Abstract
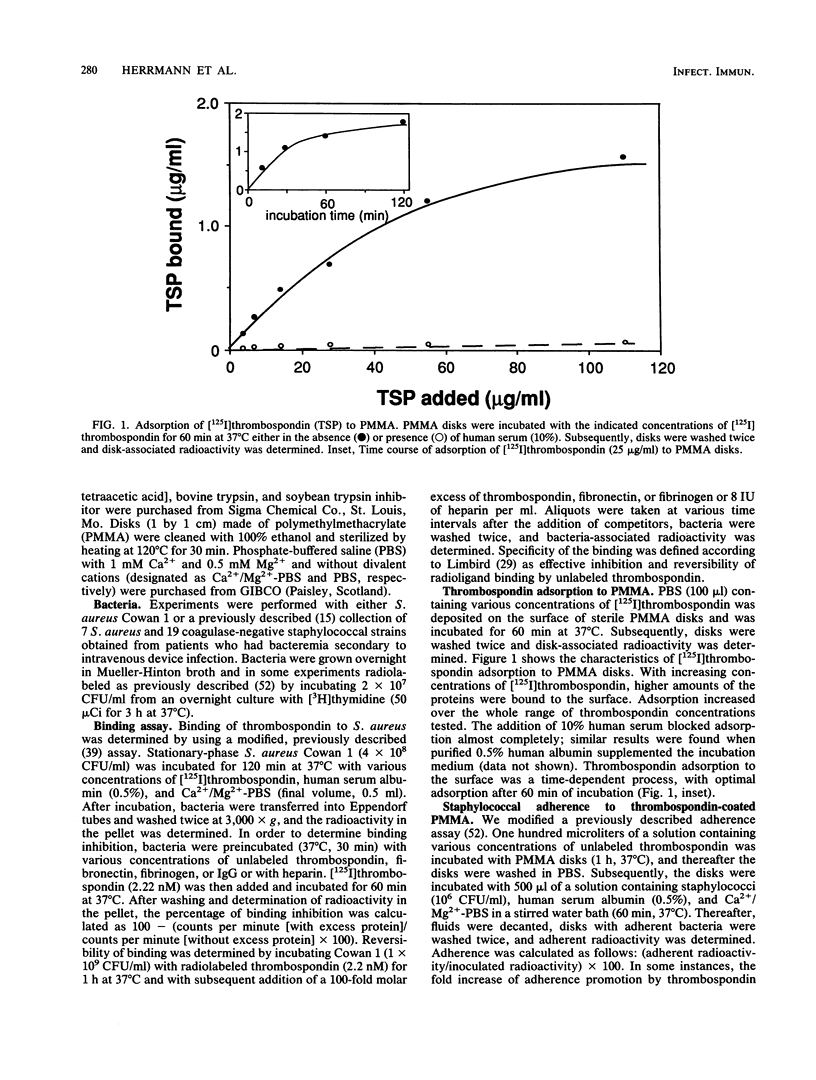
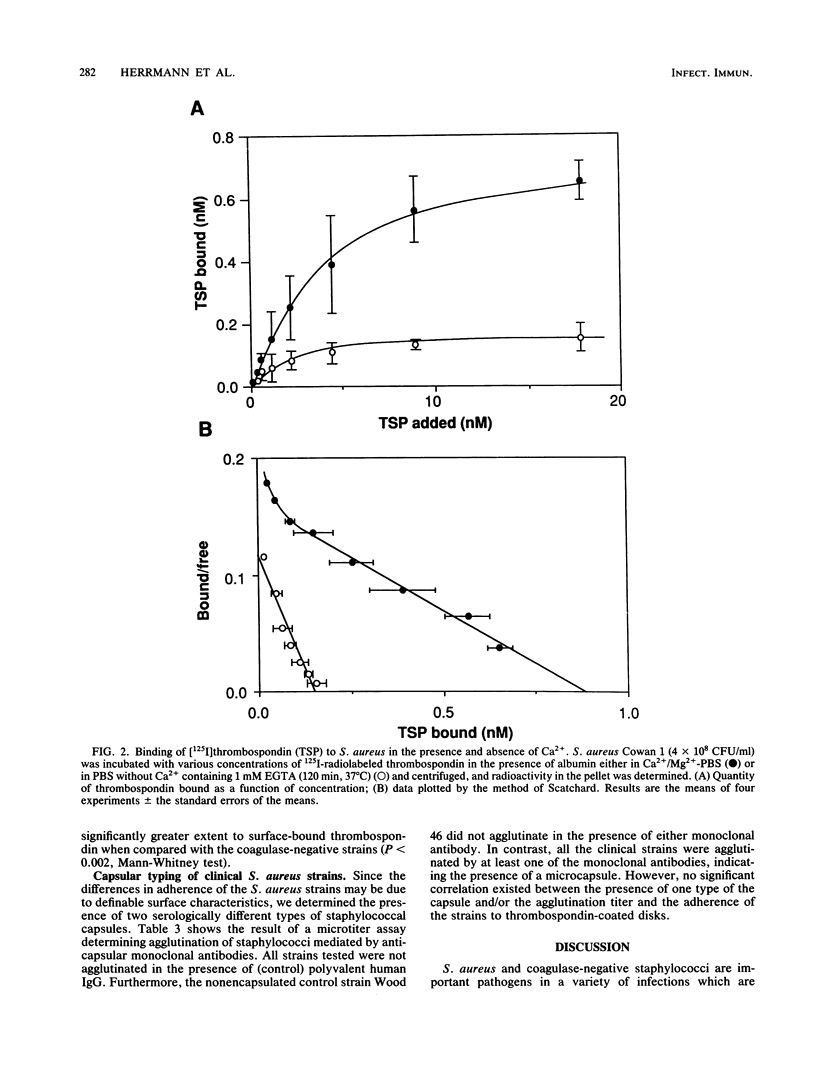
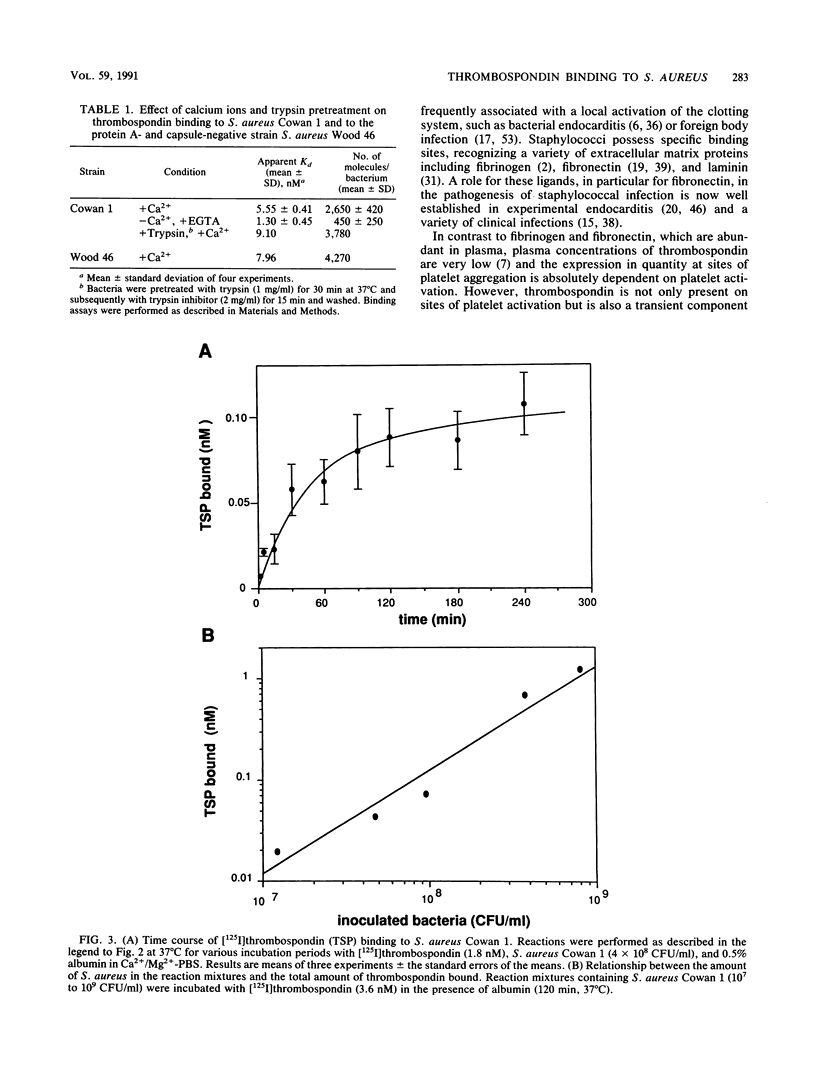
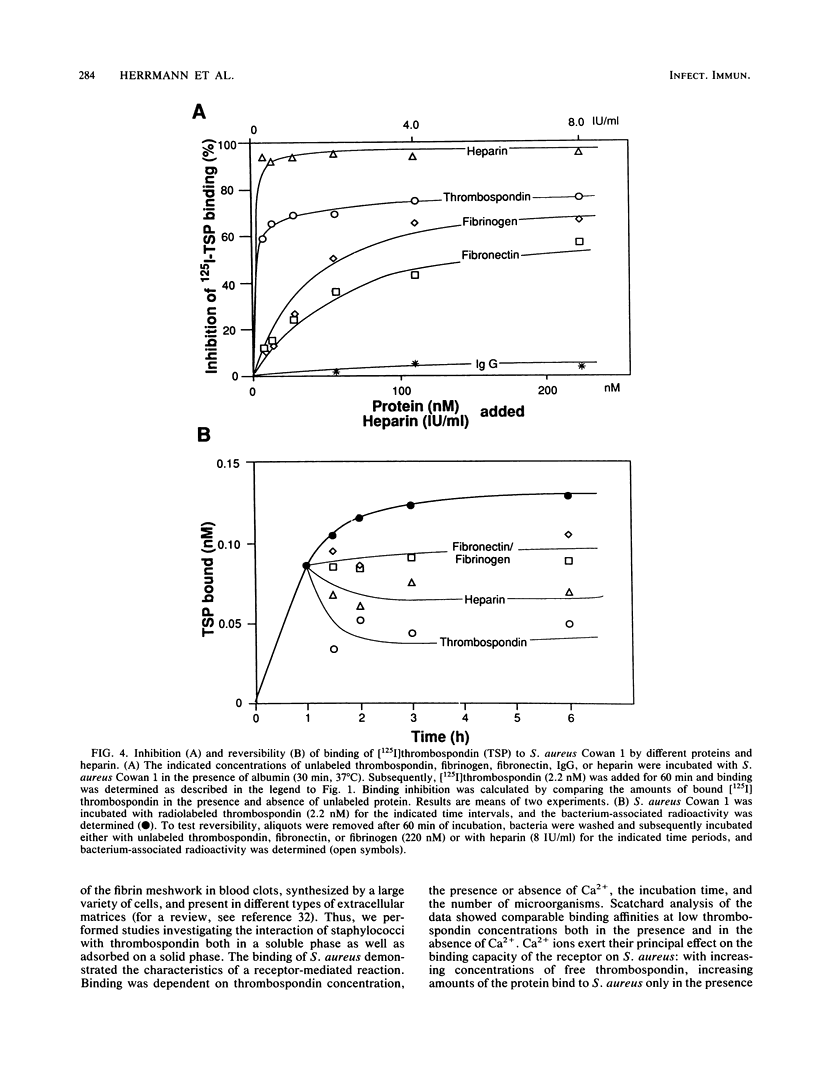
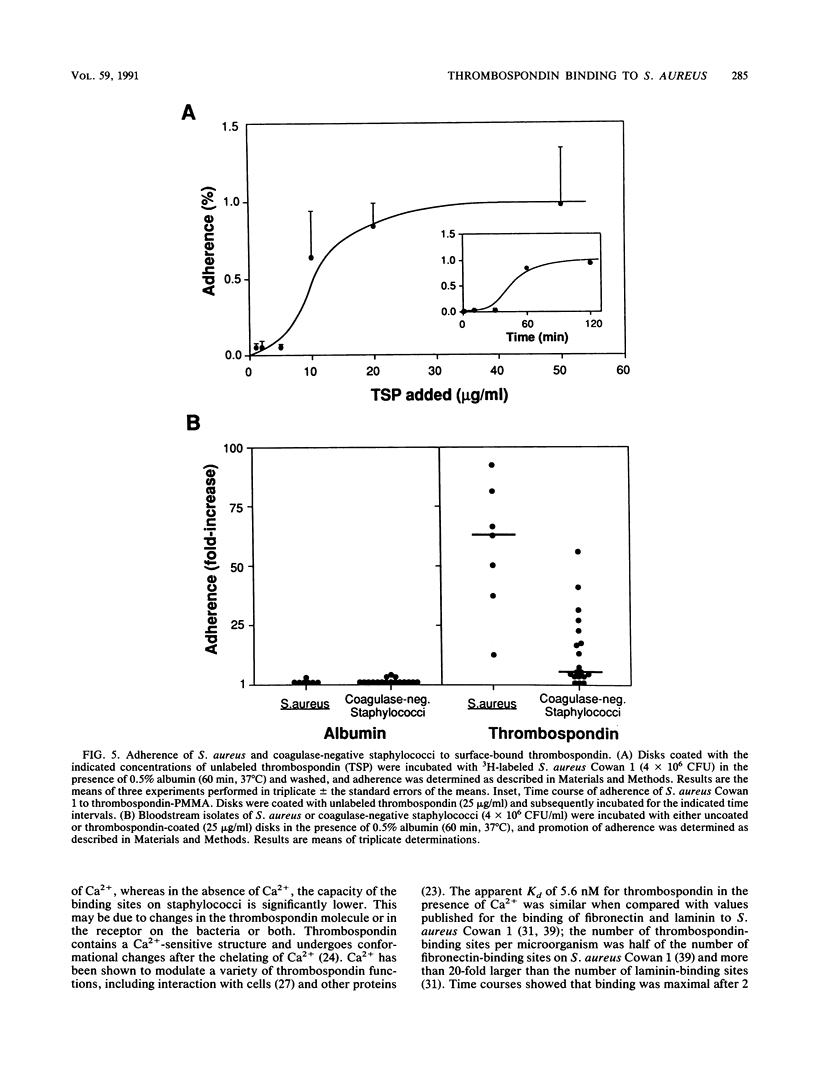
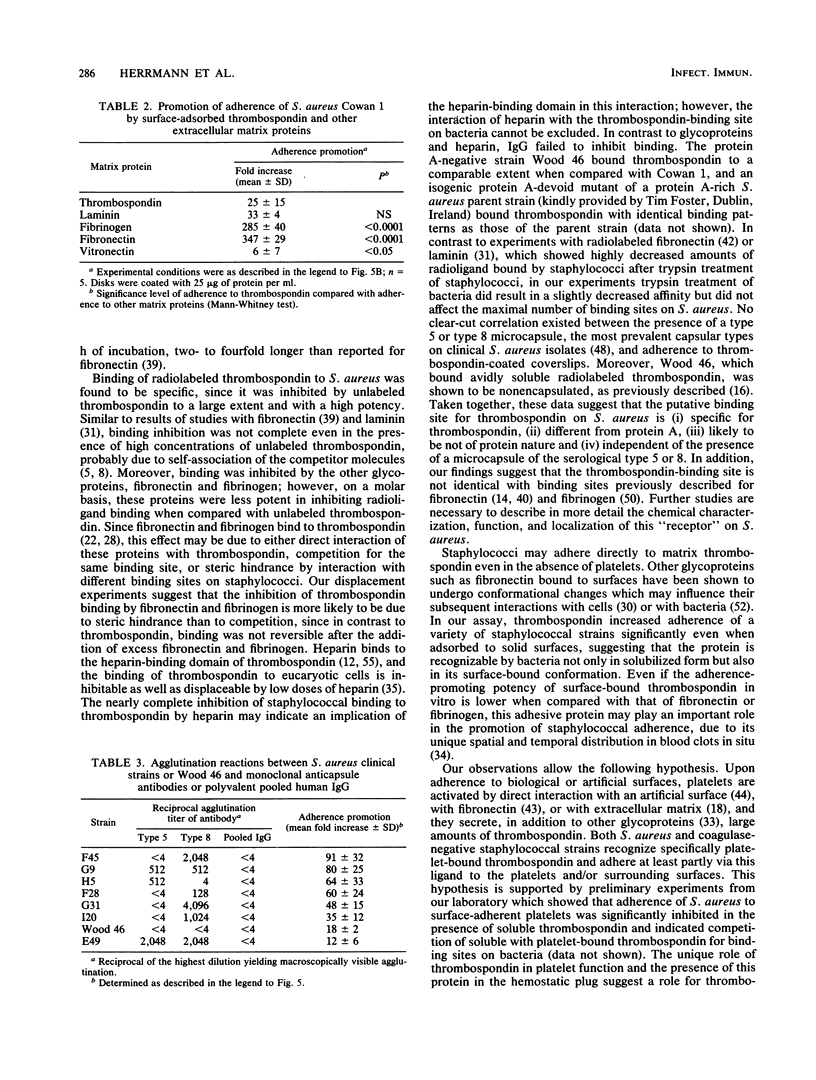
Bacterial adherence to surfaces is the determining first step in staphylococcal infections. Activated platelets mediate adherence of staphylococci to tissues during inflammation or infection; however, the molecular mechanisms of this interaction are not clearly understood. Thrombospondin, a large multifunctional glycoprotein, is the principal platelet-stored glycoprotein. It is secreted upon platelet activation and either bound to receptors on the platelet surface or released and incorporated into blood clots and extracellular matrices. To characterize thrombospondin binding to staphylococci, we incubated [125I]thrombospondin with Staphylococcus aureus Cowan 1 in the presence of albumin and separated bound and free thrombospondin by centrifugation. We found that binding was (i) specific, since it was up to 76% inhibitable and up to 60% reversible in the presence of a 100-fold excess of unlabeled thrombospondin, (ii) saturable, with an apparent dissociation constant (Kd) of 5.6 x 10(-9) M and a maximal number of 2,600 binding sites per microorganism, and (iii) Ca2+ dependent, since omission of this ion from the medium decreased significantly the binding capacity. The binding reaction was insensitive to previous trypsin treatment of bacteria, but it was strongly inhibited in the presence of heparin. Protein A-negative and -positive strains had similar binding characteristics. To determine the promotion of staphylococcal adherence to surfaces by solid-phase thrombospondin, we incubated 3H-labeled S. aureus Cowan 1 and 26 pathogenic staphylococcal isolates with thrombospondin-coated polymethylmethacrylate disks and found that adherence was significantly promoted as a function of adsorbed thrombospondin. These results indicate a role for thrombospondin as an important mediator of staphylococcal adherence to activated platelets, to blood clots, or to extracellular matrices in pyogenic infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken M. L., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F. Identification of a new class of inducible receptors on platelets. Thrombospondin interacts with platelets via a GPIIb-IIIa-independent mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1713–1716. doi: 10.1172/JCI112767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allington M. J. Fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products and the clumping of staphylococci by serum. Br J Haematol. 1967 Jul;13(4):550–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb00763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asch A. S., Barnwell J., Silverstein R. L., Nachman R. L. Isolation of the thrombospondin membrane receptor. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1054–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI112918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. A thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelet membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):240–243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. D., Westrick L. G., Mosher D. F. Incorporation of thrombospondin into fibrin clots. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7502–7508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S. Staphylococcal bacteremia and endocarditis: state of the art. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Jun;142(6):1169–1177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth W. J., Berndt M. C. Thrombospondin in clinical disease states. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1987 Jul;13(3):298–306. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth W. J., Castaldi P. A., Berndt M. C. Platelet thrombospondin haemagglutinin activity is due to aggregate formation. Thromb Res. 1985 Jul 1;39(1):29–42. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chugh T. D., Burns G. J., Shuhaiber H. J., Bahr G. M. Adherence of Staphylococcus epidermidis to fibrin-platelet clots in vitro mediated by lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):315–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.315-319.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., White J. G., Herzberg M. C. Platelet interaction with bacteria. VI. contrasting the role of fibrinogen and fibronectin. Am J Hematol. 