Abstract
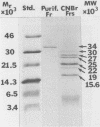
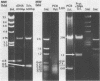
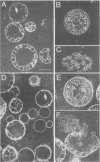
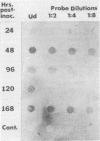
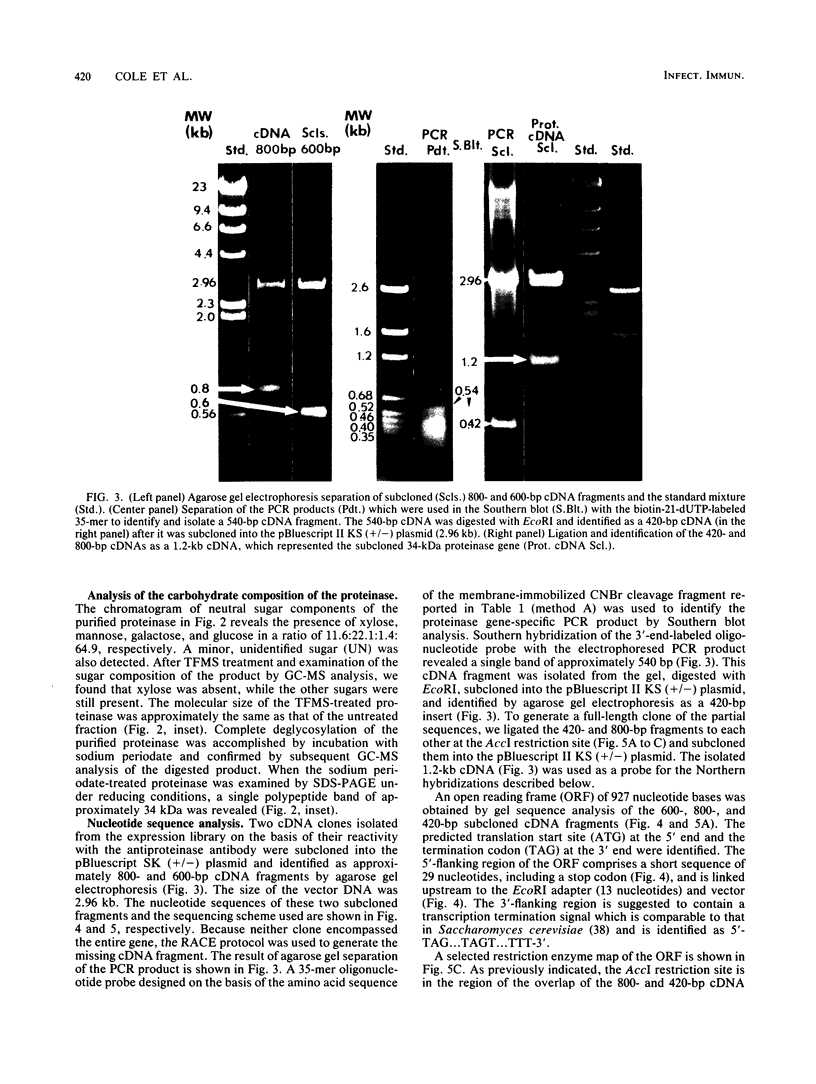
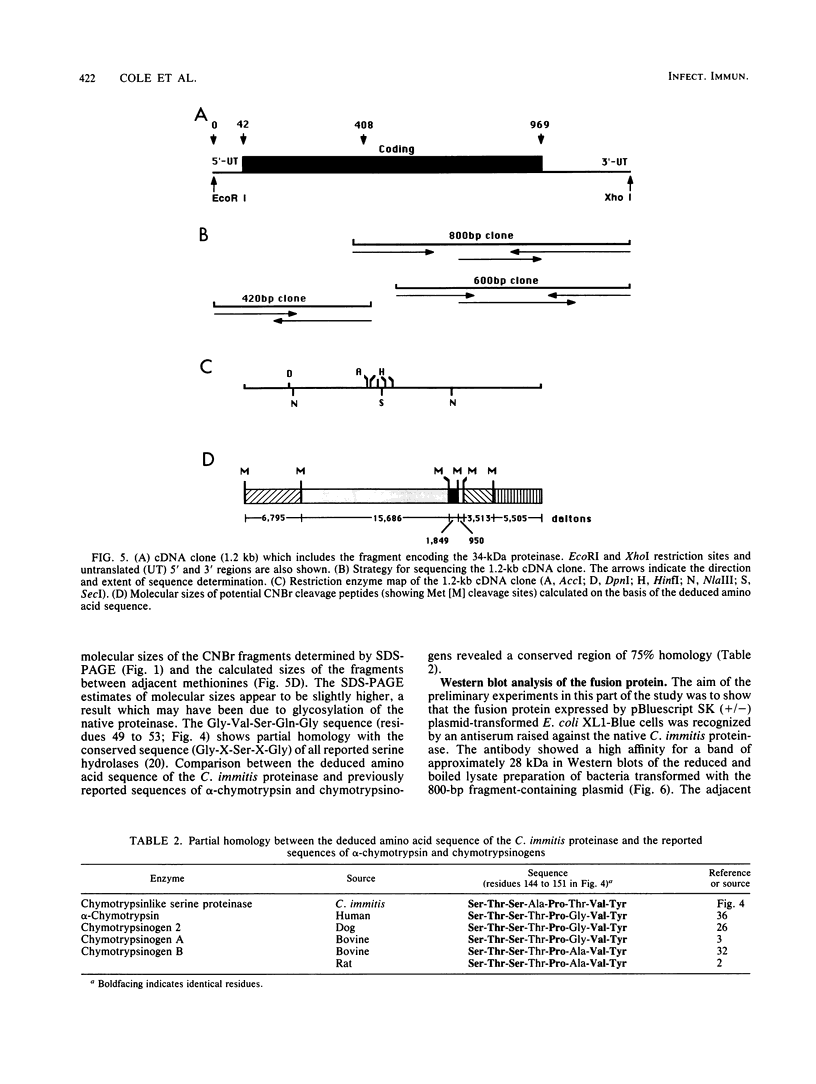
A chymotrypsinlike serine proteinase of Coccidioides immitis with an estimated molecular size of 34 kDa has been shown by immunoelectron microscopy to be associated with the walls of the parasitic cells of this human respiratory pathogen. The proteinase has been suggested to play a role in spherule development. We report the isolation of a 1.2-kb cDNA from an expression library of C. immitis constructed in the lambda ZAP II phage vector. The cDNA is suggested to encode the 34-kDa protein. We demonstrate identity between segments of the deduced amino acid sequence of the open reading frame of the 1.2-kb cDNA and three distinct sequences obtained from cyanogen bromide cleavage peptides of the purified proteinase. The occurrence of N-glycosyl linkage sites in the deduced sequence of 309 amino acids of the open reading frame (ORF) correlates with our identification of such linkage sites in the native glycosylated proteinase. A protein encoded by an 800-bp fragment of the 1.2-kb cDNA, which was produced by transformed Escherichia coli XL1-Blue, was recognized by the anti-34-kDa protein antibody in a Western blot (immunoblot). Northern (RNA) hybridization of total poly(A)-containing RNA of C. immitis with the labeled 1.2-kb cDNA clone revealed a single band of approximately 1.75 kb. Partial homology was demonstrated between the deduced amino acid sequence of the ORF (927 bp) and reported sequences of alpha-chymotrypsin and chymotrypsinogens. Expression of the proteinase gene was examined by Northern dot blot analysis of total RNA from different stages of parasitic cell development in C. immitis. Maximum levels of specific mRNA were detected during early endospore wall differentiation. The 34-kDa proteinase appears to be concentrated in walls of the parasitic cells at stages of active growth. We suggest that the enzyme may participate in wall plasticization and/or intussusception or in cell wall turnover.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Quinto C., Quiroga M., Valenzuela P., Craik C. S., Rutter W. J. Isolation and sequence of a rat chymotrypsin B gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14265–14270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow D. M., Birktoft J. J., Hartley B. S. Role of a buried acid group in the mechanism of action of chymotrypsin. Nature. 1969 Jan 25;221(5178):337–340. doi: 10.1038/221337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauer A. W., Oman C. L., Margolies M. N. Use of o-phthalaldehyde to reduce background during automated Edman degradation. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kirkland T. N., Sun S. H. An immunoreactive, water-soluble conidial wall fraction of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):657–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.657-667.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kruse D., Seshan K. R. Antigen complex of Coccidioides immitis which elicits a precipitin antibody response in patients. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2434–2446. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2434-2446.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kruse D., Zhu S. W., Seshan K. R., Wheat R. W. Composition, serologic reactivity, and immunolocalization of a 120-kilodalton tube precipitin antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):179–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.179-188.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Seshan K. R., Franco M., Bukownik E., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Isolation and morphology of an immunoreactive outer wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2686–2694. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2686-2694.