Abstract
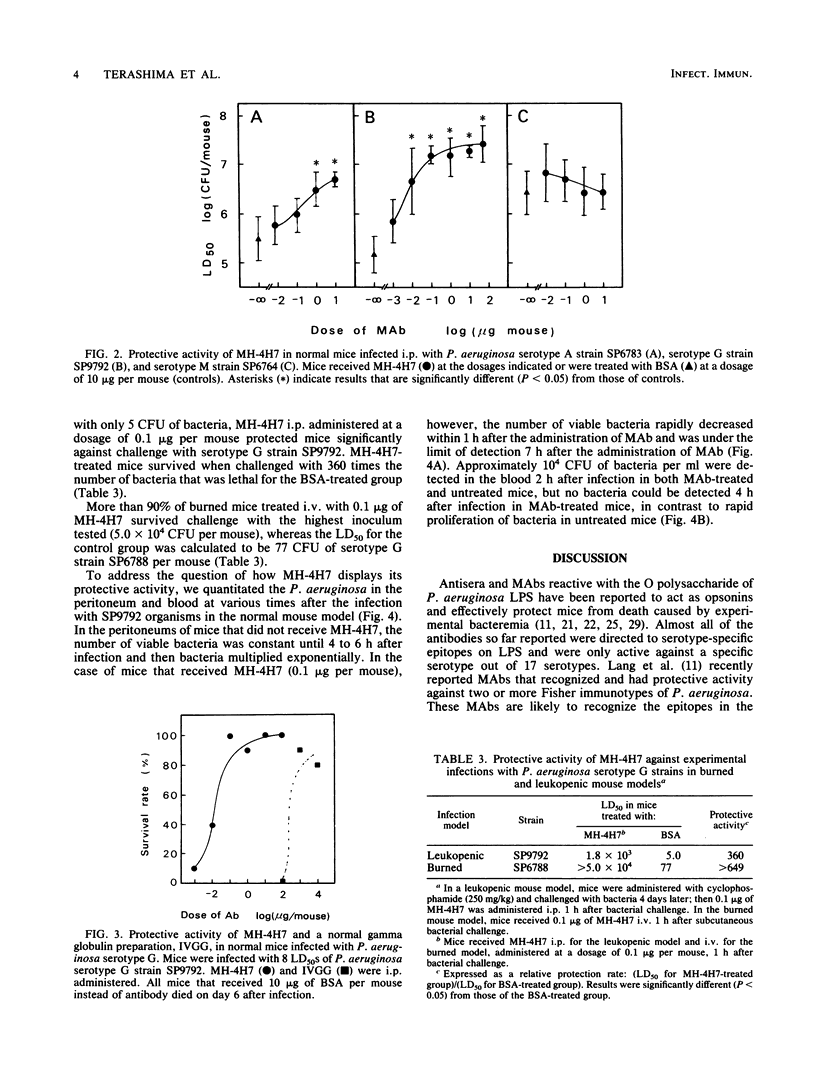
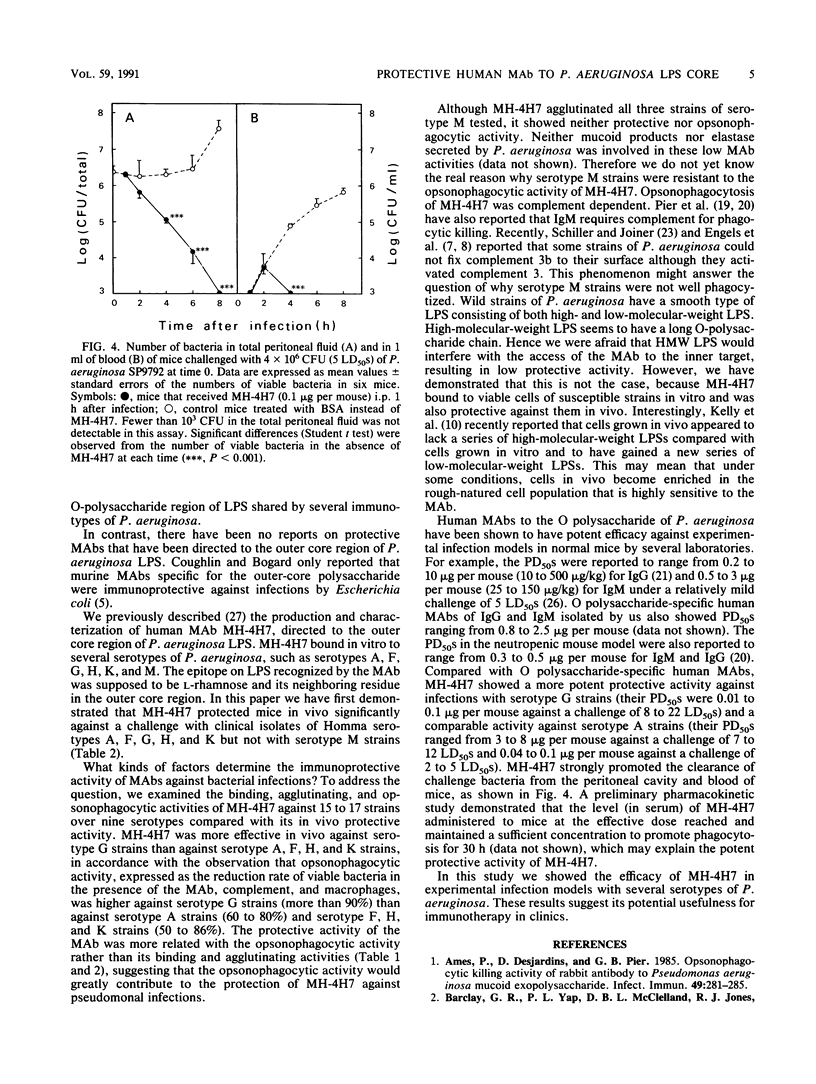
The protective activity against experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of a human monoclonal antibody, MH-4H7, which is thought to recognize L-rhamnose and its neighboring residues in the outer core region of P. aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide and which binds to strains of Homma serotypes A, F, G, H, K, and M, was studied in normal, burned, and leukopenic mice. MH-4H7 at doses of 0.1 to 1.0 micrograms per mouse (5 to 50 micrograms/kg) was effective against serotype A, F, G, H, and K clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa tested in normal mice but not against strains of serotype M, B, E, or I. The 50% protective doses were calculated to be 0.01 and 0.1 micrograms per mouse against challenge with serotype G strains and 3 to 8 micrograms per mouse against challenge with serotype A strains. MH-4H7 promoted macrophage-mediated opsonophagocytosis of serotype A, F, G, H, and K strains but not of serotype M strains. The opsonophagocytic activity, expressed as the reduction rate of viable bacteria in the presence of MH-4H7, macrophages, and complement, was higher against serotype G strains (more than 90%) than against serotype A strains (60 to 80%) and serotype F, H, and K strains (50 to 86%). It was correlated with the protective activity but not with the binding intensity of MH-4H7 to the organisms. In addition, burned and leukopenic mice as well as normal mice infected with serotype G strains recovered from a very low dosage of MH-4H7. Thus, a monoclonal antibody directed to the outer core region of P. aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide was effective against infection with a wide range of O-serotype strains of P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames P., DesJardins D., Pier G. B. Opsonophagocytic killing activity of rabbit antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):281–285. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.281-285.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay G. R., Yap P. L., McClelland D. B., Jones R. J., Roe E. A., McCann M. C., Micklem L. R., James K. Characterisation of mouse monoclonal antibodies produced by immunisation with a single serotype component of a polyvalent Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Feb;21(1):87–90. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Bolivar R., Fainstein V., Jadeja L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):279–313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. S., Roby R. E. Protective activity of an intravenous immune globulin (human) enriched in antibody against lipopolysaccharide antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am J Med. 1984 Mar 30;76(3A):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Bogard W. C., Jr Immunoprotective murine monoclonal antibodies specific for the outer-core polysaccharide and for the O-antigen of Escherichia coli 0111:B4 lipopolysaccharide (LPS). J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):557–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in a murine burn wound sepsis model by passive transfer of antitoxin A, antielastase, and antilipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1072–1079. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1072-1079.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W., Endert J., Kamps M. A., van Boven C. P. Role of lipopolysaccharide in opsonization and phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):182–189. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.182-189.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W., Endert J., Van Boven C. P. A quantitative method for assessing the third complement factor (C3) attached to the surface of opsonized Pseudomonas aeruginosa: interrelationship between C3 fixation, phagocytosis and complement consumption. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jul 16;81(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Wheeler R., Montie T. C. Flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: animal protection studies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):276–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.276-280.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Bell A., Hancock R. E. Surface characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in a chamber implant model in mice and rats. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):344–350. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.344-350.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. B., Fürer E., Larrick J. W., Cryz S. J., Jr Isolation and characterization of a human monoclonal antibody that recognizes epitopes shared by Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype 1, 3, 4, and 6 lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3851–3855. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3851-3855.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre S., Lucken R., Owen P. Smooth lipopolysaccharide is the major protective antigen for mice in the surface extract from IATS serotype 6 contributing to the polyvalent Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine PEV. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):76–84. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.76-84.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews-Greer J. M., Gilleland H. E., Jr Outer membrane protein F (porin) preparation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a protective vaccine against heterologous immunotype strains in a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1282–1291. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E. Lipopolysaccharide pseudomonas vaccine: efficacy against pulmonary infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):73–80. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Reynolds H. Y., Carbone P. P. Pseudomonas pneumonia. A retrospective study of 36 cases. Am J Med. 1973 Aug;55(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Small G. J., Lostrom M. E., Pier G. B. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibody therapy for experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.239-244.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Small G. J. Passive immune therapy for experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in the neutropenic host. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):973–978. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Thomas D. M. Characterization of the human immune response to a polysaccharide vaccine from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):206–213. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Thomas D., Small G., Siadak A., Zweerink H. In vitro and in vivo activity of polyclonal and monoclonal human immunoglobulins G, M, and A against Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):174–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.174-179.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Kawamura T., Masuho Y. Immunoprotective human monoclonal antibodies against five major serotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3581–3590. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Suzuki M., Kawamura T., Fujinaga S., Masuho Y., Tomibe K. Protection against infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to lipopolysaccharides and outer membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):570–576. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Joiner K. A. Interaction of complement with serum-sensitive and serum-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):689–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.689-694.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieritz D. D., Holder I. A. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: description of a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):688–691. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll B. J., Pollack M., Young L. S., Koles N., Gascon R., Pier G. B. Functionally active monoclonal antibody that recognizes an epitope on the O side chain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype-1 lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):656–662. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.656-662.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Okubo Y., Moriyama M., Sasaki M., Matsumoto Y., Hozumi T. Human monoclonal antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa produced by EBV-transformed cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(10):959–966. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb01328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota S., Ochi H., Ohtsuka H., Kato M., Noguchi H. Heterogeneity of the L-rhamnose residue in the outer core of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide, characterized by using human monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1691–1696. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1691-1696.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Relationship between heat-stable opsonins and type-specific lipopolysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):277–287. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Gammon M. C., Hutchison C. F., Jackson J. J., Lombardo D., Miner K. M., Puckett J. M., Sewell T. J., Sigal N. H. Human monoclonal antibodies that protect mice against challenge with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1873–1879. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1873-1879.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


