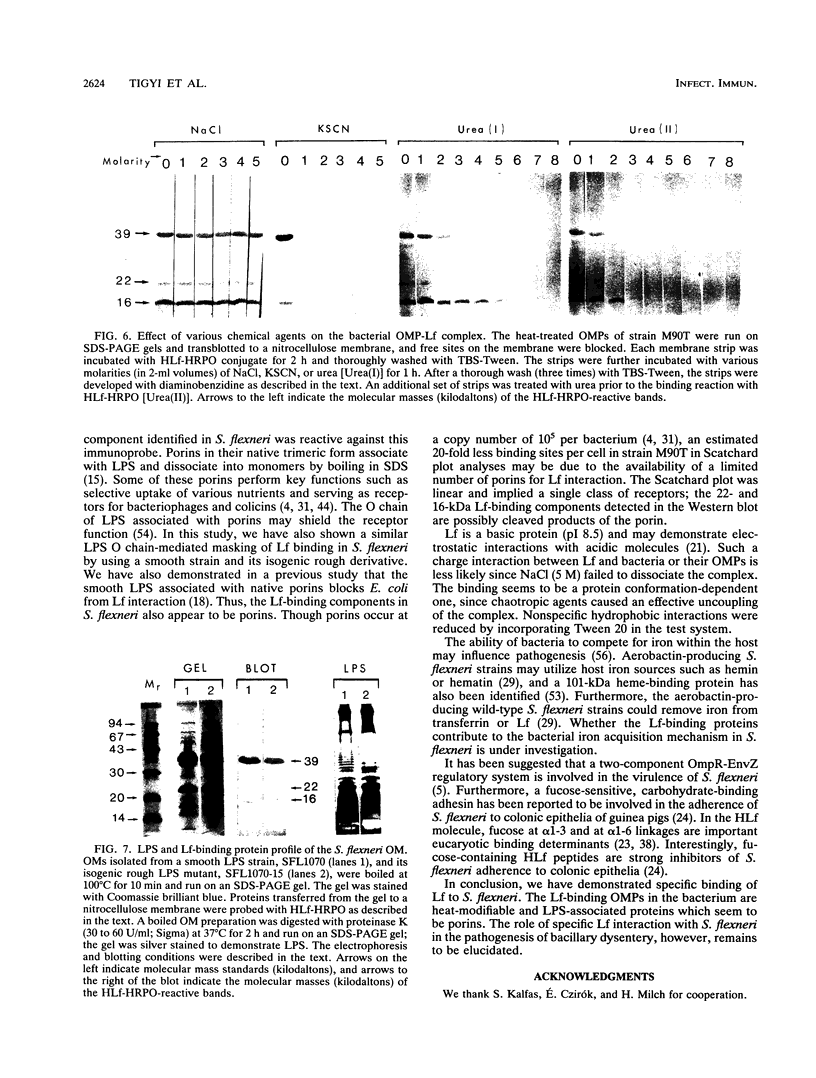
The ability of Shigella flexneri to interact with lactoferrin (Lf) was examined with a 125I-labeled protein-binding assay. The percent binding of human lactoferrin (HLf) and bovine lactoferrin (BLf) to 45 S. flexneri strains was 19 +/- 3 and 21 +/- 3 (mean +/- standard error of the mean), respectively. 125I-labeled HLf and BLf binding to strain M90T reached an equilibrium within 2 h. Unlabeled HLf and BLf displaced the 125I-HLf-bacteria interaction in a dose-dependent manner. The Lf-bacterium complex was uncoupled by KSCN or urea, but not by NaCl. The interaction was specific, and approximately 4,800 HLf binding sites (affinity constant [Ka], 690 nM) or approximately 5,700 BLf binding sites (Ka, 104 nM) per cell were estimated in strain M90T by a Scatchard plot analysis. The native cell envelope (CE) and outer membrane (OM) did not reveal Lf-binding components in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. However, after being boiled, the CE and OM preparations showed three distinct horseradish peroxidase-Lf reactive bands of about 39, 22, and 16 kDa. The 39-kDa component was also reactive to a monoclonal antibody specific for porin (PoI) proteins of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The Lf-binding protein pattern was similar with BLf or HLf, for Crb+ and Crb- strains. The protein-Lf complex was dissociable by KSCN or urea and was stable after treatment with NaCl. Variation (loss) in the O chain of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) markedly enhanced the Lf-binding capacity in the isogenic rough strain SFL1070-15 compared with its smooth parent strain, SFL1070. These data establish that Lf binds to specific components in the bacterial OM; the heat-modifiable, anti-PoI-reactive, and LPS-associated properties suggested that the Lf-binding proteins are porins in S. flexneri.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainscough E. W., Brodie A. M., Plowman J. E., Bloor S. J., Loehr J. S., Loehr T. M. Studies on human lactoferrin by electron paramagnetic resonance, fluorescence, and resonance Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 19;19(17):4072–4079. doi: 10.1021/bi00558a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. R., Cole M. F., McGhee J. R. A bactericidal effect for human lactoferrin. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):263–265. doi: 10.1126/science.327545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., De Duve C., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Association of lactoferrin with specific granules in rabbit heterophil leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Structure and function of porins from gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:359–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Fontaine A., Sansonetti P. J. The two-component regulatory system ompR-envZ controls the virulence of Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6274–6281. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6274-6281.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns M. M. Molecular genetics of virulence in Shigella. Microbiol Sci. 1985 Sep;2(9):275–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgens H. S. The biological significance of lactoferrin in haematology. Scand J Haematol. 1984 Sep;33(3):225–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1984.tb02220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen C. L., Willis A. T. Resistance of the breast-fed infant to gastroenteritis. Br Med J. 1971 Aug 7;3(5770):338–343. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5770.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary T. G., Winsor D. K., Reich D., Ruiz-Palacios G., Calva J. J. Human milk immunoglobulin A antibodies to Shigella virulence determinants. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1675–1679. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1675-1679.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens J. D., Stanton B., Stoll B., Shahid N. S., Banu H., Chowdhury A. K. Breast feeding as a determinant of severity in shigellosis. Evidence for protection throughout the first three years of life in Bangladeshi children. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Apr;123(4):710–720. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox T. M., Mazurier J., Spik G., Montreuil J., Peters T. J. Iron binding proteins and influx of iron across the duodenal brush border. Evidence for specific lactotransferrin receptors in the human intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 15;588(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90377-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalmastri C., Valenti P., Visca P., Vittorioso P., Orsi N. Enhanced antimicrobial activity of lactoferrin by binding to the bacterial surface. Microbiologica. 1988 Jul;11(3):225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., MacIntyre S., Buckley J. T., Hancock R. E. Purification and reconstitution in lipid bilayer membranes of an outer membrane, pore-forming protein of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1006–1011. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1006-1011.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich D. L., Stein M. A., Schnaitman C. A. Associations of Escherichia coli K-12 OmpF trimers with rough and smooth lipopolysaccharides. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5307–5311. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5307-5311.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. T., 3rd, Giehl T. J., LaForce F. M. Damage of the outer membrane of enteric gram-negative bacteria by lactoferrin and transferrin. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2774–2781. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2774-2781.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadó I., Erdei J., Laszlo V. G., Pászti J., Czirók E., Kontrohr T., Tóth I., Forsgren A., Naidu A. S. Correlation between human lactoferrin binding and colicin susceptibility in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2538–2543. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Washington O., Formal S. B. Shigellosis due to Shigella dysenteriae. 