Abstract
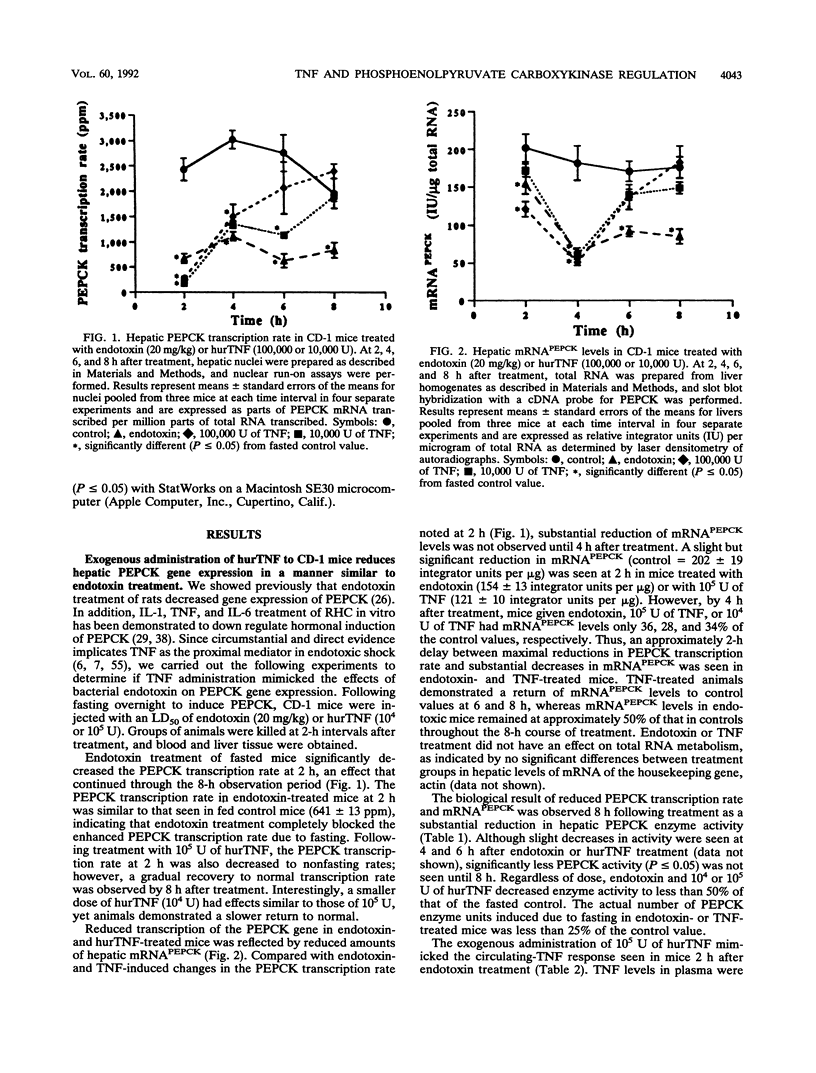
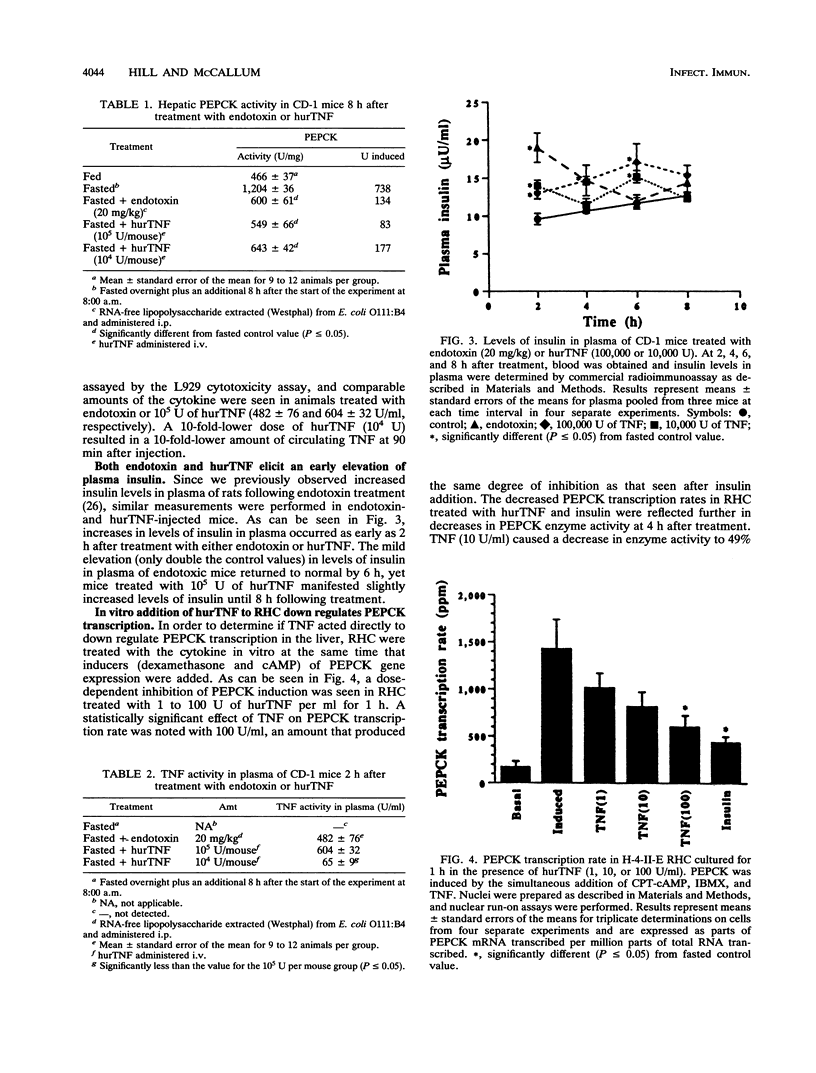
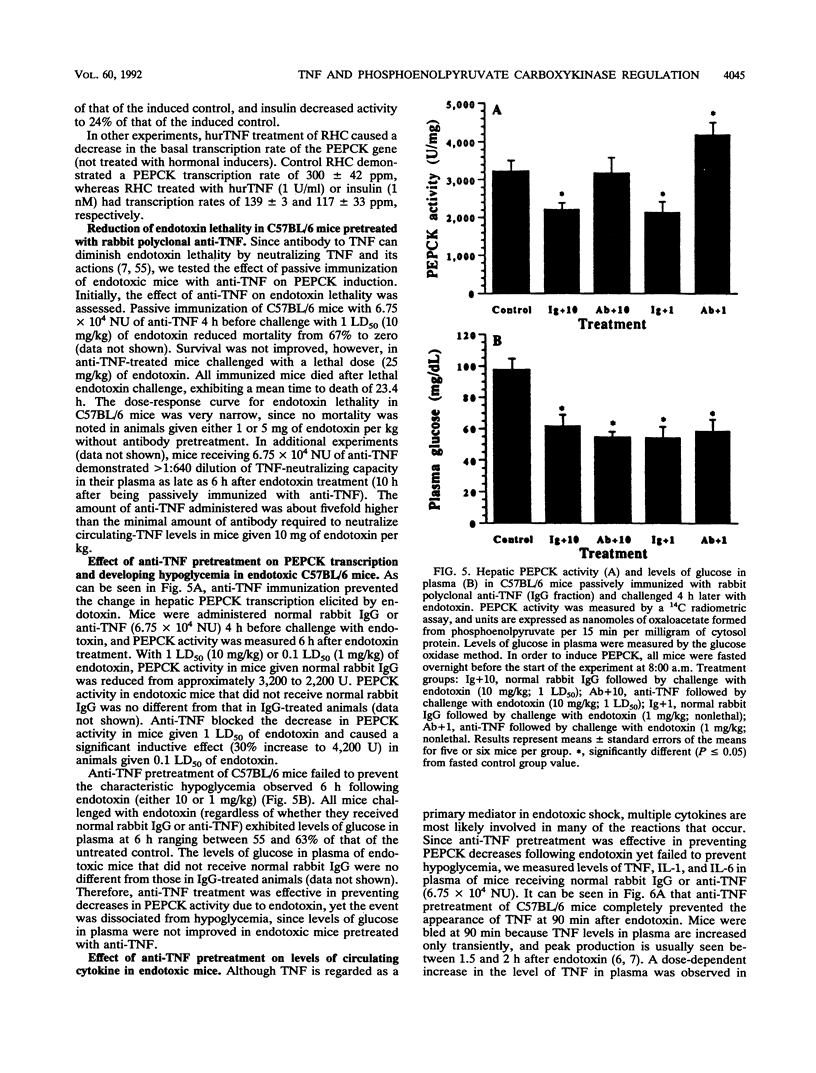
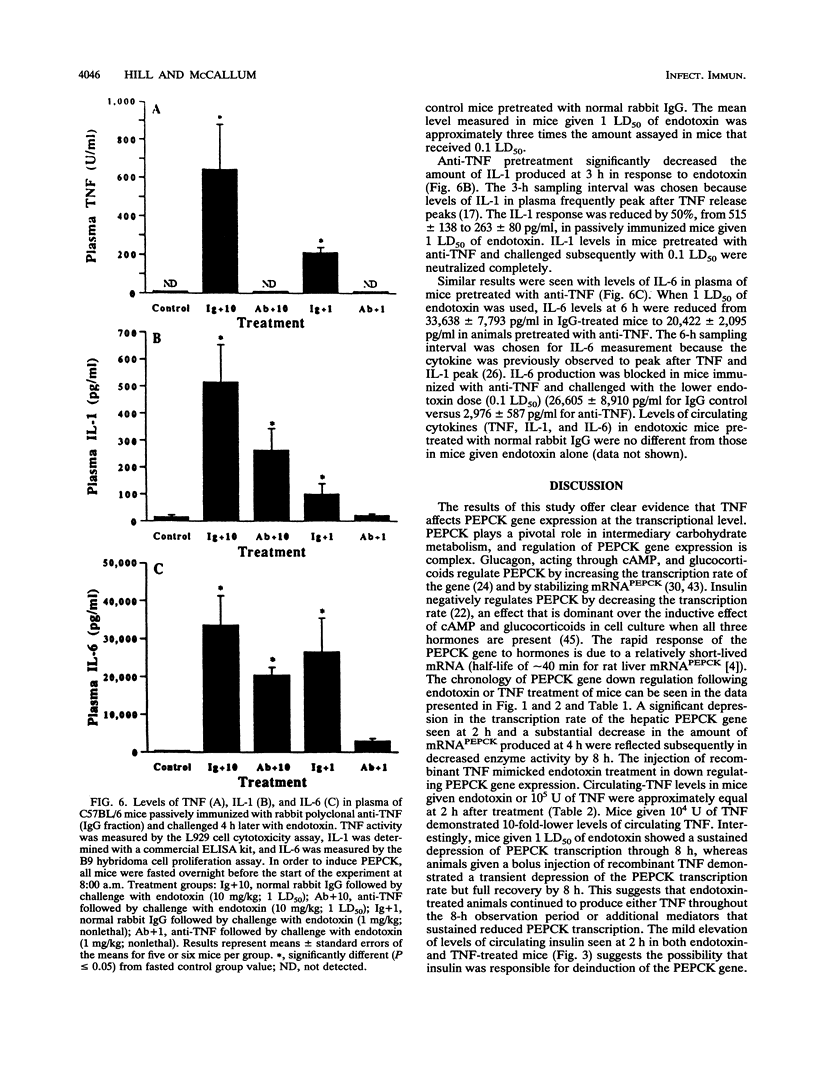
The decreased synthesis of hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), the rate-limiting enzyme of gluconeogenesis, that occurs during endotoxemia was shown previously in rats to occur at the transcriptional level. In the current study, the exogenous administration of human recombinant tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a proximal mediator of endotoxic shock, reduced the PEPCK transcription rate, mRNAPEPCK levels, and PEPCK enzyme activity in a time- and dose-dependent manner in CD-1 mice. Comparable amounts of circulating TNF were measured in mice 2 h after injection of human recombinant TNF (10(5) U) or a 50% lethal dose of Escherichia coli endotoxin (20 mg/kg). Direct action of TNF to decrease the PEPCK transcription rate was confirmed in vitro with H-4-II-E Reuber hepatoma cells, in which a dose-dependent inhibition of PEPCK transcription was observed with 1 to 100 U of TNF per ml. A role for TNF-elicited changes in PEPCK gene expression during endotoxemia was confirmed by the protective effect of rabbit polyclonal antibodies to recombinant murine TNF. C57BL/6 mice passively immunized with anti-TNF 4 h prior to endotoxin challenge exhibited normal PEPCK enzyme activity. Neutralization of circulating TNF with anti-TNF failed, however, to prevent the hypoglycemia commonly observed during endotoxemia, suggesting the participation of other mediators. Anti-TNF treatment reduced circulating interleukins 1 and 6 at 3 and 6 h after endotoxin treatment, respectively. These results suggest that during endotoxemia, the development of hypoglycemia is multifaceted and that several cytokines are most likely involved. The findings from the Reuber hepatoma cell model afford an opportunity in future work to map putative cytokine response elements in the PEPCK promoter responsible for perturbed hormonal regulation of the gene during endotoxemia.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagby G. J., Lang C. H., Hargrove D. M., Thompson J. J., Wilson L. A., Spitzer J. J. Glucose kinetics in rats infused with endotoxin-induced monokines or tumor necrosis factor. Circ Shock. 1988 Feb;24(2):111–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauss F., Dröge W., Männel D. N. Tumor necrosis factor mediates endotoxic effects in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1622–1625. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1622-1625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale E. G., Chrapkiewicz N. B., Scoble H. A., Metz R. J., Quick D. P., Noble R. L., Donelson J. E., Biemann K., Granner D. K. Rat hepatic cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Structures of the protein, messenger RNA, and gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10748–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale E. G., Hartley J. L., Granner D. K. N6,O2'-dibutyryl cycle AMP and glucose regulate the amount of messenger RNA coding for hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2022–2028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry L. J., Smythe D. S., Colwell L. S. Inhibition of hepatic enzyme induction as a sensitive assay for endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1191–1199. