Abstract
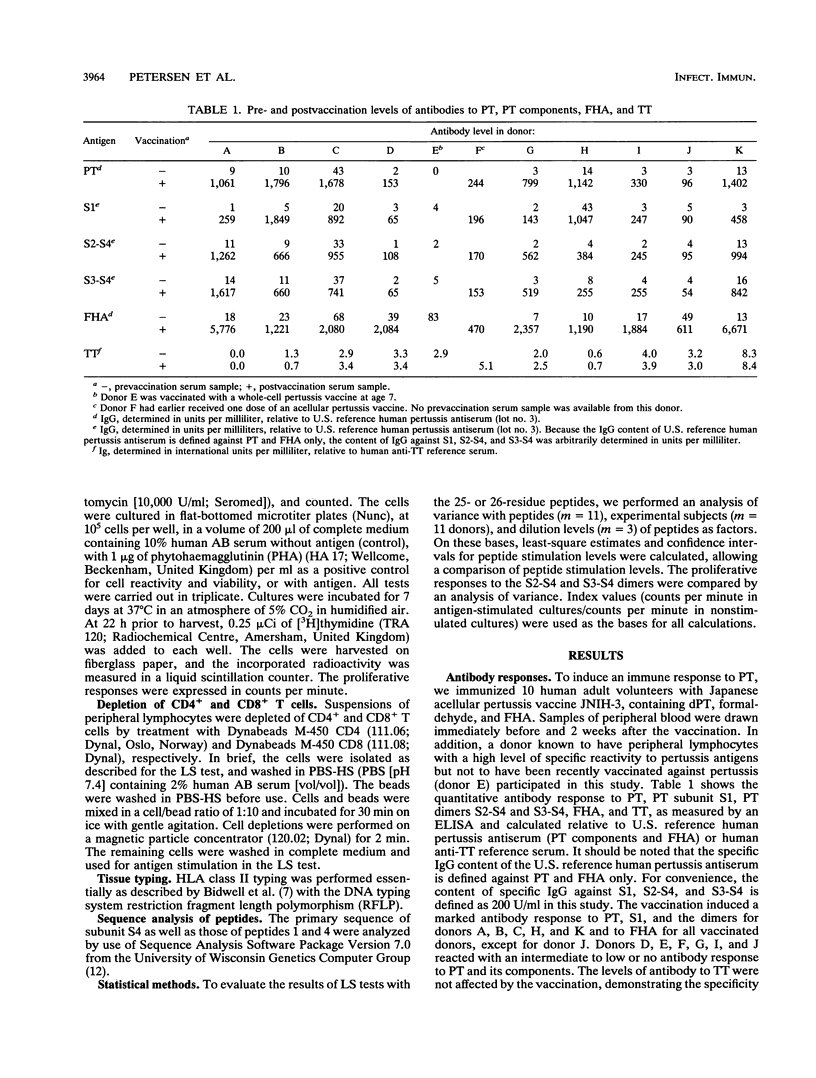
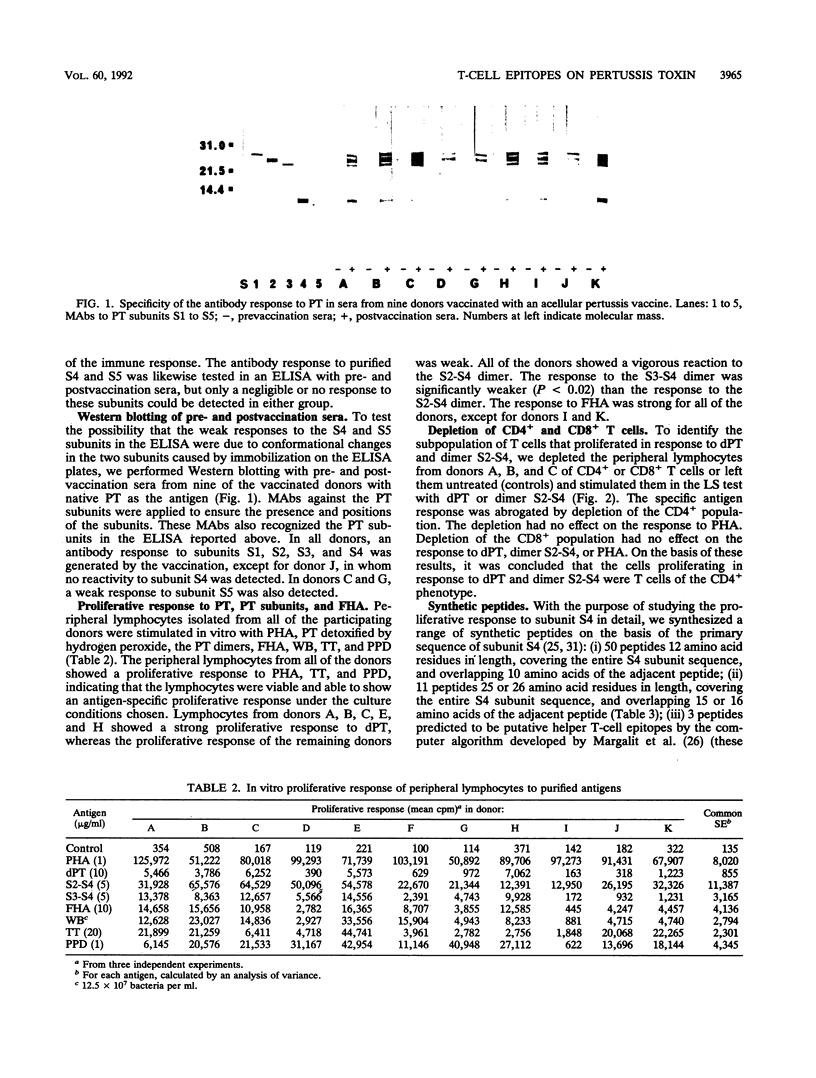
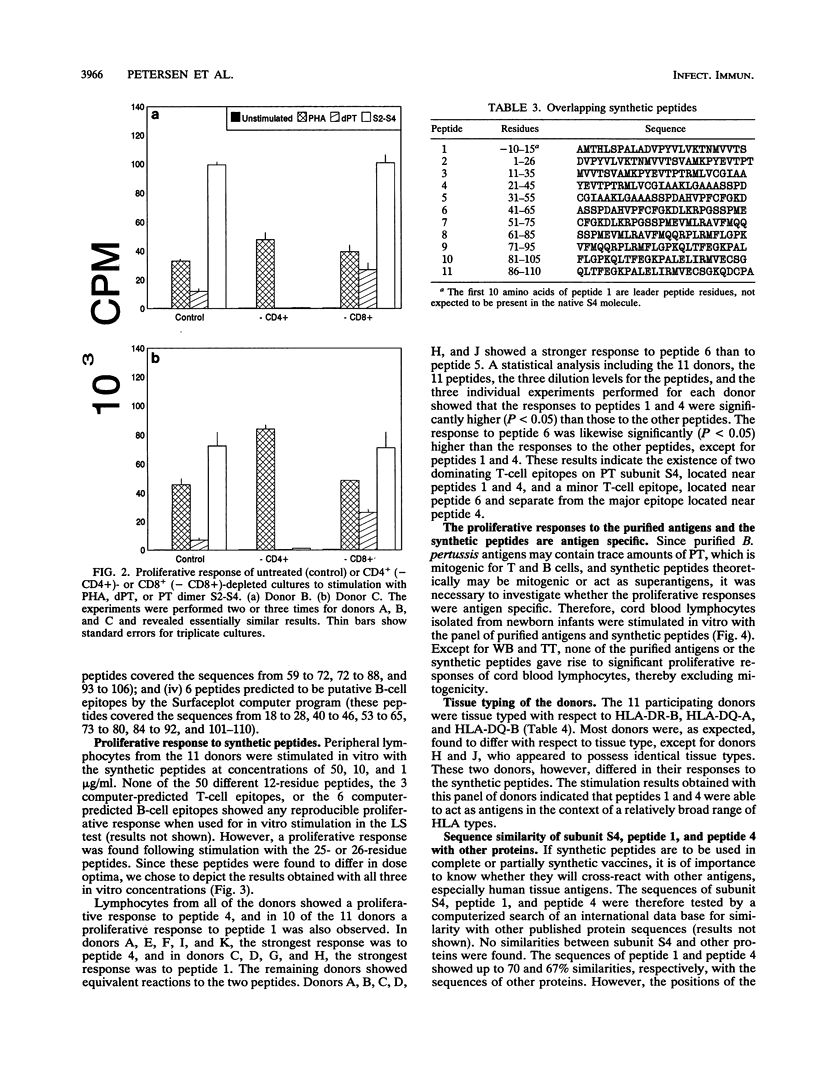
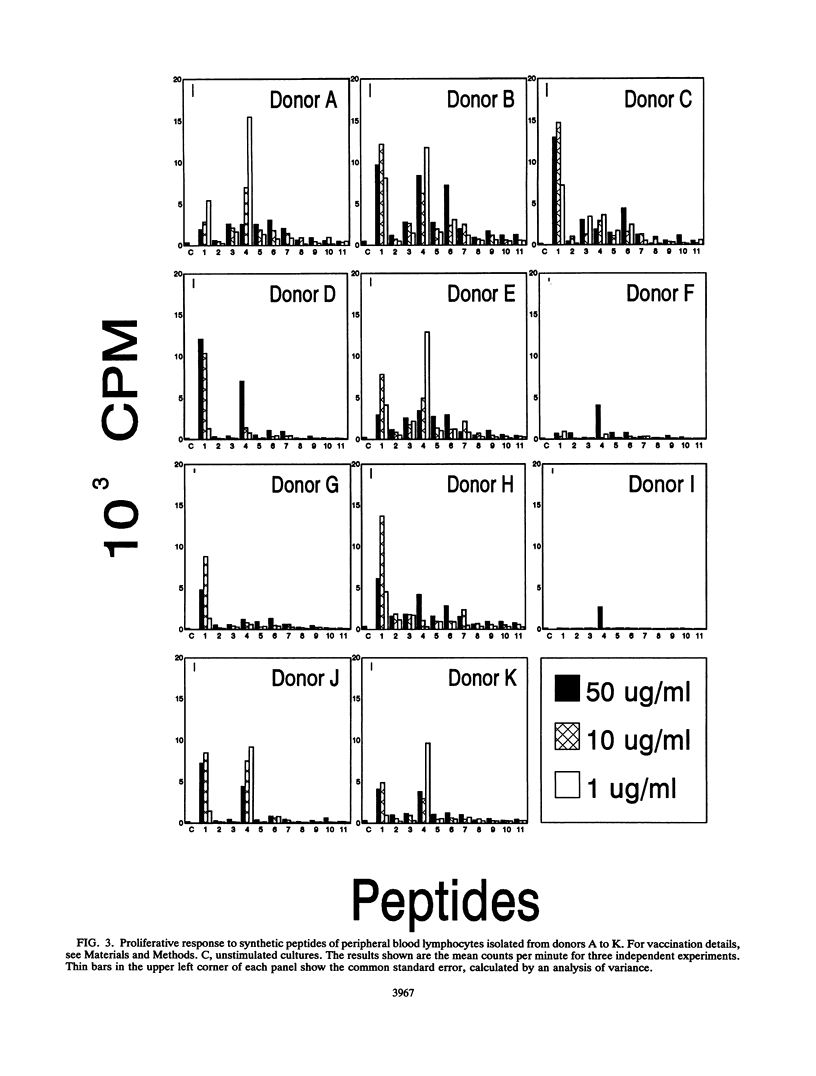
Ten adult humans were vaccinated with the Japanese acellular pertussis vaccine JNIH-3, containing detoxified pertussis toxin (PT), formaldehyde, and filamentous hemagglutinin. The vaccination induced a specific antibody response to PT and filamentous hemagglutinin, and a Western blot (immunoblot) analysis of the antibody response to PT revealed antibodies to PT subunits S1, S2, S3, S4 and S5. The response of peripheral lymphocytes to PT was assessed in an in vitro proliferation assay. A proliferative response to detoxified PT and PT dimers S2-S4 and S3-S4 was found, and it was further demonstrated that the proliferative response to detoxified PT and dimer S2-S4 was mediated by T cells of the CD4+ phenotype. The specificity of the proliferative response to subunit S4 was analyzed with a range of synthetic peptides synthesized on the basis of the primary sequence of subunit S4. The proliferative response to the peptides revealed two major and one minor T-cell epitope located in the NH2-terminal end of subunit S4.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arciniega J. L., Burns D. L., Garcia-Ortigoza E., Manclark C. R. Immune response to the B oligomer of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1132–1136. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1132-1136.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arciniega J. L., Shahin R. D., Burnette W. N., Bartley T. D., Whiteley D. W., Mar V. L., Burns D. L. Contribution of the B oligomer to the protective activity of genetically attenuated pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3407–3410. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3407-3410.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askelöf P., Rodmalm K., Abens J., Undén A., Bartfai T. Use of synthetic peptides to map antigenic sites of Bordetella pertussis toxin subunit S1. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):738–742. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askelöf P., Rodmalm K., Wrangsell G., Larsson U., Svenson S. B., Cowell J. L., Undén A., Bartfai T. Protective immunogenicity of two synthetic peptides selected from the amino acid sequence of Bordetella pertussis toxin subunit S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1347–1351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidwell J. L., Bidwell E. A., Savage D. A., Middleton D., Klouda P. T., Bradley B. A. A DNA-RFLP typing system that positively identifies serologically well-defined and ill-defined HLA-DR and DQ alleles, including DRw10. Transplantation. 