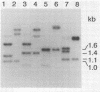
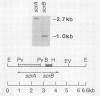
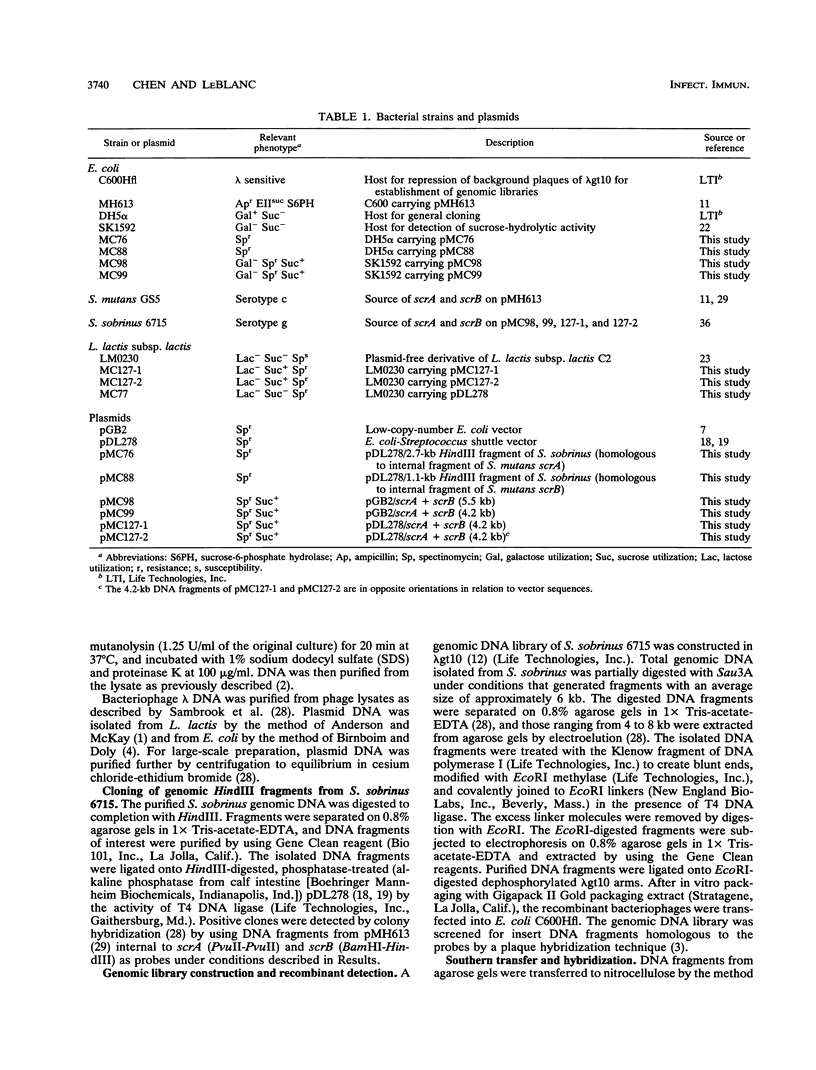
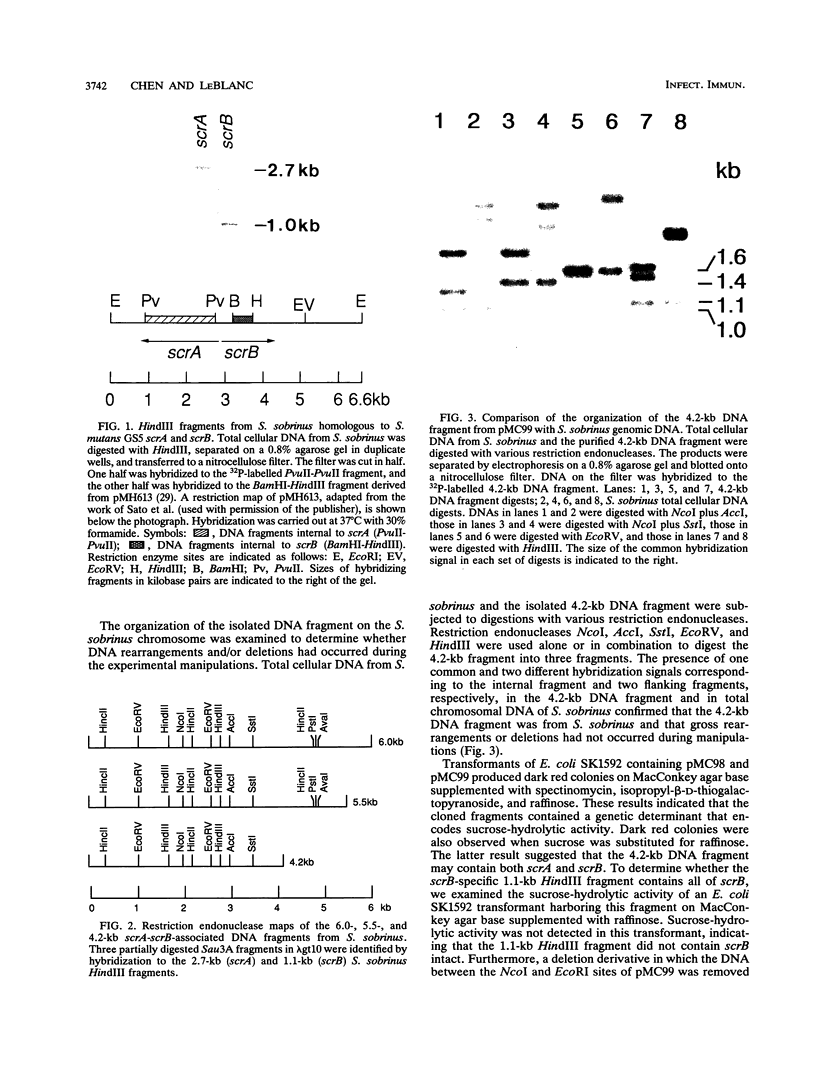
Abstract
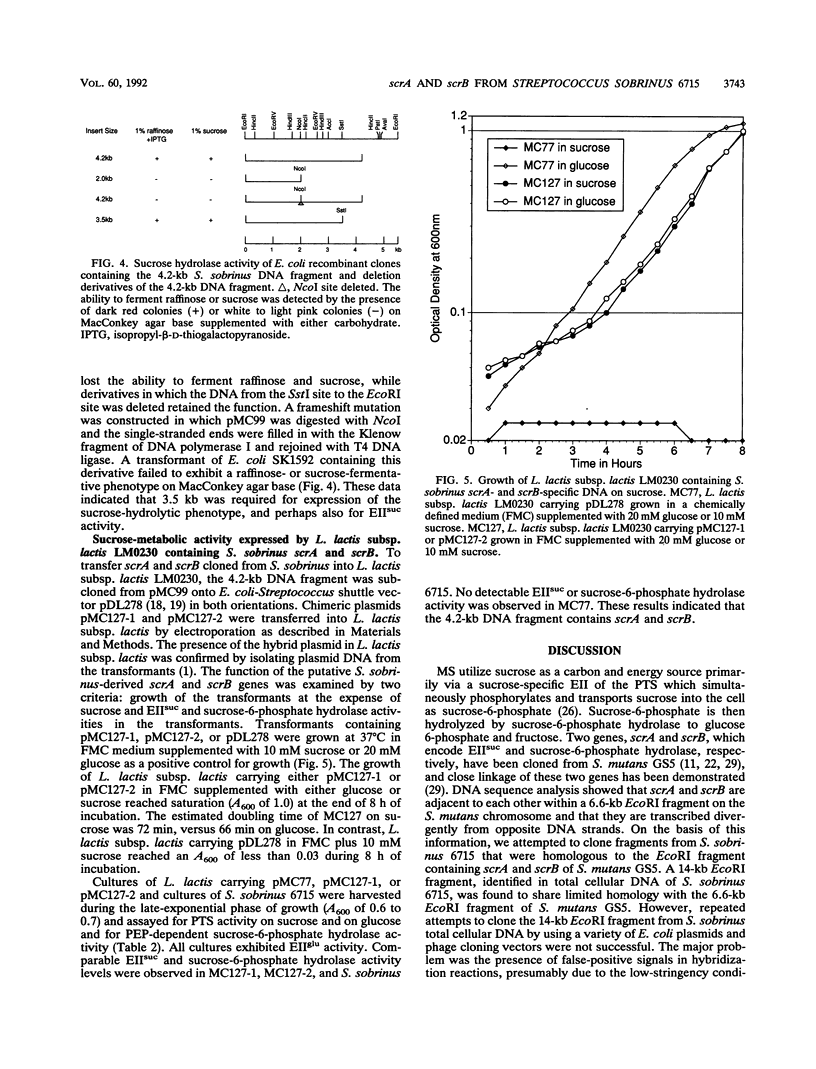
A DNA fragment containing scrA and scrB, which encode enzyme II of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system and sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase, respectively, was isolated from a lambda gt10 genomic DNA library of Streptococcus sobrinus 6715. Both genes were located on a 4.2-kb DNA fragment which was maintained stably in Escherchia coli on low-copy-number vector pGB2. The recombinant E. coli clone expressed sucrose-hydrolytic activity on MacConkey agar base supplemented with raffinose or sucrose. Results from deletion analysis showed that the sucrose-metabolic activity was contained within a 3.5-kb region. The lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis LM0230, which is devoid of sucrose-metabolic activity, was used to study the enzyme activities encoded by scrA and scrB from S. sobrinus 6715. L. lactis transformants carrying the 4.2-kb S. sobrinus-derived DNA fragment on E. coli-Streptococcus shuttle vector pDL278 were able to grow at the expense of sucrose and exhibited enzyme II and sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase activities. Results from hybridization studies and a comparison of the restriction endonuclease maps of the scrA- and scrB-containing chromosomal regions from S. mutans GS5 and S. sobrinus 6715 suggested considerable divergence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M., Porter E. V. Sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase from Streptococcus mutans. Methods Enzymol. 1982;90(Pt E):556–559. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchward G., Belin D., Nagamine Y. A pSC101-derived plasmid which shows no sequence homology to other commonly used cloning vectors. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd Genetic analysis of Streptococcus mutans virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:253–277. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa M., Aoki H., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the sucrose 6-phosphate hydrolase gene from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):582–586. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.582-586.