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1191-1199.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: an endogenous mediator of shock and inflammation. Immunol Res. 1986;5(4):281–293. doi: 10.1007/BF02935501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A., Vandekerckhove F. Cytokines and their interactions with other inflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of sepsis and septic shock. Eur J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;21(6):559–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1991.tb01410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Davies A., Baldwin S. A., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 stimulates hexose transport in fibroblasts by increasing the expression of glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13578–13583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., Buck M., Feitelberg S. P., Chojkier M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits albumin gene expression in a murine model of cachexia. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):248–255. doi: 10.1172/JCI114419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Albano E., Tetta C., Bussolino F. The molecular action of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 15;202(1):3–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tompkins R. G., Gelfand J. A., Michie H. R., Stanford G. G., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Corsetti J., Chernow B. Circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in septic shock and experimental endotoxin fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):79–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek-Shaul T., Barash V., Weidenfeld J., Friedman G., Ziv E., Shohami E., Shiloni E. Lethal hypoglycemia and hypothermia induced by administration of low doses of tumor necrosis factor to adrenalectomized rats. Metabolism. 1990 Mar;39(3):242–250. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90042-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. D., Bedrosian I., Schindler R., Cominelli F., Cannon J. G., Shaw A. R., Dinarello C. A. Detection of interleukin 1 alpha and 1 beta in rabbit tissues during endotoxemia using sensitive radioimmunoassays. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Dec;71(6):2412–2418. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.71.6.2412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeForge L. E., Remick D. G. Kinetics of TNF, IL-6, and IL-8 gene expression in LPS-stimulated human whole blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90478-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E., Marano M. A., Barber A. E., Hudson A., Lee K., Rock C. S., Hawes A. S., Thompson R. C., Hayes T. J., Anderson T. D. Comparison between effects of interleukin-1 alpha administration and sublethal endotoxemia in primates. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 2):R442–R452. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.261.2.R442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores E. A., Istfan N., Pomposelli J. J., Blackburn G. L., Bistrian B. R. Effect of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor/cachectin on glucose turnover in the rat. Metabolism. 1990 Jul;39(7):738–743. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90110-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried S. K., Zechner R. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor decreases human adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase mRNA levels, synthesis, and activity. J Lipid Res. 1989 Dec;30(12):1917–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D., Andreone T., Sasaki K., Beale E. Inhibition of transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene by insulin. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):549–551. doi: 10.1038/305549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Feingold K. R. The metabolic effects of tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines. Biotherapy. 1991;3(2):143–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02172087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn J. M., Tilghman S. M., Hanson R. W., Reshef L., Ballard F. J. Effects of cyclic adenosine monophosphate, dexamethasone and insulin on phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase synthesis in Reuber H-35 hepatoma cells. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2350–2357. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Boeije L., Aarden L. A. Functional discrimination between interleukin 6 and interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1535–1540. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. R., Stith R. D., McCallum R. E. Interleukin 1: a regulatory role in glucocorticoid-regulated hepatic metabolism. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):858–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. R., Stith R. D., McCallum R. E. Monokines mediate decreased hepatic glucocorticoid binding in endotoxemia. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Mar;41(3):236–241. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.3.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M., McCallum R. Altered transcriptional regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in rats following endotoxin treatment. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):811–816. doi: 10.1172/JCI115381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod Y., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP stabilizes the mRNA for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) against degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7747–7752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Chen Y. Q., Su M. W., Ramirez F., Uitto J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma suppress the activation of human type I collagen gene expression by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Evidence for two distinct mechanisms of inhibition at the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1489–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI114866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang C. H., Dobrescu C. Interleukin-1 induced increases in glucose utilization are insulin mediated. Life Sci. 1989;45(22):2127–2134. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. D., Zentella A., Vine W., Pekala P. H., Cerami A. Effect of endotoxin-induced monokines on glucose metabolism in the muscle cell line L6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2590–2594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz S. R., Tsiang M., Sadler J. E. Regulation of thrombomodulin by tumor necrosis factor-alpha: comparison of transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):542–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum R. E., Berry L. J. Effects of endotoxin on gluconeogenesis, glycogen synthesis, and liver glycogen synthase in mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):642–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.642-654.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum R. E. Hepatocyte-Kupffer cell interactions in the inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis by bacterial endotoxin. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;62:99–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum R. E., Seale T. W., Stith R. D. Influence of endotoxin treatment on dexamethasone induction of hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):213–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.213-219.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengozzi M., Bertini R., Sironi M., Ghezzi P. Inhibition by interleukin 1 receptor antagonist of in vivo activities of interleukin 1 in mice. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1991 Oct;10(5):405–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz C., Misset B., Fitting C., Blériot J. P., Carlet J., Cavaillon J. M. Dissociation between plasma and monocyte-associated cytokines during sepsis. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2177–2184. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen D. D., Koch S. R., Granner D. K. 3' noncoding region of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA contains a glucocorticoid-responsive mRNA-stabilizing element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7800–7804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Cripe T. P., Koch S. R., Andreone T. L., Petersen D. D., Beale E. G., Granner D. K. Multihormonal regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene transcription. The dominant role of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15242–15251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Halgunset J., Haugen O. A., Aarset H., Aarden L., Waage A., Matsushima K., Kvithyll H., Boraschi D., Lamvik J. Cytokine-associated tissue injury and lethality in mice: a comparative study. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Oct;61(1):69–82. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(06)80008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R., Christoffersen C. A., Morrison D. C. Modulation of endotoxin lethality in mice by hydrazine sulfate. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2072–2078. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2072-2078.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R., Turley B. R., Christoffersen C. A., Johnson D. C., Morrison D. C. Hydrazine sulfate protects D-galactosamine-sensitized mice against endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor/cachectin lethality: evidence of a role for the pituitary. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):357–365. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spolarics Z., Schuler A., Bagby G. J., Lang C. H., Mészáros K., Spitzer J. J. Tumor necrosis factor increases in vivo glucose uptake in hepatic nonparenchymal cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Mar;49(3):309–312. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.3.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. M., Pekala P. H. Transcriptional repression of the GLUT4 and C/EBP genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21839–21845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumida M., Sekiya K., Okuda H., Tanaka Y., Shiosaka T. Inhibitory effect of tumor necrosis factor on gene expression of hormone sensitive lipase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biochem. 1990 Jan;107(1):1–2. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Lee T. H. Tumor necrosis factor. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of its multiple actions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7313–7316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Havell E. A. Differential inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced phenomena by anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2397–2400. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2397-2400.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Henricson B. E., Neta R. Roles of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in lipopolysaccharide-induced hypoglycemia. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2494–2498. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2494-2498.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi G., Gelfand J. A., Jung W. K., Connolly R. J., Burke J. F., Dinarello C. A. Staphylococcus epidermidis induces complement activation, tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1, a shock-like state and tissue injury in rabbits without endotoxemia. Comparison to Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1925–1935. doi: 10.1172/JCI115218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner F. R., Smith P. J., Wertheimer S., Rubin C. S. Regulation of gene expression by insulin and tumor necrosis factor alpha in 3T3-L1 cells. Modulation of the transcription of genes encoding acyl-CoA synthetase and stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23525–23528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman S. H., Shellhaas J., Butler L. D. Differential regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor synthesis: effects of endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoids and the role of the pituitary-adrenal axis. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Feb;19(2):301–305. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