1988 Mar;45(3):640–646. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198803000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N., Cieplak W., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Sato H., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin S1 mutant with reduced enzyme activity and a conserved protective epitope. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2459776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiau C., Petre J., Van Damme J., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J. Protein-chemical analysis of pertussis toxin reveals homology between the subunits S2 and S3, between S1 and the A chains of enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli and identifies S2 as the haptoglobin-binding subunit. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):336–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80839-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P., Sydor M., Wu E., Zobrist G., Boux H., Klein M. Structural and functional analysis of the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin using synthetic peptides. Mol Immunol. 1991 Mar;28(3):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90068-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Magistris M. T., Romano M., Bartoloni A., Rappuoli R., Tagliabue A. Human T cell clones define S1 subunit as the most immunogenic moiety of pertussis toxin and determine its epitope map. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1519–1532. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halperin S. A., Issekutz T. B., Kasina A. Modulation of Bordetella pertussis infection with monoclonal antibodies to pertussis toxin. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):355–361. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibsen P. H., Holm A., Raaschou-Nielsen M., Petersen J. W., Capiau C., Heron I. Induction of polyclonal antibodies to the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin by synthetic peptides coupled to PPD: effect of conjugation method, adjuvant, priming and animal species. APMIS. 1992 Feb;100(2):159–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1992.tb00856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi A., Suzuki Y., Ono S., Sato H., Sato Y. Effect of heptakis (2,6-O-dimethyl) beta-cyclodextrin on the production of pertussis toxin by Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1138–1143. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1138-1143.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. Synthetic vaccines. Peptides of fortune. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):792–792. doi: 10.1038/353792a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Burnette W. N., Sublett R. D., Manclark C. R., Kenimer J. G. Epitopes on the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin recognized by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):944–950. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.944-950.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., McKinness S., Manclark C. R. Determination of T cell epitopes on the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3529–3534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. B., Ganss M. T., Cryz S. J., Jr Monoclonal antibodies that define neutralizing epitopes of pertussis toxin: conformational dependence and epitope mapping. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2660–2665. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2660-2665.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margalit H., Spouge J. L., Cornette J. L., Cease K. B., Delisi C., Berzofsky J. A. Prediction of immunodominant helper T cell antigenic sites from the primary sequence. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2213–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L. Microbial "superantigens". Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2409–2413. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2409-2413.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse J. H., Kong A. S., Lindenbaum J., Morse S. I. The mitogenic effect of the lymphocytosis promoting factor from Bordetella pertussis on human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):683–692. doi: 10.1172/JCI108820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen S., Meldal M., Rubin B., Holm A., Werdelin O. The T-lymphocyte proliferative response to synthetic peptide antigens of defined secondary structure. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Dec;30(6):723–730. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb02482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogimori K., Tamura M., Yajima M., Hashimura N., Ishii S., Ui M. Structure-function relationship of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin: biological activities of hybrid toxins reconstituted from native and methylated subunits. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1355–1363. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Cowell J. L., Burstyn D. G., Manclark C. R. Protective activities of the filamentous hemagglutinin and the lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis in mice. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):823–833. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksenberg J. R., Judd A. K., Ko C., Lim M., Fernandez R., Schoolnik G. K., Steinman L. MHC-restricted recognition of immunogenic T cell epitopes of pertussis toxin reveals determinants in man distinct from the ADP-ribosylase active site. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1855–1864. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksenberg J. R., Ko C., Judd A. K., Lim M., Kent A., Schoolnik G. K., Steinman L. Multiple T and B cell epitopes in the S1 subunit ("A"-monomer) of the pertussis toxin molecule. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4227–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olander R. M., Muotiala A., Himanen J. P., Karvonen M., Airaksinen U., Runeberg-Nyman K. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of pertussis toxin subunit S1 produced by Bacillus subtilis. Microb Pathog. 1991 Feb;10(2):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90076-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen J. W., Ibsen P. H., Bentzon M. W., Capiau C., Heron I. The cell mediated and humoral immune response to vaccination with acellular and whole cell pertussis vaccine in adult humans. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1991 Oct;3(5):279–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1991.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podda A., Nencioni L., De Magistris M. T., Di Tommaso A., Bossù P., Nuti S., Pileri P., Peppoloni S., Bugnoli M., Ruggiero P. Metabolic, humoral, and cellular responses in adult volunteers immunized with the genetically inactivated pertussis toxin mutant PT-9K/129G. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):861–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presentini R., Perin F., Ancilli G., Nucci D., Bartoloni A., Rappuoli R., Antoni G. Studies of the antigenic structure of two cross-reacting proteins, pertussis and cholera toxins, using synthetic peptides. Mol Immunol. 1989 Jan;26(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redhead K. Serum antibody responses to the outer membrane proteins of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):724–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.724-729.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Irons L. I., Ashworth L. A. Pertussis vaccine: present status and future prospects. Vaccine. 1985 Mar;3(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Ito A., Chiba J., Sato Y. Monoclonal antibody against pertussis toxin: effect on toxin activity and pertussis infections. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):422–428. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.422-428.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Sato Y., Ohishi I. Comparison of pertussis toxin (PT)-neutralizing activities and mouse-protective activities of anti-PT mouse monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3832–3835. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3832-3835.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Izumiya K., Sato H., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Role of antibody to leukocytosis-promoting factor hemagglutinin and to filamentous hemagglutinin in immunity to pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1223–1231. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1223-1231.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., Raupach B., Szulczynski M., Marzillier J. Identification of linear B-cell determinants of pertussis toxin associated with the receptor recognition site of the S3 subunit. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1402–1408. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1402-1408.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., Schmidt W. Inhibition of pertussis toxin binding to model receptors by antipeptide antibodies directed at an antigenic domain of the S2 subunit. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3828–3833. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3828-3833.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W., Schmidt M. A. Mapping of linear B-cell epitopes of the S2 subunit of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):438–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.438-445.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabrook R. N., Robinson A., Sharma R. P., Irons L. I., Ashworth L. A., Price C. P., Atkinson T. Recognition of pertussis toxin by antibodies to synthetic peptides. Mol Immunol. 1990 Aug;27(8):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90087-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahin R. D., Witvliet M. H., Manclark C. R. Mechanism of pertussis toxin B oligomer-mediated protection against Bordetella pertussis respiratory infection. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4063–4068. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4063-4068.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. G., Redhead K., Lambert H. P. Human serum antibody responses to Bordetella pertussis infection and pertussis vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):211–218. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