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Mimura C. S., Scott P. J., Thompson P. W. Identification and properties of distinct sucrose and glucose phosphotransferase enzyme II activities in Streptococcus mutans 6715g. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):854–856. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.854-856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L., Reeves R. E. Inducible phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent hexose phosphotransferase activities in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1339–1344. doi: 10.1042/bj1281339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization of extracellular glucosyltransferase activity of Steptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):738–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.738-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Crow V. L., Lee L. N., Garon C. F. Influence of the lactose plasmid on the metabolism of galactose by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):878–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.878-884.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Lee L. N. Characterization of two tetracycline resistance determinants in Streptococcus faecalis JH1. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):835–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.835-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J., Jacobson G. R. Starvation-induced stimulation of sugar uptake in Streptococcus mutans is due to an effect on the activities of preexisting proteins of the phosphotransferase system. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2594–2600. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2594-2600.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunsford R. D., Macrina F. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of scrB, the structural gene for the Streptococcus mutans phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):426–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.426-434.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Efstathiou J. D. Transductional evidence for plasmid linkage of lactose metabolism in streptococcus lactis C2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.45-52.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palchaudhuri S., Rahn S., Santos D. S., Maas W. K. Characterization of plasmids in a sucrose-fermenting strain of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1402–1403. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1402-1403.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell Ian B., Achen Marc G., Hillier Alan J., Davidson Barrie E. A Simple and Rapid Method for Genetic Transformation of Lactic Streptococci by Electroporation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):655–660. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.655-660.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Saier M. H., Jr, Deutscher J., Grenier F., Thompson J., Hengstenberg W. The phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in gram-positive bacteria: properties, mechanism, and regulation. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988;15(4):297–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418809104461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robeson J. P., Barletta R. G., Curtiss R., 3rd Expression of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.211-221.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Poy F., Jacobson G. R., Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization and sequence analysis of the scrA gene encoding enzyme IIScr of the Streptococcus mutans phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.263-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee A. M., Tanzer J. M. Effect of growth conditions on sucrose phosphotransferase activity of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):922–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.922-927.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee A. M., Tanzer J. M. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase activity in Streptococcus mutans NCTC 10449. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):821–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.821-828.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee A. M., Tanzer J. M. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase activity in five serotypes of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):783–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.783-786.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee A. M., Tanzer J. M. Sucrose transport by Streptococcus mutans. Evidence for multiple transport systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 22;692(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90392-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.865-868.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]