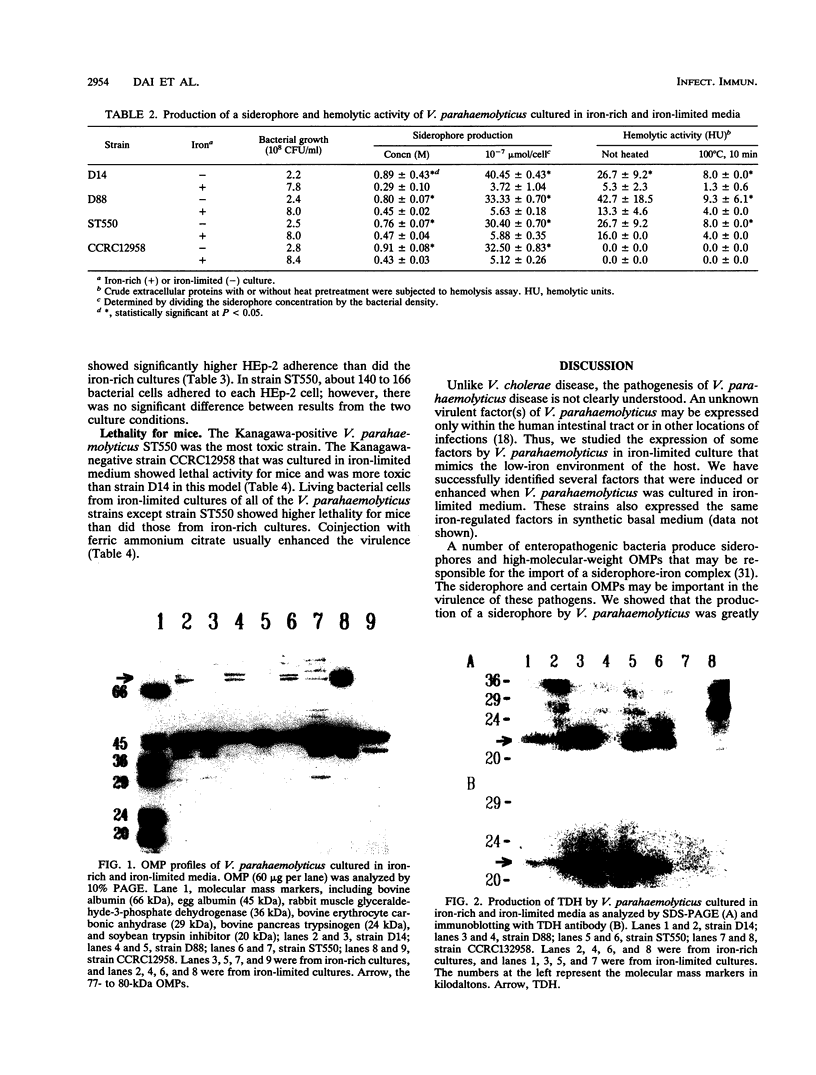
Abstract
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is one of the most important enteropathogens in Taiwan, Japan, and other coastal regions. The pathogenesis of V. parahaemolyticus disease is not clearly understood. The expression of some factors by V. parahaemolyticus in iron-rich and iron-limited media was analyzed. In the clinical hemolytic strains, the production of a siderophore, two outer membrane proteins (77 and 80 kDa), and thermostable direct hemolysin was significantly enhanced in iron-limited culture, and hemolytic activities, cell hydrophobicity, HEp-2 cell adherence, and lethality for mice were also enhanced. The environmental nonhemolytic strain CCRC12958 that was cultured in iron-limited medium exhibited lethal activity for mice, and other factors except hemolysis were also enhanced like the responses of clinical strains were. These results suggested that a virulent factor(s) of V. parahaemolyticus may be induced or enhanced under iron-limited conditions. The iron-regulated factors reported in this paper may be important in the pathogenesis of V. parahaemolyticus disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carniel E., Mazigh D., Mollaret H. H. Expression of iron-regulated proteins in Yersinia species and their relation to virulence. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):277–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.277-280.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Clark A. G. Production of the Kanagawa hemolysin by Vibrio parahaemolyticus in a synthetic medium. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):60–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.60-63.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Hodges L. L. Outer membrane proteins induced under conditions of iron limitation in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum 775. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):223–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.223-227.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson J. S., Koohmaraie M. Cell surface charge characteristics and their relationship to bacterial attachment to meat surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):832–836. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.832-836.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskill M. E., Khan S. A. Regulation of the enterotoxin B gene in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6276–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., DiRita V. J., Calderwood S. B. Identification of an iron-regulated virulence determinant in Vibrio cholerae, using TnphoA mutagenesis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.55-60.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Abad-Lapuebla M. A., Ni Y. X., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Characterization of a new thermostable direct haemolysin produced by a Kanagawa-phenomenon-negative clinical isolate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Feb;137(2):253–259. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Chearskul S., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Immunological methods for detection of Kanagawa phenomenon of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):600–603. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.600-603.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Ni Y. X., Hata A., Yoh M., Miwatani T., Okamoto T., Goshima K., Takakura H., Tsunasawa S., Sakiyama F. Properties of a hemolysin related to the thermostable direct hemolysin produced by a Kanagawa phenomenon negative, clinical isolate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Jun;36(6):395–399. doi: 10.1139/m90-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Ni Y., Miwatani T. Purification of a TDH-related hemolysin produced by a Kanagawa phenomenon-negative clinical isolate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus 06: K46. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;48(2):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Shimizu M., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Isolation of a factor causing morphological changes of chinese hamster ovary cells from the culture filtrate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1028-1033.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Taga S., Takeda T., Hasibuan M. A., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Identification of lethal toxin with the thermostable direct hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and some physicochemical properties of the purified toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.133-139.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hondo S., Goto I., Minematsu I., Ikeda N., Asano N., Ishibashi M., Kinoshita Y., Nishibuchi N., Honda T., Miwatani T. Gastroenteritis due to Kanagawa negative Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Lancet. 