Abstract
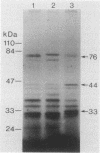
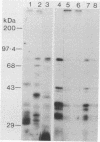
Streptococcus gordonii Challis incorporated exogenous [3H]palmitate into 13 polypeptides extractable from intact cells with sodium dodecyl sulfate. A 76-kDa surface-exposed polypeptide, implicated previously as a cell aggregation determinant, was shown to be one of these lipid-modified polypeptides. Differences in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis patterns of lipopolypeptides were detected with mutants of S. gordonii that were altered in adherence, aggregation, coaggregation, or hydrophobicity. Lipid-modified polypeptides, tightly associated with the cell membrane, may be involved in the expression of cell surface properties of S. gordonii important for colonization of the human oral cavity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alloing G., Trombe M. C., Claverys J. P. The ami locus of the gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae is similar to binding protein-dependent transport operons of gram-negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):633–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demuth D. R., Golub E. E., Malamud D. Streptococcal-host interactions. Structural and functional analysis of a Streptococcus sanguis receptor for a human salivary glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7120–7126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson P. R., Herzberg M. C. A collagen-like immunodeterminant on the surface of Streptococcus sanguis induces platelet aggregation. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3360–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fachon-Kalweit S., Elder B. L., Fives-Taylor P. Antibodies that bind to fimbriae block adhesion of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):617–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.617-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenno J. C., LeBlanc D. J., Fives-Taylor P. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a type 1 fimbrial gene of Streptococcus sanguis FW213. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3527–3533. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3527-3533.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganeshkumar N., Hannam P. M., Kolenbrander P. E., McBride B. C. Nucleotide sequence of a gene coding for a saliva-binding protein (SsaB) from Streptococcus sanguis 12 and possible role of the protein in coaggregation with actinomyces. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1093–1099. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1093-1099.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganeshkumar N., Song M., McBride B. C. Cloning of a Streptococcus sanguis adhesin which mediates binding to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1150–1157. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1150-1157.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J. Adherent interactions which may affect microbial ecology in the mouth. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):378–385. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630030401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Alloing G., Schmidt T., Claverys J. P., Dudler R., Hofnung M. Evidence for high affinity binding-protein dependent transport systems in gram-positive bacteria and in Mycoplasma. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3971–3974. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt R. M., Thoren-Gordon M., Curtiss R., 3rd Regions of the Streptococcus sobrinus spaA gene encoding major determinants of antigen I. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3988–4001. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3988-4001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Gallagher M. P., Jamieson D. J., Higgins C. F. Molecular characterization of the oligopeptide permease of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90332-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Carter D. A. Cell surface mutants of Streptococcus sanguis with altered adherence properties. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1988 Jun;3(2):53–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1988.tb00081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Easingwood R. A. Insertional inactivation of the gene encoding a 76-kilodalton cell surface polypeptide in Streptococcus gordonii Challis has a pleiotropic effect on cell surface composition and properties. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3689–3697. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3689-3697.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Lala H. C., Shepherd M. G. Coaggregation of Streptococcus sanguis and other streptococci with Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1429–1436. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1429-1436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F. Novobiocin-resistant mutants of Streptococcus sanguis with reduced cell hydrophobicity and defective in coaggregation. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1909–1918. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N. Characterization of Streptococcus gordonii (S. sanguis) PK488 adhesin-mediated coaggregation with Actinomyces naeslundii PK606. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3064–3072. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3064-3072.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Surface recognition among oral bacteria: multigeneric coaggregations and their mediators. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;17(2):137–159. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPolla R. J., Haron J. A., Kelly C. G., Taylor W. R., Bohart C., Hendricks M., Pyati J. P., Graff R. T., Ma J. K., Lehner T. Sequence and structural analysis of surface protein antigen I/II (SpaA) of Streptococcus sobrinus. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2677–2685. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2677-2685.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J. S., Sarvas M., Brammar W. J., Neugebauer K., Wu H. C. Bacillus licheniformis penicillinase synthesized in Escherichia coli contains covalently linked fatty acid and glyceride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3506–3510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont R. J., Rosan B., Baker C. T., Nelson G. M. Characterization of an adhesion antigen of Streptococcus sanguis G9B. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2417–2423. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2417-2423.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Progulske-Fox A., Erdos G. W., Piacentini D. A., Ayakawa G. Y., Crowley P. J., Bleiweis A. S. Construction and characterization of isogenic mutants of Streptococcus mutans deficient in major surface protein antigen P1 (I/II). Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3306–3313. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3306-3313.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., McBride B. C. Aggregation of Streptococcus sanguis by a neuraminidase-sensitive component of serum and crevicular fluid. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1073–1080. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1073-1080.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. B., Lampen J. O. Glyceride-cysteine lipoproteins and secretion by Gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):315–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.315-322.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi V., Fischetti V. A. Identification of an endogenous membrane anchor-cleaving enzyme for group A streptococcal M protein. Its implication for the attachment of surface proteins in gram-positive bacteria. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2119–2133. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Baker C. T., Nelson G. M., Berman R., Lamont R. J., Demuth D. R. Cloning and expression of an adhesin antigen of Streptococcus sanguis G9B in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Mar;135(3):531–538. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-3-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Filamentous phage pre-coat is an integral membrane protein: analysis by a new method of membrane preparation. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90387-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Buss J. E. The covalent modification of eukaryotic proteins with lipid. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1449–1453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Tokunaga M. Biogenesis of lipoproteins in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:127–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Yu F., Inouye M. A single amino acid determinant of the membrane localization of lipoproteins in E. coli. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]