Abstract
In vivo administration of various doses of recombinant interleukin-1 alpha to B10.D2/n mice chronically infected with Leishmania donovani resulted in enhanced formation of granulomas and in vitro production of gamma interferon. By direct microscopical enumeration, reduction in gross parasite burden in the viscera was not observed, however. These data highlight an important discordance between granuloma formation per se and parasite elimination and suggest that interleukin-1 deficiency alone cannot account for the chronicity of this disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck G., Habicht G. S., Benach J. L., Miller F. Interleukin 1: a common endogenous mediator of inflammation and the local Shwartzman reaction. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3025–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. M., Roach T. I., Kiderlen A., Kaye P. M. Role of Lsh in regulating macrophage priming/activation. Res Immunol. 1989 Oct;140(8):798–805. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(89)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castelli M. P., Black P. L., Schneider M., Pennington R., Abe F., Talmadge J. E. Protective, restorative, and therapeutic properties of recombinant human IL-1 in rodent models. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3830–3837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. R., Grau G. E., Pechère J. C. Role of TNF and IL-1 in infections with Toxoplasma gondii. Immunology. 1990 Jan;69(1):33–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Kelly N., Bernton E., Gemski P. Pretreatment with recombinant murine tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin and murine interleukin 1 alpha protects mice from lethal bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2021–2027. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Colditz I. G., Movat H. Z. The role of interleukin-1 in neutrophil leukocyte emigration induced by endotoxin. Am J Pathol. 1986 Sep;124(3):367–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F. Recombinant murine interleukin-1 alpha enhancement of nonspecific antibacterial resistance. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2061–2065. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2061-2065.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F., Young K. M., Cooley A. J., Kurtz R. S. Effects of murine recombinant interleukin 1 alpha on the host response to bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):962–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Canono B. P., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Genetically determined resistance to listeriosis is associated with increased accumulation of inflammatory neutrophils and macrophages which have enhanced listericidal activity. Immunology. 1985 Jul;55(3):511–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Ikejima T., Warner S. J., Orencole S. F., Lonnemann G., Cannon J. G., Libby P. Interleukin 1 induces interleukin 1. I. Induction of circulating interleukin 1 in rabbits in vivo and in human mononuclear cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1902–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and the pathogenesis of the acute-phase response. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 29;311(22):1413–1418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411293112205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granstein R. D., Margolis R., Mizel S. B., Sauder D. N. In vivo inflammatory activity of epidermal cell-derived thymocyte activating factor and recombinant interleukin 1 in the mouse. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Holaday B. J., Coffman R. L., Locksley R. M. Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):59–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Coulie P. G., Olive D., Van Snick J. Synergistic activation of human T cells by interleukin 1 and interleukin 6. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):653–656. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye P. M., Cooke A., Lund T., Wattie M., Blackwell J. M. Altered course of visceral leishmaniasis in mice expressing transgenic I-E molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):357–364. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
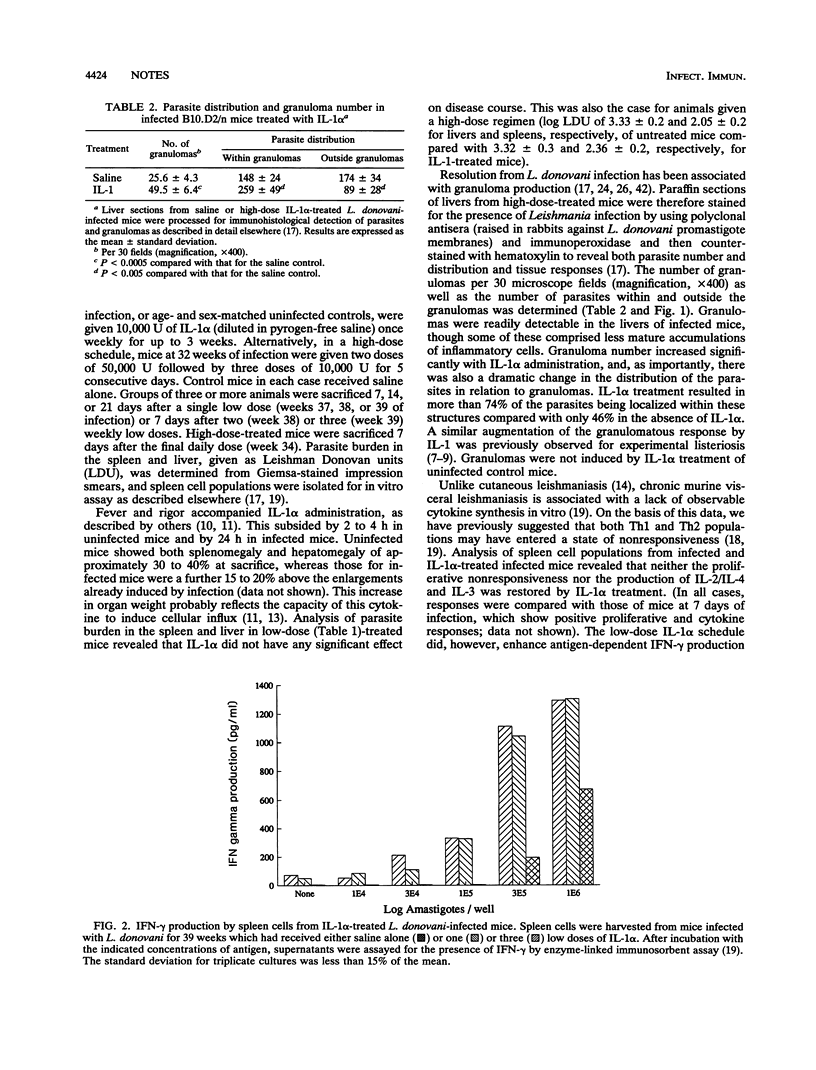
- Kaye P. M., Curry A. J., Bancroft G. J., Lang T. Antigen processing and presentation: modelling with Leishmania. Behring Inst Mitt. 1991 Feb;(88):13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
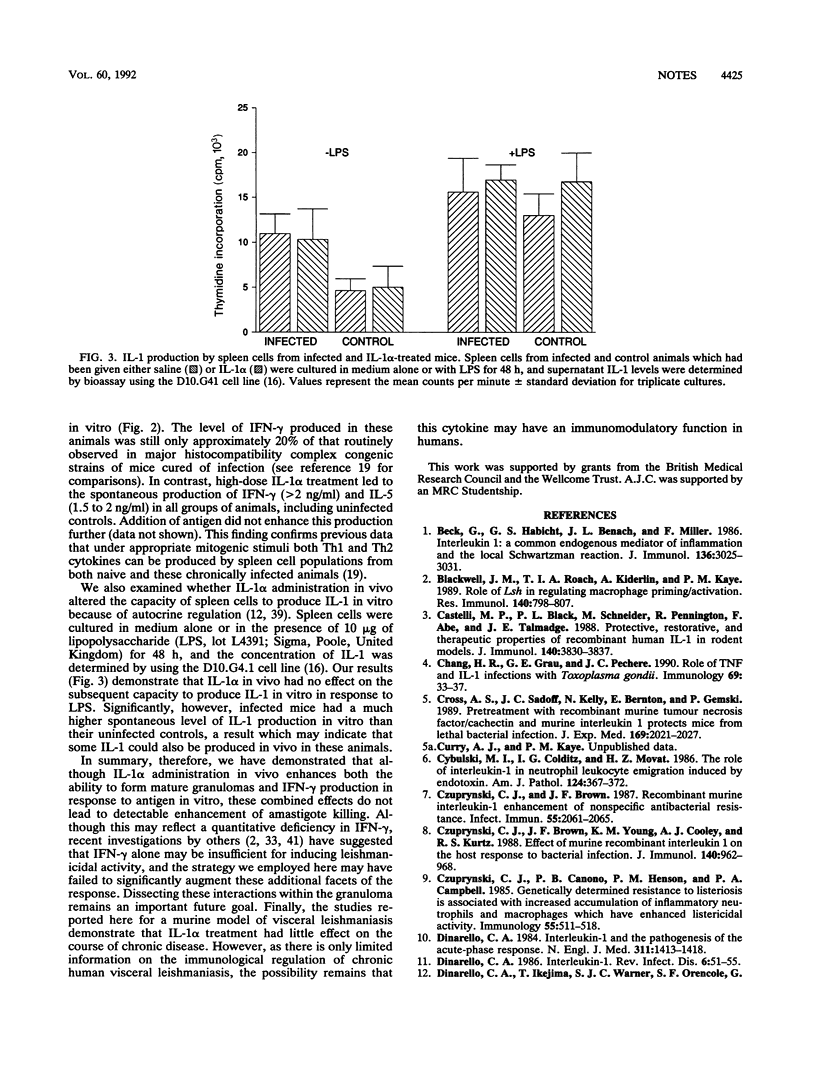
- Kaye P. M., Curry A. J., Blackwell J. M. Differential production of Th1- and Th2-derived cytokines does not determine the genetically controlled or vaccine-induced rate of cure in murine visceral leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2763–2770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killar L. M., Hatfield C. A., Carding S. R., Pan M., Winterrowd G. E., Bottomly K. In vivo administration of interleukin 1 elicits increased Ia antigen expression on B cells through the induction of interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2205–2210. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlander R. J., Hoffman M., Kratz S. S., Gates J. Comparison of the effects of IL-1 alpha and TNF-alpha on phagocyte accumulation and murine antibacterial immunity. Cell Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;123(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman A. H., Chin J., Schmidt J. A., Abbas A. K. Role of interleukin 1 in the activation of T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9699–9703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElrath M. J., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. The dynamics of granuloma formation in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1927–1937. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Masur H., Keithly J. S. Cell-mediated immune response in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. I. Correlation between resistance to Leishmania donovani and lymphokine-generating capacity. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Stern J. J., Welte K., Rubin B. Y., Carriero S. M., Nathan C. F. Experimental visceral leishmaniasis: production of interleukin 2 and interferon-gamma, tissue immune reaction, and response to treatment with interleukin 2 and interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2290–2297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol A. D., Bonventre P. F. Visceral leishmaniasis in congenic mice of susceptible and resistant phenotypes: immunosuppression by adherent spleen cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):160–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.160-168.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki Y., Ohashi T., Minami A., Nakamura S. Enhanced resistance of mice to bacterial infection induced by recombinant human interleukin-1a. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1436–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1436-1440.