Abstract
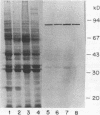
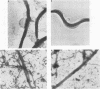
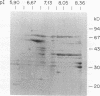
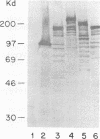
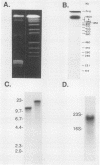
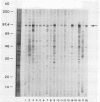
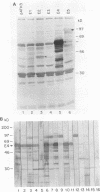
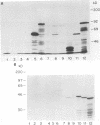
Using immunoblots, we identified proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized by sera from 62 patients with either acute or chronic Lyme disease. In all groups studied, the 41-kDa flagellar protein and a relatively minor 93-kDa protein (p93) were the most commonly recognized antigens in patients with acute and chronic disease due to B. burgdorferi. A murine monoclonal antibody (MAb 181.1) was developed against p93, and the antigen was detected by immunoblot analysis in four European and American strains of B. burgdorferi. On two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, p93 had an apparent pI of 6.8. Immunoelectronmicroscopy with MAb 181.1 demonstrated that p93 is located within the protoplasmic cylinder compartment of the organism. The gene encoding p93 was retrieved from a phage expression library. The derived amino acid sequence of p93 confirmed chemical characterization of the antigen, including its amino-terminal peptide sequence. The derived amino acid sequence predicted it to be predominantly alpha helical. A prominent antigenic domain located at the carboxy portion of the protein was recognized by human and rabbit polyclonal antisera and human (MAb D4) and mouse (MAb 181.1) MAbs.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann R., Kabatzki J., Boisten H. P., Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Hartung S., Runne U. Ixodes ricinus spirochete and European erythema chronicum migrans disease. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):573–580. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. L., Anderson N. G. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXII. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple gradient-slab gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):341–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Brehmer-Andersson E., Hovmark A. Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans--a spirochetosis. Clinical and histopathological picture based on 32 patients; course and relationship to erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius. Am J Dermatopathol. 1986 Jun;8(3):209–219. doi: 10.1097/00000372-198606000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hederstedt B., Hovmark A. The spirochetal etiology of erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius. Acta Derm Venereol. 1984;64(4):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Cutaneous manifestations in Ixodes-borne Borrelia spirochetosis. Int J Dermatol. 1987 May;26(4):215–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1987.tb00902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Olsson I. Clinical manifestations of erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius in 161 patients. A comparison with Lyme disease. Acta Derm Venereol. 1985;65(1):43–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Olsson I., Hovmark A. Erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius in Sweden. A study on 231 patients. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Grunwaldt E., Steere A. C. Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):504–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI110998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Hanrahan J. P., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., Bast T. F., Cameron D. J., Ziegler J. L., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):740–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W. Erythema chronicum migrans of Lyme disease. Arch Dermatol. 1984 Aug;120(8):1017–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W., Kaplan M. H., Rothenberg I. R., Barbour A. G. Isolation and characterization of the Lyme disease spirochete from the skin of patients with erythema chronicum migrans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985 Sep;13(3):444–449. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(85)70187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Molecular analysis of linear plasmid-encoded major surface proteins, OspA and OspB, of the Lyme disease spirochaete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreiro M. M., Laux D. C., Nelson D. R. Characterization of the heat shock response and identification of heat shock protein antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2186–2191. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2186-2191.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluss R. G., Boothby J. T. Thermoregulation of protein synthesis in Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1038–1042. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1038-1042.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Antibody response in Lyme disease: evaluation of diagnostic tests. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):789–795. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Volkman D. J., Luft B. J., Halperin J. J., Thomas J., Golightly M. G. Seronegative Lyme disease. Dissociation of specific T- and B-lymphocyte responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 1;319(22):1441–1446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812013192203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferdows M. S., Barbour A. G. Megabase-sized linear DNA in the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5969–5973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S. Identification of cysteine-containing peptides in protein digests by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 1;142(2):336–339. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90473-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann G. S., Kramer M., Göbel U. B., Wallich R. Nucleotide sequence of a gene encoding the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3590–3590. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. L., Jurkovich P., Kramber J. M., Johnson R. C. Molecular detection of persistent Borrelia burgdorferi in the urine of patients with active Lyme disease. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):269–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.269-278.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halperin J. J., Luft B. J., Anand A. K., Roque C. T., Alvarez O., Volkman D. J., Dattwyler R. J. Lyme neuroborreliosis: central nervous system manifestations. Neurology. 1989 Jun;39(6):753–759. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Bangsborg J. M., Fjordvang H., Pedersen N. S., Hindersson P. Immunochemical characterization of and isolation of the gene for a Borrelia burgdorferi immunodominant 60-kilodalton antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2047–2053. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2047-2053.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., LaQuier F. W., Barbour A. G. Organization of genes encoding two outer membrane proteins of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi within a single transcriptional unit. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):207–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.207-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. F., Russell H., Farshy C. E., Sampson J. S., Larsen S. A. Evaluation of sera from patients with Lyme disease in the fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorption test for syphilis. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;13(4):232–236. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198610000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörstrup P., Ackermann R. Durch Zecken übertragene Meningopolyneuritis (Garin-Bujadoux, Bannwarth. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr Grenzgeb. 1973 Nov;41(11):583–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W., Luft B. J., Munoz P., Dattwyler R. J., Gorevic P. D. Cross-antigenicity between the major surface proteins (ospA and ospB) and other proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):284–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy T. E., Gawinowicz M. A., Barzilai A., Kandel E. R., Sweatt J. D. Sequencing of proteins from two-dimensional gels by using in situ digestion and transfer of peptides to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes: application to proteins associated with sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7008–7012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logigian E. L., Kaplan R. F., Steere A. C. Chronic neurologic manifestations of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 22;323(21):1438–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011223232102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Jiang W., Munoz P., Dattwyler R. J., Gorevic P. D. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3637–3645. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3637-3645.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C. Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Meegan J. M., Anderson J. F., Chappell W. A. Comparison of an indirect fluorescent-antibody test with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serological studies of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.181-184.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz L. E., Wobig G. H., Duffy J., Katzmann J. A. Ticks, spirochetes, and new diagnostic tests for Lyme disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1985 Jun;60(6):402–406. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60851-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhlemann M. F., Wright D. J., Black C. Serology of Lyme disease. Lancet. 1986 Mar 8;1(8480):553–554. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90903-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perng G. C., LeFebvre R. B., Johnson R. C. Further characterization of a potent immunogen and the chromosomal gene encoding it in the Lyme disease agent, Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2070–2074. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2070-2074.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell H., Sampson J. S., Schmid G. P., Wilkinson H. W., Plikaytis B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and indirect immunofluorescence assay for Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W. H., Mudri S., Dattwyler R. J., Luft B. J. Mapping antibody-binding domains of the major outer surface membrane protein (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1911–1915. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1911-1915.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Schrumpf M. E., Schwan T. G. Reactivity of human Lyme borreliosis sera with a 39-kilodalton antigen specific to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1329–1337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1329-1337.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Craft J. E., Hutchinson G. J., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Spieler P. N., Stenn K. S., Malawista S. E. The early clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):76–82. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Gibofsky A., Patarroyo M. E., Winchester R. J., Hardin J. A., Malawista S. E. Chronic Lyme arthritis. Clinical and immunogenetic differentiation from rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jun;90(6):896–901. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-6-896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Craft J. E., Shrestha M., Kornblatt A. N., Malawista S. E. Recovery of Lyme disease spirochetes from patients. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):557–560. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Hutchinson G. J., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Craft J. E., DeSanna E. T., Malawista S. E. Treatment of the early manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):22–26. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiernstedt G., Gustafsson R., Karlsson M., Svenungsson B., Sköldenberg B. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of neuroborreliosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:46–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31837.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C. A simple method for extraction of RNA from E. coli utilizing diethyl pyrocarbonate. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman D. J., Luft B. J., Gorevic P. D., Schultz J., Padovano L. Characterization of an immunoreactive 93-kDa core protein of Borrelia burgdorferi with a human IgG monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3177–3182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. J., McDougall J., Wittmann-Liebold B. Extended N-terminal sequencing of proteins of archaebacterial ribosomes blotted from two-dimensional gels onto glass fiber and poly(vinylidene difluoride) membrane. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6867–6876. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Busch K. V. Immunochemical and immunological analysis of European Borrelia burgdorferi strains. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):92–102. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Wickner W., Goodman J. M. Sequence of the leader peptidase gene of Escherichia coli and the orientation of leader peptidase in the bacterial envelope. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):12073–12080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]