1987 Feb 7;1(8528):331–332. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iijima Y., Yamada H., Shinoda S. Adherence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its relation to pathogenicity. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Dec;27(12):1252–1259. doi: 10.1139/m81-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Weinberg L., Ciarkowski J., West P., Colwell R. R. Wound infection caused by Kanagawa-negative Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):811–812. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.811-812.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonson G., Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. Vibrio cholerae expresses cell surface antigens during intestinal infection which are not expressed during in vitro culture. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1809–1815. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1809-1815.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. W., Colwell R. R., Kaper J. B. Vibrio parahaemolyticus and related halophilic Vibrios. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1982;10(1):77–124. doi: 10.3109/10408418209113506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karunasagar I., Joseph S. W., Twedt R. M., Hada H., Colwell R. R. Enhancement of Vibrio parahaemolyticus virulence by lysed erythrocyte factor and iron. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):141–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.141-144.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Kawata T. Isolation and characterization of the outer membrane from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3185–3196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Zink D. L. Plasmid-associated cell surface charge and hydrophobicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):540–543. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.540-543.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter L., Silverman M. Iron regulation of swarmer cell differentiation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):731–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.731-736.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakasone N., Iwanaga M. Pili of a Vibrio parahaemolyticus strain as a possible colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.61-69.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Kaper J. B. Duplication and variation of the thermostable direct haemolysin (tdh) gene in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):87–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Bahavar M. A., Jinguji Y., Miwatani T. Interaction of thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus with human erythrocytes. Biken J. 1975 Dec;18(4):187–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar B. L., Kumar R., De S. P., Pal S. C. Hemolytic activity of and lethal toxin production by environmental strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2696–2698. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2696-2698.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyn B., Neilands J. B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jan;160(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel S. P., Payne S. M. Effect of iron limitation on growth, siderophore production, and expression of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.148-155.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M. Iron-regulated hemolysin production and utilization of heme and hemoglobin by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2891–2895. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2891-2895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y. Thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Pharmacol Ther. 1982;19(1):123–146. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(82)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmasky M. E., Salinas P. C., Actis L. A., Crosa J. H. Increased production of the siderophore anguibactin mediated by pJM1-like plasmids in Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1608–1614. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1608-1614.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunasawa S., Sugihara A., Masaki T., Sakiyama F., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Narita K. Amino acid sequence of thermostable direct hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Biochem. 1987 Jan;101(1):111–121. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Adherence targets of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in human small intestines. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2410–2419. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2410-2419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]