Abstract
The polymerase chain reaction method was used to amplify DNA from the fourth variable segment of the gene encoding the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Direct sequencing of the amplified DNA from prototype strains confirmed previously identified nucleotide sequence differences that were specific for each serovar. This analysis revealed differences in the DNA sequences of prototype strains C/UW-1 and G/IOL-238 from those of prototype strains C/TW-3 and G/UW-57, sequenced previously. This method was also used to determine the serovar types of C. trachomatis in 125 urogenital specimens from infected patients. The most common serovars were E (38%), F (17%), and G and D (14% each). Serovar D was found significantly more often in specimens from men than in specimens from women (P = 0.004). Conversely, serovar G was found significantly more often in specimens from women than in specimens from men (P = 0.026). Only two serovar G isolates gave sequences identical to that of the prototype strain G/IOL-238, suggesting that this strain may be a serovar variant. Three isolates (D+, G-, and J') gave sequences which have not been reported previously. One isolate had the same sequence as the D- serovar variant. Sequence analysis of amplified DNA reveals subtle differences between C. trachomatis strains and provides a very sensitive method for molecular epidemiological analysis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehr W., Zhang Y. X., Joseph T., Su H., Nano F. E., Everett K. D., Caldwell H. D. Mapping antigenic domains expressed by Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4000–4004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
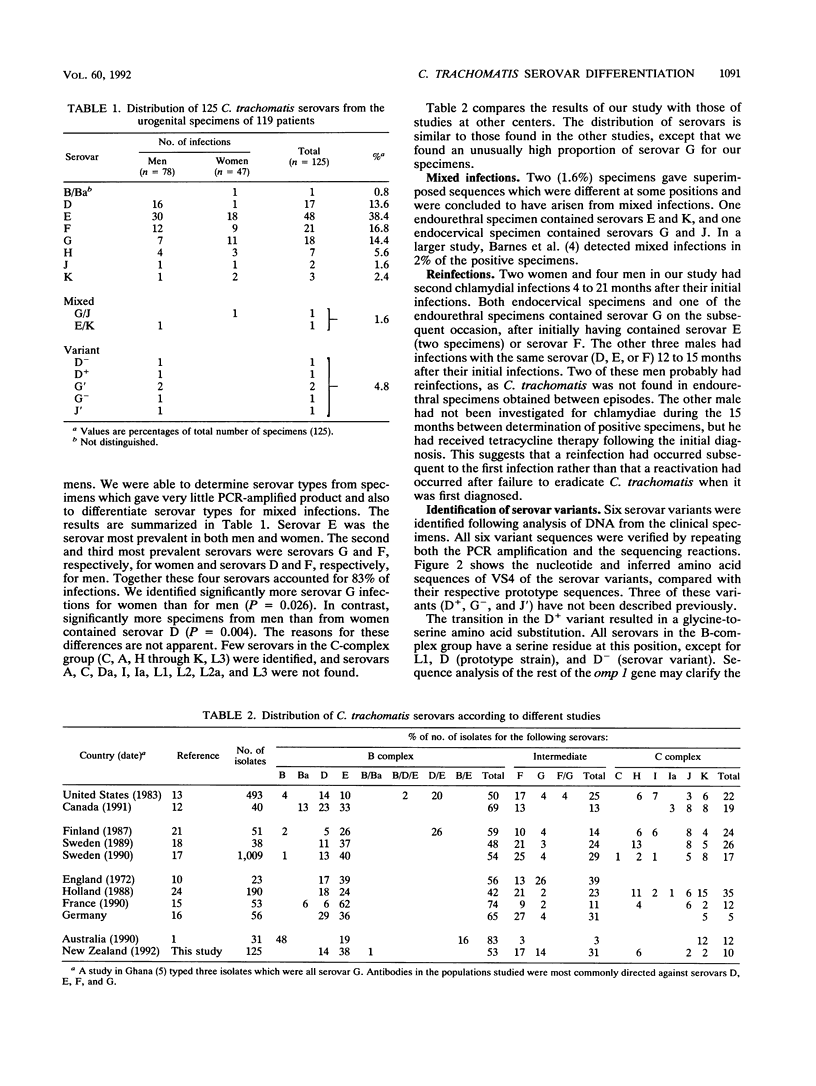
- Barnes R. C., Rompalo A. M., Stamm W. E. Comparison of Chlamydia trachomatis serovars causing rectal and cervical infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;156(6):953–958. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.6.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes R. C., Suchland R. J., Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Stamm W. E. Detection of multiple serovars of Chlamydia trachomatis in genital infections. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):985–989. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentsi C., Klufio C. A., Perine P. L., Bell T. A., Cles L. D., Koester C. M., Wang S. P. Genital infections with Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Ghanaian women. Genitourin Med. 1985 Feb;61(1):48–50. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Stewart S., Johnson S., Taylor H. Tear and serum antibody response to Chlamydia trachomatis antigens during acute chlamydial conjunctivitis in monkeys as determined by immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):93–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.93-98.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J. L., Pannetier C., Jaulin C., Kourilsky P. Optimal conditions for directly sequencing double-stranded PCR products with sequenase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4028–4028. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D., Patton M., Stephens R. S. Direct sequence evaluation of the major outer membrane protein gene variant regions of Chlamydia trachomatis subtypes D', I', and L2'. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1579–1582. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1579-1582.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer R. S., Treharne J. D., Jones B. R., Herring J. Chlamydial infection. Results of micro-immunofluorescence tests for the detection of type-specific antibody in certain chlamydial infections. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):452–459. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraiz J., Jones R. B. Chlamydial infections. Annu Rev Med. 1988;39:357–370. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.39.020188.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E. H., Deslandes S., Veilleux S., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D. Typing Chlamydia trachomatis by detection of restriction fragment length polymorphism in the gene encoding the major outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1103–1107. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Holmes K. K., Grayston J. T. Immunotypes of Chlamydia trachomatis isolates in Seattle, Washington. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.865-868.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncan T., Eb F., Orfila J. Monoclonal antibodies in serovar determination of 53 Chlamydia trachomatis isolates from Amiens, France. Res Microbiol. 1990 Jul-Aug;141(6):695–701. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90063-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näher H., Petzoldt D. Serovar distribution of urogenital C trachomatis isolates in Germany. Genitourin Med. 1991 Apr;67(2):114–116. doi: 10.1136/sti.67.2.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson K., Osser S. Serovars of Chlamydia trachomatis causing postabortion salpingitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;8(9):795–798. doi: 10.1007/BF02185848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikku P., Wang S. P. Chlamydia trachomatis immunotypes in Finland. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1987 Apr;95(2):131–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb03100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Sanchez-Pescador R., Wagar E. A., Inouye C., Urdea M. S. Diversity of Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3879–3885. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3879-3885.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Wagar E. A., Schoolnik G. K. High-resolution mapping of serovar-specific and common antigenic determinants of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):817–831. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenvoort J. H., Suchland R. J., Stamm W. E. Serovar distribution of urogenital Chlamydia trachomatis strains in The Netherlands. Genitourin Med. 1988 Jun;64(3):159–161. doi: 10.1136/sti.64.3.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Three new serovars of Chlamydia trachomatis: Da, Ia, and L2a. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):403–405. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Barnes R. C., Stephens R. S., Grayston J. T. Immunotyping of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):791–800. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Zhang Y. X., Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences for the four variable domains of the major outer membrane proteins of the 15 Chlamydia trachomatis serovars. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1040-1049.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. X., Stewart S., Joseph T., Taylor H. R., Caldwell H. D. Protective monoclonal antibodies recognize epitopes located on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong G. M., Brunham R. C. Antigenic determinants of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein resolved at a single amino acid level. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1141–1147. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1141-1147.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


