Abstract
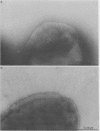
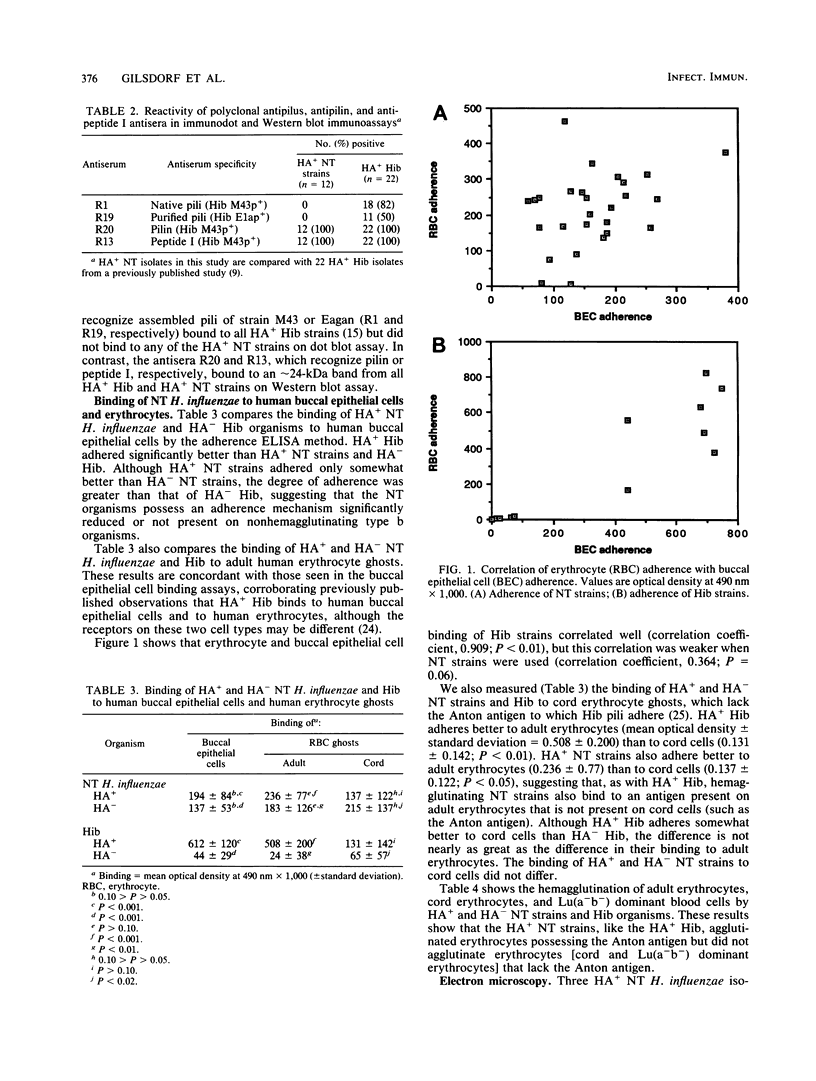
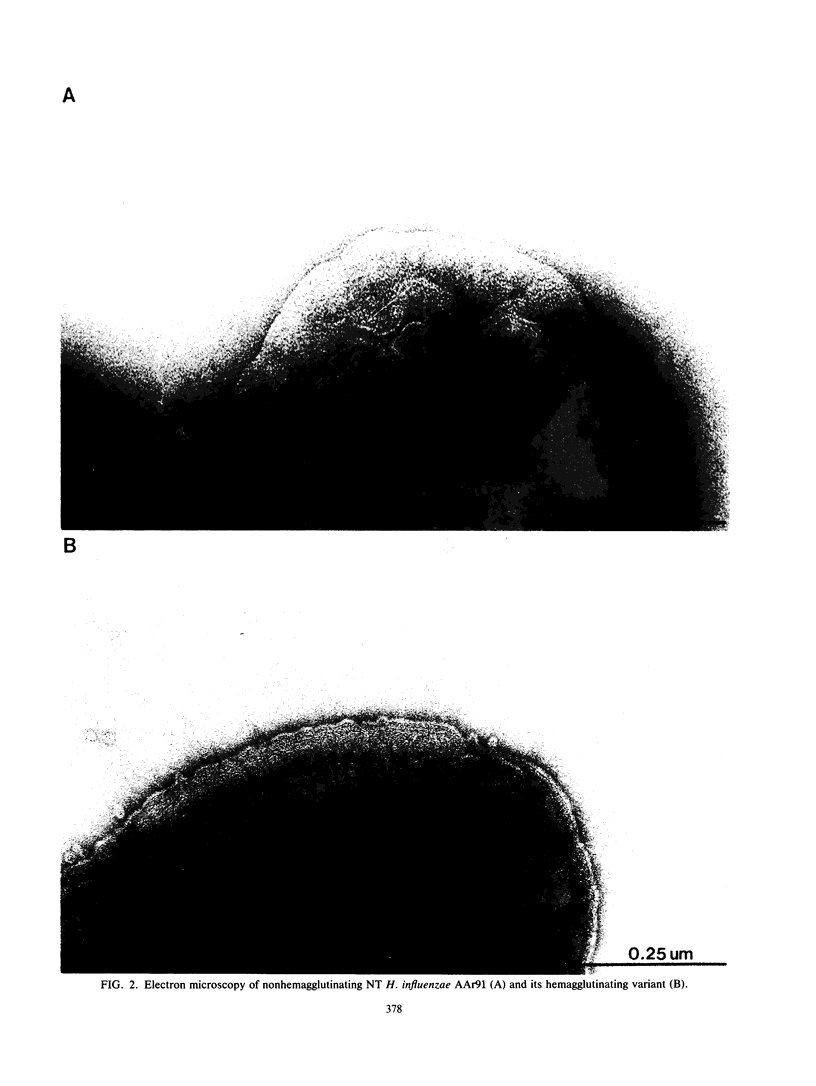
Thirty-eight clinical isolates of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae were tested for the presence of hemagglutinating pili similar to those of H. influenzae type b (Hib) that mediate buccal epithelial cell adherence. Four endogenously hemagglutinating (HA+) strains were identified, and eight additional HA+ variants were obtained from HA- strains by erythrocyte enrichment. All 12 HA+ nontypeable H. influenzae isolates bound antisera directed against denatured pilins of Hib, but none bound antisera against assembled native pili of Hib. In erythrocyte- and buccal-cell-binding assays, HA+ nontypeable H. influenzae binding was reduced compared with HA+ Hib binding and was not significantly different from HA- nontypeable H. influenzae binding. Both HA- and HA+ nontypeable H. influenzae binding was increased over binding of HA- Hib. HA+ nontypeable H. influenzae strains agglutinated adult erythrocytes that possess the Anton antigen, which is thought to be the receptor for Hib pili, and did not agglutinate cord or Lu(a-b-) dominant erythrocytes, which lack the Anton antigen. Electron microscopy of HA- and HA+ variants of three nontypeable H. influenzae strains showed few or no surface appendages on the HA- organisms, but piluslike structures were seen on many organisms from two HA+ nontypeable H. influenzae strains and on a few organisms from one strain. Thus, nontypeable H. influenzae appears to possess structures that are immunologically similar to the pilins that make up the hemagglutinating pili of Hib. However, nontypeable H. influenzae appears to also possess mechanisms for erythrocyte and buccal cell adherence that are not directly correlated with the presence of a hemagglutinating pilus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P. W., Pichichero M. E., Connor E. M. Enhanced nasopharyngeal colonization of rats by piliated Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):565–568. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.565-568.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakaletz L. O., Tallan B. M., Hoepf T., DeMaria T. F., Birck H. G., Lim D. J. Frequency of fimbriation of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae and its ability to adhere to chinchilla and human respiratory epithelium. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):331–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.331-335.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr, Carter M. J., Derber D. B., Kar S., Kramarik J. A., To A. C., To S. C., Wood S. W. Design and development of pilus vaccines for Haemophilus influenzae diseases. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S54–S61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman T., Grass S., Munson R., Jr Molecular cloning, expression, and sequence of the pilin gene from nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae M37. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1716–1722. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1716-1722.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor E. M., Loeb M. R. A hemadsorption method for detection of colonies of Haemophilus influenzae type b expressing fimbriae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Nov;148(5):855–860. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.5.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley M. M., Stephens D. S., Kaplan S. L., Mason E. O., Jr Pilus- and non-pilus-mediated interactions of Haemophilus influenzae type b with human erythrocytes and human nasopharyngeal mucosa. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):274–280. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney L. J., Marrs C. F., Bektesh S. L., Gilsdorf J. R. Comparison and analysis of the nucleotide sequences of pilin genes from Haemophilus influenzae type b strains Eagan and M43. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1991–1996. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1991-1996.