Abstract
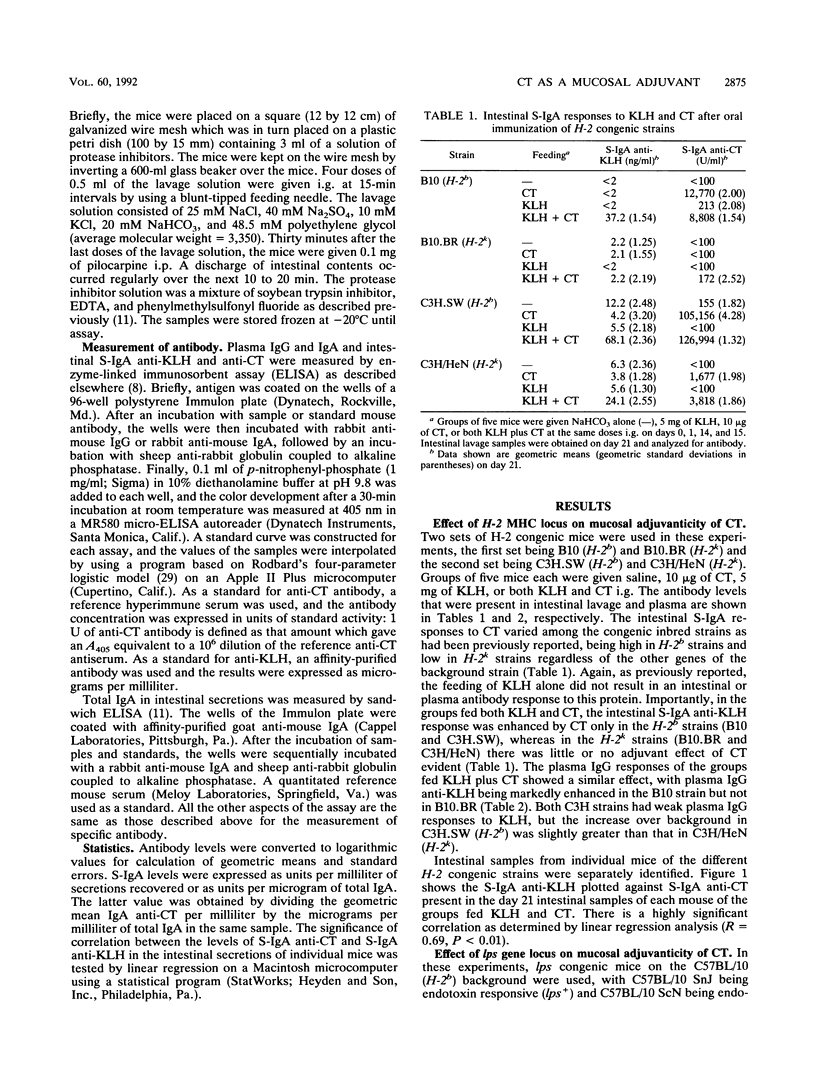
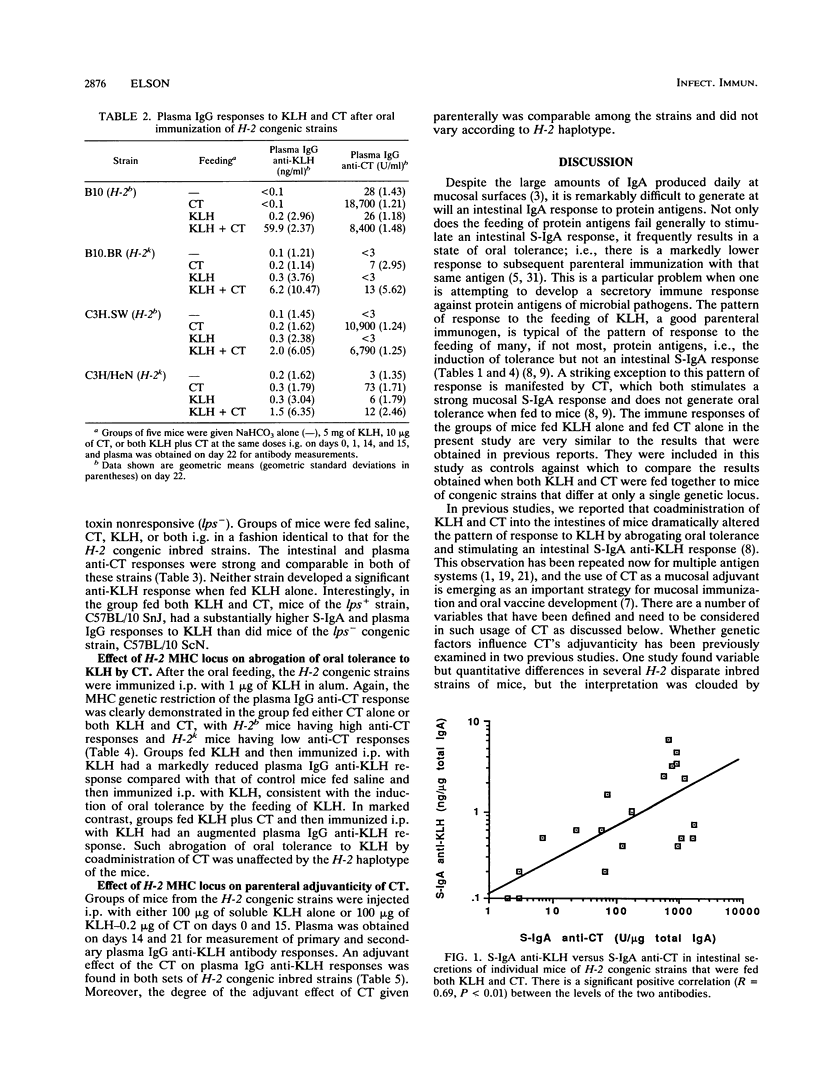
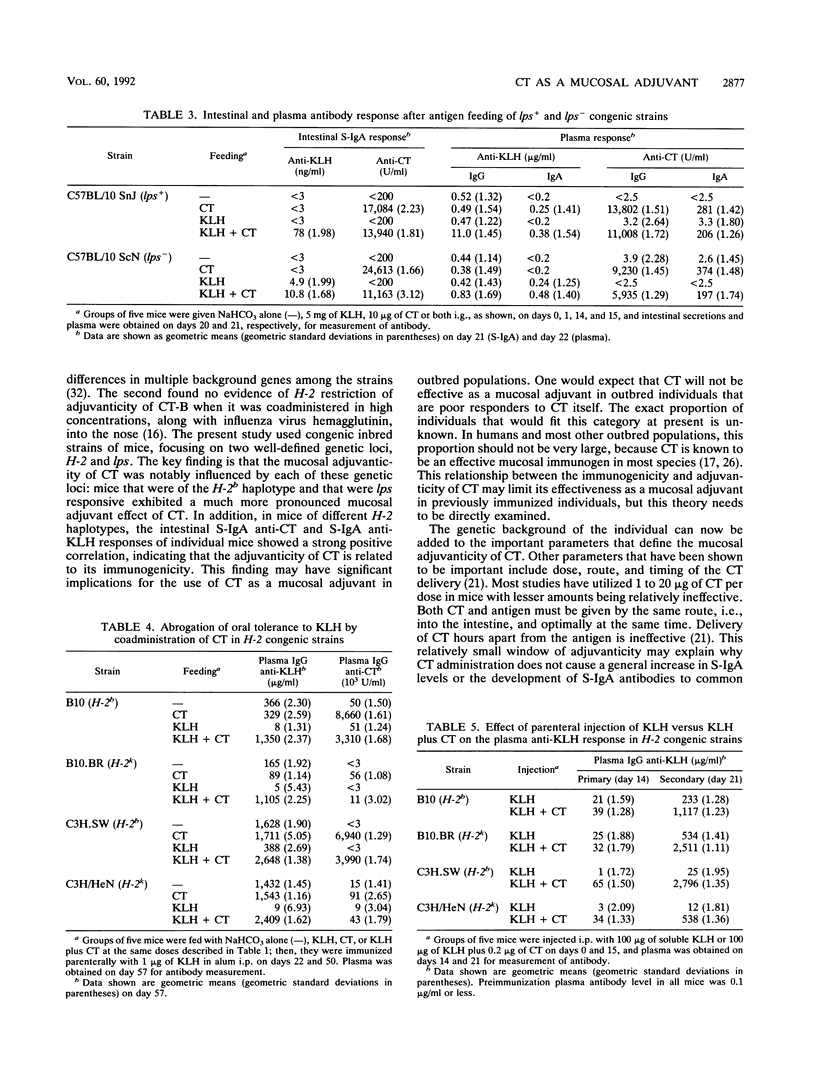
In previous studies we found that cholera toxin (CT) can act as a mucosal adjuvant; i.e., it can stimulate an intestinal secretory immunoglobulin A (S-IgA) response to an unrelated protein antigen when both are fed together to mice. The purpose of this study was to determine whether the mucosal adjuvanticity of CT is restricted by either H-2 major histocompatibility complex or lps genes by using congenic inbred strains that differ at only a single genetic locus. Groups of five mice each were fed saline, CT (10 micrograms), keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) (5 mg), or both CT and KLH on four different days, and samples of intestinal secretions and plasma were obtained 1 week after the last feeding. In the mice fed both CT and KLH, the intestinal S-IgA anti-KLH response was higher in H-2b congenic strains than in H-2k congenic strains, and in addition there was a highly significant positive correlation between the intestinal S-IgA anti-KLH and S-IgA anti-CT responses in the intestinal secretions of individual mice. Similarly, in the lps congenic strains, mice of the endotoxin-responsive strain that were fed both CT and KLH had substantially higher S-IgA and plasma IgG responses to KLH than did mice of the endotoxin-unresponsive strain. The effect of CT on the induction of oral tolerance to KLH in the H-2 congenic strains was also examined. In contrast to the results above, the abrogation of oral tolerance to KLH by CT occurred in all strains regardless of H-2 haplotype. Similarly, the adjuvant effect of CT on plasma IgG anti-KLH responses after both were given together intraperitoneally was not restricted by H-2. I conclude that the mucosal adjuvanticity of CT is influenced by both the H-2 and lps genetic loci and that it appears to depend on a vigorous mucosal immune response to CT itself.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessen D., Fischetti V. A. Influence of intranasal immunization with synthetic peptides corresponding to conserved epitopes of M protein on mucosal colonization by group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2666–2672. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2666-2672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Genetics of bacterial enterotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:577–605. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Overview of the mucosal immune system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;146:13–25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74529-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromander A., Holmgren J., Lycke N. Cholera toxin stimulates IL-1 production and enhances antigen presentation by macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):2908–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Cholera toxin feeding did not induce oral tolerance in mice and abrogated oral tolerance to an unrelated protein antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2892–2897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Generalized systemic and mucosal immunity in mice after mucosal stimulation with cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2736–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Genetic control of the murine immune response to cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):930–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Ir gene control of the murine secretory IgA response to cholera toxin. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Mar;17(3):425–428. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W., Lefkowitz J. A lavage technique allowing repeated measurement of IgA antibody in mouse intestinal secretions. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Suzuki A., Yamakawa T., Wang C. H., Bonhomme F., Miyashita N., Moriwaki K. Expression of GM1 and GD1a in liver of wild mice. J Biochem. 1984 Jan;95(1):7–12. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi Y., Tamura S. I., Suzuki Y., Nagamine T., Aizawa C., Shimada K., Kurata T. H-2-unrestricted adjuvant effect of cholera toxin B subunit on murine antibody responses to influenza virus haemagglutinin. Immunology. 1991 Mar;72(3):329–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Lönnroth I., Fall-Persson M., Markman B., Lundbeck H. Development of improved cholera vaccine based on subunit toxoid. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):602–604. doi: 10.1038/269602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON A. G., GAINES S., LANDY M. Studies on the O antigen of Salmonella typhosa. V. Enhancement of antibody response to protein antigens by the purified lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1956 Feb 1;103(2):225–246. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X. P., Lamm M. E., Nedrud J. G. Oral administration of cholera toxin-Sendai virus conjugate potentiates gut and respiratory immunity against Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1495–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Bromander A. K., Ekman L., Karlsson U., Holmgren J. Cellular basis of immunomodulation by cholera toxin in vitro with possible association to the adjuvant function in vivo. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Holmgren J. Strong adjuvant properties of cholera toxin on gut mucosal immune responses to orally presented antigens. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):301–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Karlsson U., Sjölander A., Magnusson K. E. The adjuvant action of cholera toxin is associated with an increased intestinal permeability for luminal antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Jun;33(6):691–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Strober W. Cholera toxin promotes B cell isotype differentiation. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3781–3787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedrud J. G., Sigmund N. Cholera toxin as a mucosal adjuvant: III. Antibody responses to nontarget dietary antigens are not increased. Reg Immunol. 1990;3(5):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Kaper J. B., Mekalanos J. J., Cray W. C., Jr, Richardson K. Determinants of the immunogenicity of live virulent and mutant Vibrio cholerae O1 in rabbit intestine. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):477–481. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.477-481.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. The role of antigen form and function in the primary and secondary intestinal immune responses to cholera toxin and toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):195–206. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. H., Kuhn R. E. Studies on the genetic and cellular control of sensitivity to enterotoxins in the sealed adult mouse model. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):522–528. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.522-528.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Graeff A. S., Yarchoan R., Strober W. Simultaneous induction of antigen-specific IgA helper T cells and IgG suppressor T cells in the murine Peyer's patch after protein feeding. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2079–2083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaizumi M., Hashimoto Y., Suzuki A., Yamakawa T., Kiuchi Y., Moriwaki K. The locus controlling liver GM1(NeuGc) expression is mapped 1 cM centromeric to H-2K. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(1):57–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00404445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., Parrott M. V. The induction of tolerance to a soluble protein antigen by oral administration. Immunology. 1974 Oct;27(4):631–639. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. D., Stokes C. R., Bourne F. J. Adjuvant effect of cholera toxin on the mucosal immune response to soluble proteins. Differences between mouse strains and protein antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jun;29(6):739–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


