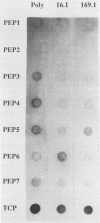
Abstract
From a collection of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) that recognize the native structure of the toxin-coregulated pilus of Vibrio cholerae, two protective MAbs (16.1 and 169.1) were used to localize the corresponding epitopes on the pilus. These MAbs were shown to specifically recognize the carboxyl half of the TcpA pilin subunit, as determined by their recognition of proteolytic fragments and hybrid pilin proteins. The positions of the epitopes were precisely determined through the use of overlapping synthetic peptides corresponding to this region of the pilin. The MAbs were found to recognize adjacent peptides, delineating a region between residues 157 and 199. Since the protective nature is specific for these two antibodies, the findings suggest that this region defines a domain that participates in toxin-coregulated pilus-mediated colonization and therefore represents a target for studies of its potential as an immunogen for incorporation into a component cholera vaccine.
Full text
PDF


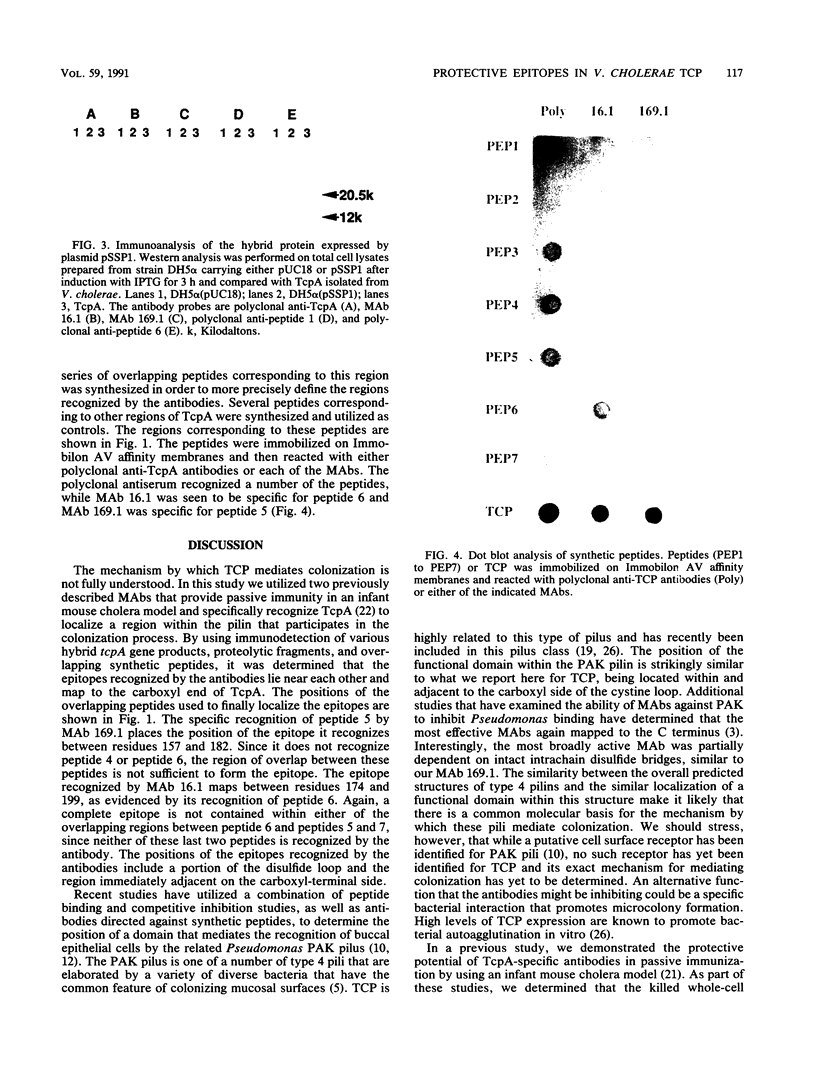

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Sastry P. A., Hodges R. S., Lee K. K., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. Inhibition of pilus-mediated adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human buccal epithelial cells by monoclonal antibodies directed against pili. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):124–130. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.124-130.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehara M., Ishibashi M., Ichinose Y., Iwanaga M., Shimotori S., Naito T. Purification and partial characterization of fimbriae of Vibrio cholerae O1. Vaccine. 1987 Dec;5(4):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn T. M., Reiser J., Germanier R., Cryz S. J., Jr Cell-associated hemagglutinin-deficient mutant of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):942–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.942-946.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS E., WITKOP B. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: the methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1856–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. H., Vial P. A., Kaper J. B., Mekalanos J. J., Levine M. M. Morphological studies on fimbriae expressed by Vibrio cholerae 01. Microb Pathog. 1988 Apr;4(4):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Hall R. H., Losonsky G., Mekalanos J. J., Taylor R. K., Levine M. M. Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili, and the toxR regulon are essential for Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis in humans. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1487–1492. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Doig P., Lee K. K., Sastry P. A., Paranchych W., Todd T., Hodges R. S. Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilus adhesin: confirmation that the pilin structural protein subunit contains a human epithelial cell-binding domain. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3720–3726. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3720-3726.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. K., Doig P., Irvin R. T., Paranchych W., Hodges R. S. Mapping the surface regions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilin: the importance of the C-terminal region for adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1493–1499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L. New knowledge on pathogenesis of bacterial enteric infections as applied to vaccine development. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):510–550. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.510-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Mekalanos J. J. Characterization of the Vibrio cholerae ToxR regulon: identification of novel genes involved in intestinal colonization. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2822-2829.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. E., Taylor R. K. Vibrio cholerae O395 tcpA pilin gene sequence and comparison of predicted protein structural features to those of type 4 pilins. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3042–3049. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3042-3049.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Mekalanos J. J., Taylor R. K. Antibodies directed against the toxin-coregulated pilus isolated from Vibrio cholerae provide protection in the infant mouse experimental cholera model. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1231–1236. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J. Broad-host-range vectors for delivery of TnphoA: use in genetic analysis of secreted virulence determinants of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1870–1878. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1870-1878.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R., Shaw C., Peterson K., Spears P., Mekalanos J. Safe, live Vibrio cholerae vaccines? Vaccine. 1988 Apr;6(2):151–154. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(88)80019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweedy J. M., Park R. W., Hodgkiss W. Evidence for the presence of fimbriae (pili) on vibrio species. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Apr;51(2):235–244. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q. Y., Shively J. E. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. VIII. Improved electroblotting of proteins onto membranes and derivatized glass-fiber sheets. Anal Biochem. 1988 Apr;170(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]