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankewycz O. G., Yui M., Kelley V. E., Strom T. B. The cascading, interrelated roles of interleukin-1, interleukin-2, and interleukin-6 in murine anti-CD3-driven T cell proliferation. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Apr;55(1):67–85. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Finke J. H. Interleukin 2 deficiency in murine Leishmaniasis donovani and its relationship to depressed spleen cell responses to phytohemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1487–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Ng W., Wilson C. B., McMaster W. R., Burchett S. K. Modulation of in vitro monocyte cytokine responses to Leishmania donovani. Interferon-gamma prevents parasite-induced inhibition of interleukin 1 production and primes monocytes to respond to Leishmania by producing both tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1914–1924. doi: 10.1172/JCI114654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E. Parasite accessory cell interactions in murine leishmaniasis. I. Evasion and stimulus-dependent suppression of the macrophage interleukin 1 response by Leishmania donovani. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1919–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach T. I., Kiderlen A. F., Blackwell J. M. Role of inorganic nitrogen oxides and tumor necrosis factor alpha in killing Leishmania donovani amastigotes in gamma interferon-lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages from Lshs and Lshr congenic mouse strains. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3935–3944. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3935-3944.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires K. E., Schreiber R. D., McElrath M. J., Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Murray H. W. Experimental visceral leishmaniasis: role of endogenous IFN-gamma in host defense and tissue granulomatous response. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4244–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. The basis for the immunoregulatory role of macrophages and other accessory cells. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):551–557. doi: 10.1126/science.2437650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van't Wout J. W., Van der Meer J. W., Barza M., Dinarello C. A. Protection of neutropenic mice from lethal Candida albicans infection by recombinant interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jul;18(7):1143–1146. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Wauters P., Van Snick J. Accessory factors involved in murine T cell activation. Distinct roles of interleukin 6, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. T., Unanue E. R. The costimulatory function of antigen-presenting cells. Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser W. Y., Pozzi L. M., David J. R. Human recombinant migration inhibitory factor activates human macrophages to kill Leishmania donovani. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):2006–2011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Innes D. J., Sousa A. D., Pearson R. D. Early histopathology of experimental infection with Leishmania donovani in hamsters. J Parasitol. 1987 Feb;73(1):55–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. W., Barza M., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. A low dose of recombinant interleukin 1 protects granulocytopenic mice from lethal gram-negative infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1620–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]