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., Ferrieri P. Adherence of Haemophilus influenzae to human epithelial cells. Scand J Infect Dis. 1984;16(3):271–278. doi: 10.3109/00365548409070400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., Forney L. J., LiPuma J. J. Reactivity of Haemophilus influenzae type b anti-pili antibodies. Microb Pathog. 1989 Oct;7(4):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R. Haemophilus influenzae non-type b infections in children. Am J Dis Child. 1987 Oct;141(10):1063–1065. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.141.10.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., Marrs C. F., McCrea K. W., Forney L. J. Cloning, expression, and sequence analysis of the Haemophilus influenzae type b strain M43p+ pilin gene. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1065–1072. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1065-1072.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., McCrea K., Forney L. Conserved and nonconserved epitopes among Haemophilus influenzae type b pili. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2252–2257. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2252-2257.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Langermann S., Clegg H. W., Kessler T. W., Goldman D. A., Gilsdorf J. R. Adherence of piliated Haemophilus influenzae type b to human oropharyngeal cells. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):564–564. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langermann S., Wright A. Molecular analysis of the Haemophilus influenzae type b pilin gene. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):221–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Gilsdorf J. R. Structural and serological relatedness of Haemophilus influenzae type b pili. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1051–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1051-1056.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L., Wiedermann B. L., Norrod E. P., Stenback W. A. Frequency and properties of naturally occurring adherent piliated strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):98–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.98-103.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Courtney H. S., Schifferli D. M., Beachey E. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for adherence of bacteria to animal cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):512–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.512-516.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E. Adherence of Haemophilus influenzae to human buccal and pharyngeal epithelial cells: relationship to pilation. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):107–116. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E., Loeb M., Anderson, Smith D. H. Do pili play a role in pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type B? Lancet. 1982 Oct 30;2(8305):960–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Geme J. W., 3rd, Falkow S. Haemophilus influenzae adheres to and enters cultured human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4036–4044. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4036-4044.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyant R. S., Bibb W. F., Stephens D. S., Holloway B. P., Moo-Penn W. F., Birkness K. A., Helsel L. O., Mayer L. W. Purification and characterization of a pilin specific for Brazilian purpuric fever-associated Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius (H. aegyptius) strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):756–763. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.756-763.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Poole J., Geelen L., Zanen H. C. The erythrocyte and epithelial cell receptors for Haemophilus influenzae are expressed independently. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2355–2358. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2355-2358.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]