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Zhu S. W., Pan S. C., Yuan L., Kruse D., Sun S. H. Isolation of antigens with proteolytic activity from Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1524–1534. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1524-1534.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Chaloupka J., Vinter V. Turnover of cell walls in microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):554–567. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.554-567.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge A. S., Faltynek C. R., Hof L., Reichert L. E., Jr, Weber P. Deglycosylation of glycoproteins by trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland T. N., Zhu S. W., Kruse D., Hsu L. L., Seshan K. R., Cole G. T. Coccidioides immitis fractions which are antigenic for immune T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3952–3961. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3952-3961.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Gel protein stains: silver stain. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:441–447. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Jr, Nguyen N. Y., Liu T. Y. Reproducible high yield sequencing of proteins electrophoretically separated and transferred to an inert support. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6005–6008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappagianis D., Zimmer B. L. Serology of coccidioidomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):247–268. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastor F. I., Herrero E., Sentandreu R. Metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae envelope mannoproteins. Arch Microbiol. 1982 Aug;132(2):144–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00508720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky S. D., LaForge K. S., Luc V., Scheele G. Identification of cDNA clones encoding secretory isoenzyme forms: sequence determination of canine pancreatic prechymotrypsinogen 2 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7486–7490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakanari J. A., Staunton C. E., Eakin A. E., Craik C. S., McKerrow J. H. Serine proteases from nematode and protozoan parasites: isolation of sequence homologs using generic molecular probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4863–4867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Nice E. C. In situ cyanogen bromide cleavage of N-terminally blocked proteins in a gas-phase sequencer. Biochem Int. 1984 Jun;8(6):787–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smillie L. B., Furka A., Nagabhushan N., Stevenson K. J., Parkes C. O. Structure of chymotrypsinogen B compared with chymotrypsinogen A and trypsinogen. Nature. 1968 Apr 27;218(5139):343–346. doi: 10.1038/218343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. H., Cole G. T., Drutz D. J., Harrison J. L. Electron-microscopic observations of the Coccidioides immitis parasitic cycle in vivo. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Jun;24(3):183–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihisa T., Anraku Y. Nucleotide sequence of AMS1, the structure gene of vacuolar alpha-mannosidase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):908–915. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T. Characterization of a proteinase inhibitor isolated from the fungal pathogen Coccidioides immitis. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):729–736. doi: 10.1042/bj2570729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular proteinase of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1970-1978.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T., Sun S. H. Possible role of a proteinase in endosporulation of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1551–1559. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1551-1559.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Towards a comparative anatomy of N-terminal topogenic protein sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]