Abstract
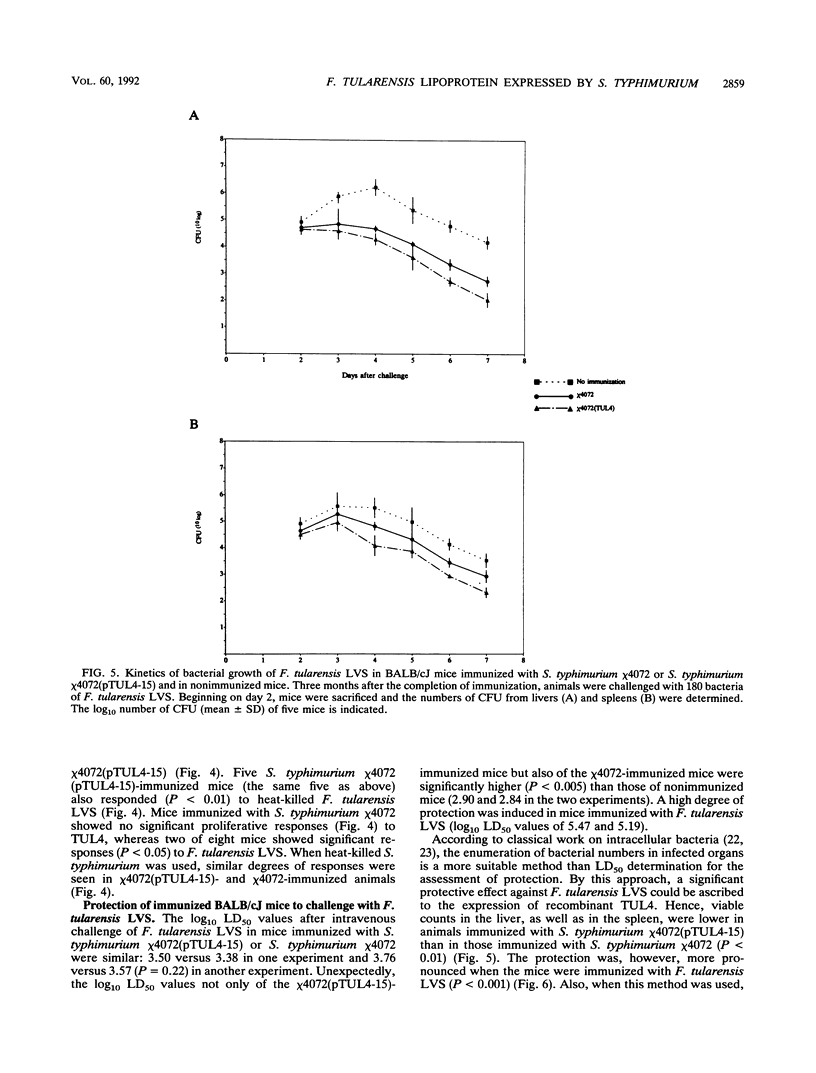
A 17-kDa lipoprotein, TUL4, of the facultative intracellular bacterium Francisella tularensis is one of several membrane proteins that induce an in vitro response in T cells from F. tularensis-primed humans. A DNA fragment of the live vaccine strain F. tularensis LVS encoding TUL4 was cloned into Salmonella typhimurium chi 4072, an attenuated delta cya delta crp mutant. Expression of the protein by the recombinant S. typhimurium chi 4072 (pTUL4-15) was maintained after passage in BALB/cJ mice. When mice were immunized with S. typhimurium chi 4072(pTUL4-15), some animals showed an antibody response and a T-cell response to TUL4. When the immunized mice were challenged with the live vaccine strain F. tularensis LVS, bacterial counts in the liver and spleen were lower than in animals immunized with S. typhimurium chi 4072. Immunization with F. tularensis LVS caused a much stronger protection against the challenge than did immunization with S. typhimurium chi 4072(pTUL4-15). The present study demonstrated that the 17-kDa lipoprotein TUL4 of F. tularensis is involved in a protective immunity to tularemia. Possibly, several T-cell-reactive proteins of the organism have to contribute for optimal protection to be achieved.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A., Kumar S., Jaffe R., Hone D., Gross M., Sadoff J. Oral Salmonella: malaria circumsporozoite recombinants induce specific CD8+ cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1083–1090. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony L. D., Burke R. D., Nano F. E. Growth of Francisella spp. in rodent macrophages. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3291–3296. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3291-3296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony L. S., Kongshavn P. A. Experimental murine tularemia caused by Francisella tularensis, live vaccine strain: a model of acquired cellular resistance. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jan;2(1):3–14. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1951 Sep;62(3):293–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.3.293-300.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berche P., Gaillard J. L., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes as a prerequisite for in vivo induction of T cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2266–2271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Thole J. E., Sathish M., Bosecker B. A., Sela S., de Carvalho E. F., Esser R. E. Protein antigens of Mycobacterium leprae. Res Microbiol. 1990 Sep-Oct;141(7-8):859–871. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Vaccines and cell-mediated immunity. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):371–402. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.371-402.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Goldschmidt R. M., Fletchall N. B., Kelly S. M. Avirulent Salmonella typhimurium delta cya delta crp oral vaccine strains expressing a streptococcal colonization and virulence antigen. Vaccine. 1988 Apr;6(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(88)80020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M. Salmonella typhimurium deletion mutants lacking adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP receptor protein are avirulent and immunogenic. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3035–3043. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3035-3043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortier A. H., Slayter M. V., Ziemba R., Meltzer M. S., Nacy C. A. Live vaccine strain of Francisella tularensis: infection and immunity in mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2922–2928. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2922-2928.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J. Salmonella-based vaccines. Vaccine. 1990 Feb;8(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90169-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes L. J., Conlan J. W., Everson J. S., Ward M. E., Clarke I. N. Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein epitopes expressed as fusions with LamB in an attenuated aro A strain of Salmonella typhimurium; their application as potential immunogens. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Jul;137(7):1557–1564. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-7-1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg E. M., Cohen S. N. Transformation of Salmonella typhimurium by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1072–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1072-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveton C., Barnass S., Champion B., Lucas S., De Souza B., Nicol M., Banerjee D., Rook G. T-cell-mediated protection of mice against virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):390–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.390-395.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell D. J., Sweeney K. J., O'Callaghan D., Hormaeche C. E., Liew F. Y., Dougan G. Salmonella typhimurium aroA mutants as carriers of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit to the murine secretory and systemic immune systems. Microb Pathog. 1987 Mar;2(3):211–221. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T. A novel peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein found in the cell envelope of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1979 Oct;86(4):991–1000. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauciel C. Role of CD4+ T cells and T-independent mechanisms in acquired resistance to Salmonella typhimurium infection. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1265–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newborg M. F., North R. J. On the mechanism of T cell-independent anti-Listeria resistance in nude mice. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):571–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton S. M., Jacob C. O., Stocker B. A. Immune response to cholera toxin epitope inserted in Salmonella flagellin. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.2468182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Miller E. S., Roberts A. D., Furney S. K., Griffin J. P., Dobos K. M., Chi D., Rivoire B., Brennan P. J. T lymphocytes mediating protection and cellular cytolysis during the course of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Evidence for different kinetics and recognition of a wide spectrum of protein antigens. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier T. P., Kehoe M. A., Beachey E. H. Protective immunity evoked by oral administration of attenuated aroA Salmonella typhimurium expressing cloned streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):25–32. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertsson J. A., Lindberg A. A., Hoiseth S., Stocker B. A. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: protection and survival of virulent challenge bacteria after immunization with live or inactivated vaccines. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):742–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.742-750.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Wolf-Watz H. Immunospecific T-lymphocyte stimulation by membrane proteins from Francisella tularensis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):641–644. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.641-644.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Wolf-Watz H., Löfgren S. Antigen from Francisella tularensis: nonidentity between determinants participating in cell-mediated and humoral reactions. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):101–106. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.101-106.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. Phage P22-mutants with increased or decreased transduction abilities. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00270447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M. The effects of cyclosporin A on the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:397–423. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt A., Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Jaurin B. Molecular cloning and expression of a T-cell stimulating membrane protein of Francisella tularensis. Microb Pathog. 1989 Jun;6(6):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt A., Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Jaurin B. Nucleotide sequence and T cell epitopes of a membrane protein of Francisella tularensis. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):311–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt A., Sandström G., Tärnvik A. Several membrane polypeptides of the live vaccine strain Francisella tularensis LVS stimulate T cells from naturally infected individuals. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.43-48.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt A., Tärnvik A., Sandström G. The T-cell-stimulating 17-kilodalton protein of Francisella tularensis LVS is a lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3163–3168. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3163-3168.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel T. J., Mayfield J. E., Tabatabai L. B., Wannemuehler M. J. Oral immunization of mice with attenuated Salmonella typhimurium containing a recombinant plasmid which codes for production of a 31-kilodalton protein of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2048–2055. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2048-2055.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
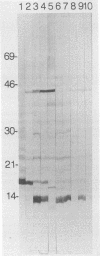
- Surcel H. M. Diversity of Francisella tularensis antigens recognized by human T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2664–2668. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2664-2668.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Mayer L. W., Tam M. R. Antigenicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane protein(s) III detected by immunoprecipitation and Western blot transfer with a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):668–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.668-672.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D. M., Fairweather N., Button L. L., McMaster W. R., Kahl L. P., Liew F. Y. Oral Salmonella typhimurium (AroA-) vaccine expressing a major leishmanial surface protein (gp63) preferentially induces T helper 1 cells and protective immunity against leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2281–2285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B. Stress-induced proteins and the immune response to leprosy. Microbiol Sci. 1988 May;5(5):143–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]