1. Relative importance of mucosal invasion versus toxin production in pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):523–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman A. Association of lactoferrin with other proteins, as demonstrated by changes in electrophoretic mobility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):380–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen A. Z., Maeland J. A. A conserved domain on enterobacterial porin protein analysed by monoclonal antibody. APMIS. 1991 Jan;99(1):49–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1991.tb05117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V. Clearance and binding of native and defucosylated lactoferrin. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):249–257. doi: 10.1042/bj2120249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izhar M., Nuchamowitz Y., Mirelman D. Adherence of Shigella flexneri to guinea pig intestinal cells is mediated by a mucosal adhesion. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1110–1118. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1110-1118.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore A. R., Erdei J., Naidu S. S., Falsen E., Forsgren A., Naidu A. S. Specific binding of lactoferrin to Aeromonas hydrophila. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Sep 15;67(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90454-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor K. M., Daskaleros P. A., Robinson R. E., Payne S. M. Virulence of iron transport mutants of Shigella flexneri and utilization of host iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):594–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.594-599.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Heremans J. F., Prignot J. J., Wauters G. Immunohistochemical localization and bacteriostatic properties of an iron-binding protein from bronchial mucus. Thorax. 1966 Nov;21(6):538–544. doi: 10.1136/thx.21.6.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Heremans J. F., Schonne E. Lactoferrin, an iron-binding protein in neutrophilic leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):643–658. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L. J., Wyatt R. G. The uniqueness of human milk. Host resistance to infection. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971 Aug;24(8):976–986. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/24.8.976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Sansonetti P. J. Genetic determinants of Shigella pathogenicity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:127–150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz-Boutigue M. H., Jollès J., Mazurier J., Schoentgen F., Legrand D., Spik G., Montreuil J., Jollès P. Human lactotransferrin: amino acid sequence and structural comparisons with other transferrins. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):659–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from lactoferrin. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):915–920. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.915-920.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu A. S., Miedzobrodzki J., Andersson M., Nilsson L. E., Forsgren A., Watts J. L. Bovine lactoferrin binding to six species of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine intramammary infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2312–2319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2312-2319.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu A. S., Miedzobrodzki J., Musser J. M., Rosdahl V. T., Hedström S. A., Forsgren A. Human lactoferrin binding in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Jun;34(6):323–328. doi: 10.1099/00222615-34-6-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu S. S., Erdei J., Czirók E., Kalfas S., Gadó I., Thorén A., Forsgren A., Naidu A. S. Specific binding of lactoferrin to Escherichia coli isolated from human intestinal infections. APMIS. 1991 Dec;99(12):1142–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Nagai T., Nakaya R., Kondo S., Murakami M., Hisatsune K. HeLa cell invasiveness and O antigen of Shigella flexneri as separate and prerequisite attributes of virulence to evoke keratoconjunctivitis in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):505–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.505-513.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D., Reiter B. Inhibition of bacteria by lactoferrin and other iron-chelating agents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):351–365. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. The critical role of iron in host-bacterial interactions. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1428–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI109062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M. Synthesis and utilization of siderophores by Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1420–1424. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1420-1424.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B. Identification of the transferrin- and lactoferrin-binding proteins in Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):121–130. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the human lactoferrin-binding protein from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1144-1149.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stugard C. E., Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. A 101-kilodalton heme-binding protein associated with congo red binding and virulence of Shigella flexneri and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli strains. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3534–3539. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3534-3539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. The involvement of lactoferrin in the hyposideremia of acute inflammation. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1068–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R. E., Szuchet S. The molecular weight of bovine lactoferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 30;393(1):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ley P., de Graaff P., Tommassen J. Shielding of Escherichia coli outer membrane proteins as receptors for bacteriophages and colicins by O-antigenic chains of lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):449–451. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.449-451.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]