Abstract
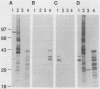
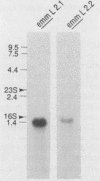
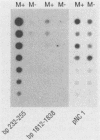
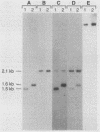
M protein is a key virulence factor present on the surface of group A streptococci. M protein is defined by its antiphagocytic function, whereas M-like proteins, while structurally related to M proteins, lack an established antiphagocytic function. Group A streptococci can be divided into two main groups (class I and II) on the basis of the presence or absence of certain antigenic epitopes within the M and M-like molecules, and importantly, the two classes correlate with the disease-causing potential of group A streptococci. In an effort to better understand this family of molecules, a 2.8-kb region containing the two M protein-like genes from a class II isolate (serotype 2) was cloned and sequenced. The two genes lie adjacent to one another on the chromosome, separated by 211 bp, and have many structural features in common. The emmL2.1-derived product (ML2.1 protein) is immunoreactive with type-specific antiserum, a property associated with M proteins. The cloned product of the downstream gene, emmL2.2 (ML2.2 protein), is an immunoglobulin A (IgA)-binding protein, binding human myeloma IgA. Interestingly, the RNA transcript levels of emmL2.1 exceed that of emmL2.2 by at least 32-fold. Northern (RNA) hybridization and primer extension studies suggest that the RNA transcripts of emmL2.1 and emmL2.2 are monocistronic. The ML2.1 and ML2.2 proteins exhibit 53% amino acid sequence identity and differ primarily in their amino termini and peptidoglycan-spanning domains and in a Glu-Gln-rich region present only in the ML2.1 protein. However, the previously described M-like, IgA-binding protein from a serotype 4 isolate (Arp4) displays a higher level of amino acid sequence homology with the ML2.1 molecule than with the IgA-binding ML2.2 protein. Amino acid sequence alignments between all M and M-like proteins characterized to date suggest the existence of two fundamental M or M-like gene subclasses within class II organisms, represented by emmL2.1 and emmL2.2. In addition, IgA-binding activity can be found within both types of molecules.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Seyer J. M., Dale J. B., Simpson W. A., Kang A. H. Type-specific protective immunity evoked by synthetic peptide of Streptococcus pyogenes M protein. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):457–459. doi: 10.1038/292457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen D. E., Fischetti V. A. Differentiation between two biologically distinct classes of group A streptococci by limited substitutions of amino acids within the shared region of M protein-like molecules. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1757–1764. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen D., Fischetti V. A. A human IgG receptor of group A streptococci is associated with tissue site of infection and streptococcal class. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):747–754. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen D., Jones K. F., Fischetti V. A. Evidence for two distinct classes of streptococcal M protein and their relationship to rheumatic fever. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):269–283. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Identification of a gene that regulates expression of M protein, the major virulence determinant of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8677–8681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Parry D. A. Alpha-helical coiled coils and bundles: how to design an alpha-helical protein. Proteins. 1990;7(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Manjula B. N., Scott J. R. Streptococcal M6 protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Localization, purification, and comparison with streptococcal-derived M protein. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1083–1095. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Scott J. R. Size variation of the M protein in group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1384–1401. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Parry D. A., Trus B. L., Hollingshead S. K., Scott J. R., Manjula B. N. Conformational characteristics of the complete sequence of group A streptococcal M6 protein. Proteins. 1988;3(1):60–69. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: molecular design and biological behavior. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jul;2(3):285–314. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frithz E., Hedén L. O., Lindahl G. Extensive sequence homology between IgA receptor and M proteins in Streptococcus pyogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1111–1119. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomi H., Hozumi T., Hattori S., Tagawa C., Kishimoto F., Björck L. The gene sequence and some properties of protein H. A novel IgG-binding protein. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):4046–4052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guss B., Eliasson M., Olsson A., Uhlén M., Frej A. K., Jörnvall H., Flock J. I., Lindberg M. Structure of the IgG-binding regions of streptococcal protein G. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1567–1575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haanes-Fritz E., Kraus W., Burdett V., Dale J. B., Beachey E. H., Cleary P. Comparison of the leader sequences of four group A streptococcal M protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4667–4677. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haanes E. J., Cleary P. P. Identification of a divergent M protein gene and an M protein-related gene family in Streptococcus pyogenes serotype 49. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6397–6408. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6397-6408.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D. G., Boyle M. D., Cleary P. P. Isolated DNA repeat region from fcrA76, the Fc-binding protein gene from an M-type 76 strain of group A streptococci, encodes a protein with Fc-binding activity. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2071–2079. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D. G., Cleary P. P. Fc-receptor and M-protein genes of group A streptococci are products of gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4741–4745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. A highly conserved region present in transcripts encoding heterologous M proteins of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3237–3239. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3237-3239.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Size variation in group A streptococcal M protein is generated by homologous recombination between intragenic repeats. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):196–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00331578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. T., Malke H., Ferretti J. J. Heterogeneity of the streptokinase gene in group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):502–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.502-506.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. F., Fischetti V. A. The importance of the location of antibody binding on the M6 protein for opsonization and phagocytosis of group A M6 streptococci. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1114–1123. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. F., Khan S. A., Erickson B. W., Hollingshead S. K., Scott J. R., Fischetti V. A. Immunochemical localization and amino acid sequences of crossreactive epitopes within the group A streptococcal M6 protein. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1226–1238. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Gray L., Beachey E., Kehoe M. Antigenic variation among group A streptococcal M proteins. Nucleotide sequence of the serotype 5 M protein gene and its relationship with genes encoding types 6 and 24 M proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5668–5673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouw A. R., Beachey E. H., Burdett V. Molecular evolution of streptococcal M protein: cloning and nucleotide sequence of the type 24 M protein gene and relation to other genes of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):676–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.676-684.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi V., Fischetti V. A. Isolation and characterization of the cell-associated region of group A streptococcal M6 protein. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2618–2624. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2618-2624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Casal J., Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Mry, a trans-acting positive regulator of the M protein gene of Streptococcus pyogenes with similarity to the receptor proteins of two-component regulatory systems. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2617–2624. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2617-2624.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Flicker P. F., Cohen C., Manjula B. N., Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: alpha-helical coiled-coil structure and arrangement on the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4689–4693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. C., Spanier J. G., Jones S. J., Simpson W. J., Cleary P. P. Streptococcus pyogenes type 12 M protein gene regulation by upstream sequences. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5633–5640. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5633-5640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saravani G. A., Martin D. R. Opacity factor from group A streptococci is an apoproteinase. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 1;56(1-2):35–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalén C. The group A streptococcal receptor for human IgA binds IgA via the Fc-fragment. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Oct;88(5):271–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R., Pulliam W. M., Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A. Relationship of M protein genes in group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1822–1826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Cleary P. P. Expression of M type 12 protein by a group A streptococcus exhibits phaselike variation: evidence for coregulation of colony opacity determinants and M protein. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2448–2455. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2448-2455.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., LaPenta D., Chen C., Cleary P. P. Coregulation of type 12 M protein and streptococcal C5a peptidase genes in group A streptococci: evidence for a virulence regulon controlled by the virR locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):696–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.696-700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjodahl J. Repetitive sequences in protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Arrangement of five regions within the protein, four being highly homologous and Fc-binding. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):343–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]