1980;9(1):43–53. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830090106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., White J. G. Platelet interaction with bacteria. I. Reaction phases and effects of inhibitors. Am J Pathol. 1971 Nov;65(2):367–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit V. M., Grant G. A., Santoro S. A., Frazier W. A. Isolation and characterization of a heparin-binding domain from the amino terminus of platelet thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10100–10105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröman G., Switalski L. M., Speziale P., Hök M. Isolation and characterization of a fibronectin receptor from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6564–6571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann M., Vaudaux P. E., Pittet D., Auckenthaler R., Lew P. D., Schumacher-Perdreau F., Peters G., Waldvogel F. A. Fibronectin, fibrinogen, and laminin act as mediators of adherence of clinical staphylococcal isolates to foreign material. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):693–701. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Fournier J. M., Vann W. F., Arbeit R., Schneerson R. S., Robbins J. B. Method for the serological typing of the capsular polysaccharides of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):445–447. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.445-447.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloster F. E. Complications of artificial heart valves. JAMA. 1979 May 18;241(20):2201–2203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Harrison J. L., Misra R. P. Aggregated platelets enhance adherence of Candida yeasts to endothelium. J Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;160(4):669–677. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.4.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers J. M., Proctor R. A. Reduced adherence to traumatized rat heart valves by a low-fibronectin-binding mutant of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2306–2312. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2306-2312.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahav J., Lawler J., Gimbrone M. A. Thrombospondin interactions with fibronectin and fibrinogen. Mutual inhibition in binding. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;145(1):151–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J. W., Slayter H. S., Coligan J. E. Isolation and characterization of a high molecular weight glycoprotein from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8609–8616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Chao F. C., Cohen C. M. Evidence for calcium-sensitive structure in platelet thrombospondin. Isolation and partial characterization of thrombospondin in the presence of calcium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12257–12265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Hynes R. O. Structural organization of the thrombospondin molecule. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1987 Jul;13(3):245–254. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J. The structural and functional properties of thrombospondin. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1197–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Weinstein R., Hynes R. O. Cell attachment to thrombospondin: the role of ARG-GLY-ASP, calcium, and integrin receptors. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2351–2361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung L. L., Nachman R. L. Complex formation of platelet thrombospondin with fibrinogen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):542–549. doi: 10.1172/JCI110646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindon J. N., McManama G., Kushner L., Merrill E. W., Salzman E. W. Does the conformation of adsorbed fibrinogen dictate platelet interactions with artificial surfaces? Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):355–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Physiology of thrombospondin. Annu Rev Med. 1990;41:85–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.41.020190.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Mosher D. F. Localization of thrombospondin in clots formed in situ. Blood. 1985 Nov;66(5):1098–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Westrick L. G., Esko J. D., Mosher D. F. Altered metabolism of thrombospondin by Chinese hamster ovary cells defective in glycosaminoglycan synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6400–6406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., McKenzie S. O. Infections due to Staphylococcus aureus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Sep;56(5):383–409. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197709000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K., Prasanna H. R. Ca2+-mediated association of glycoprotein G (thrombinsensitive protein, thrombospondin) with human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11629–11632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Christman G., Mosher D. F. Fibronectin-induced agglutination of Staphylococcus aureus correlates with invasiveness. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Oct;104(4):455–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Mosher D. F., Olbrantz P. J. Fibronectin binding to Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14788–14794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raja R. H., Raucci G., Hook M. Peptide analogs to a fibronectin receptor inhibit attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to fibronectin-containing substrates. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2593–2598. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2593-2598.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén C., Rubin K., Speziale P., Hök M., Lindberg M., Wadström T. Fibronectin receptors from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W., Lindon J., McManama G., Ware J. A. Role of fibrinogen in activation of platelets by artificial surfaces. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;516:184–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb33040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Strunk R. W., Balian G., Calderone R. A. Microbial adhesion to fibronectin in vitro correlates with production of endocarditis in rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Dec;180(3):474–482. doi: 10.3181/00379727-180-42205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Valone J. A., Sande M. A. Bacterial adherence in the pathogenesis of endocarditis. Interaction of bacterial dextran, platelets, and fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1394–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI109057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Samra Z., Karakawa W. W., Vann W. F., Schneerson R., Malik Z. Encapsulation and capsular types in isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from different sources and relationship to phage types. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):828–834. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.828-834.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullam P. M., Drake T. A., Sande M. A. Pathogenesis of endocarditis. Am J Med. 1985 Jun 28;78(6B):110–115. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usui Y. Biochemical properties of fibrinogen binding protein (clumping factor) of the staphylococcal cell surface. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Sep;262(3):287–297. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P. E., Waldvogel F. A., Morgenthaler J. J., Nydegger U. E. Adsorption of fibronectin onto polymethylmethacrylate and promotion of Staphylococcus aureus adherence. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):768–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.768-774.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P., Suzuki R., Waldvogel F. A., Morgenthaler J. J., Nydegger U. E. Foreign body infection: role of fibronectin as a ligand for the adherence of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):546–553. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldvogel F. A., Papageorgiou P. S. Osteomyelitis: the past decade. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 14;303(7):360–370. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008143030703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff R., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Interaction of thrombospondin with resting and stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6840–6846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabkowitz R., Lowe J. B., Dixit V. M. Expression and initial characterization of a recombinant human thrombospondin heparin binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10888–10896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


