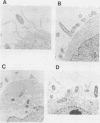
Abstract
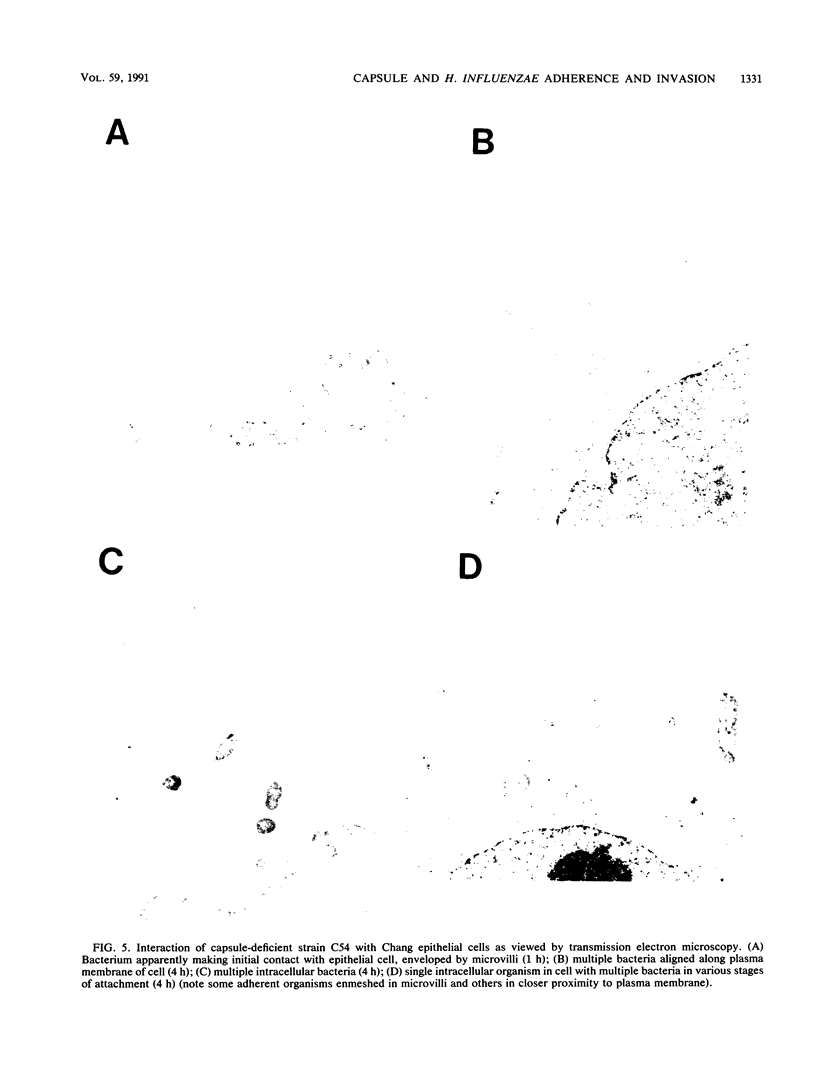
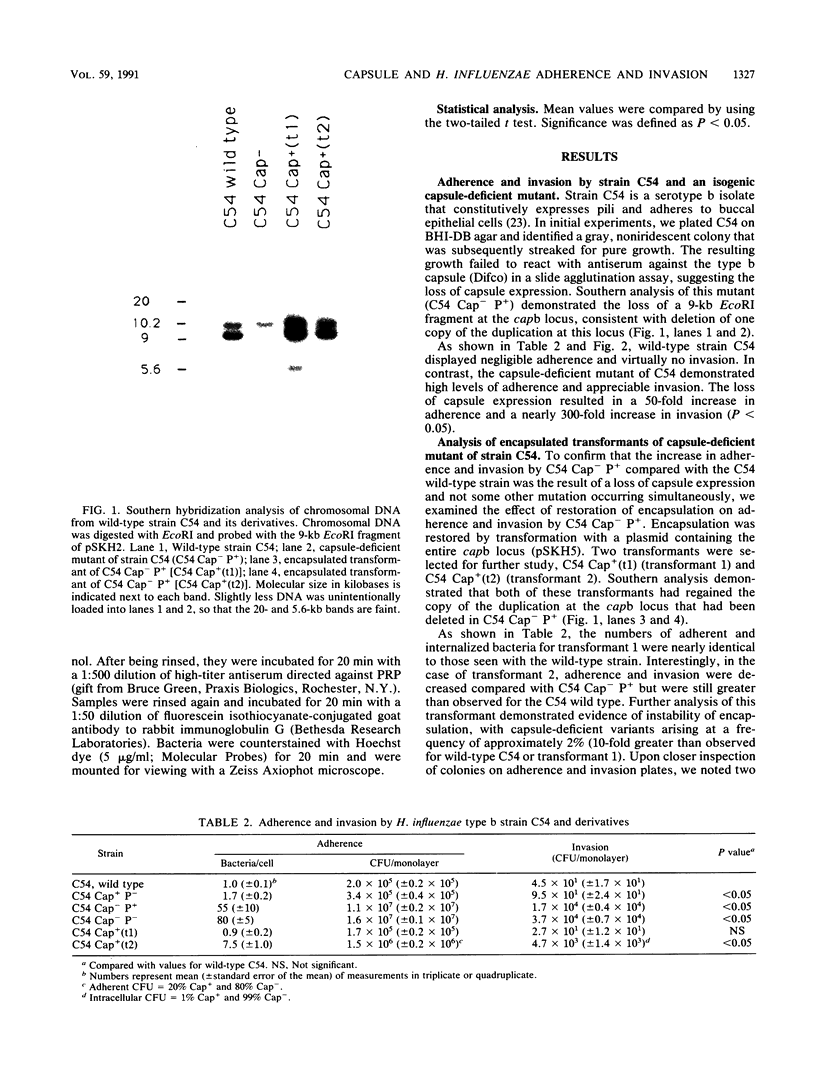
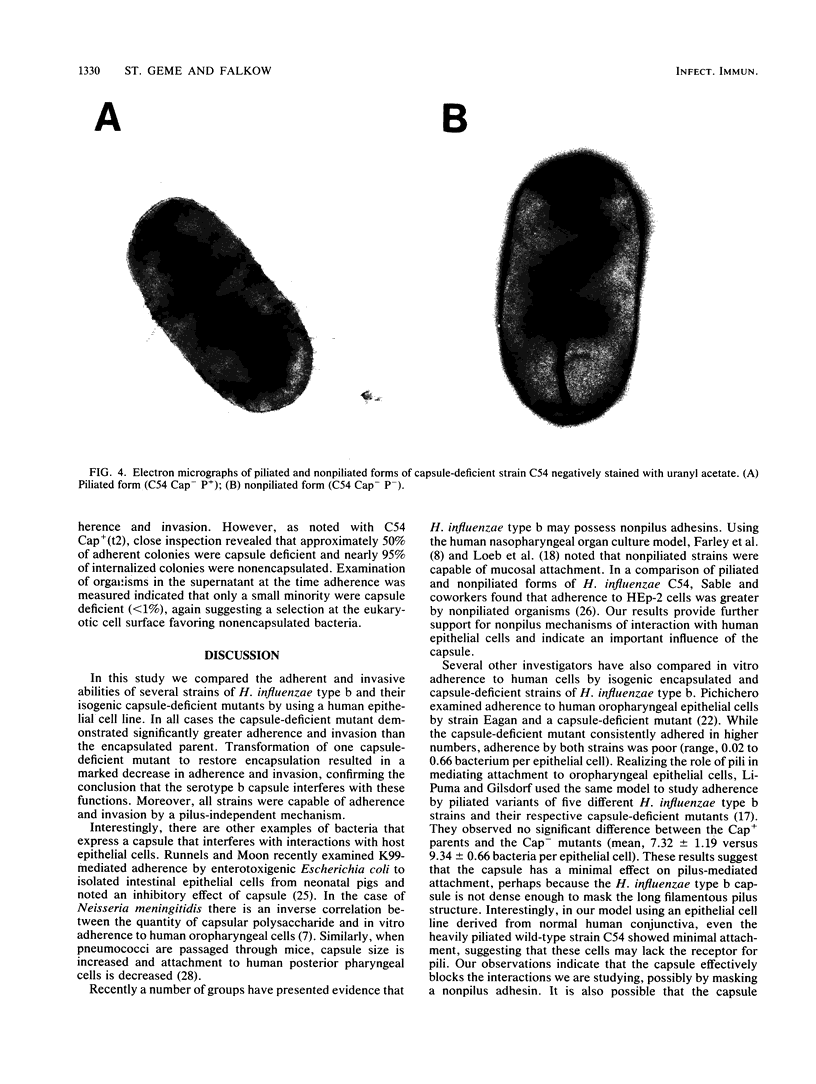
Haemophilus influenzae type b is a common cause of systemic bacterial disease in children, and the serotype b capsule is a major determinant of virulence. Nevertheless, as a consequence of the genetic configuration of the capb locus, type b strains become capsule deficient at a high frequency. To investigate the potential biological relevance of the predisposition to capsule loss, we compared the adherent and invasive abilities of several strains of H. influenzae type b and their isogenic capsule-deficient mutants by using cultured human epithelial cells. In all cases the capsule-deficient mutant demonstrated significantly greater adherence and invasion than the encapsulated parent. Transformation of one capsule-deficient mutant to restore encapsulation resulted in a marked decrease in adherence and invasion. All strains were capable of adherence and invasion by a pilus-independent mechanism. We conclude that capsule loss by H. influenzae type b results in enhanced in vitro adherence and invasion, properties that may be relevant to colonization of the nasopharynx and persistence within the respiratory tract. These observations suggest an explanation for the evolution of the capb locus as directly repeated segments of DNA with a consequent predisposition to recombination resulting in capsule loss.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan I., Loeb M. R., Moxon E. R. Limited genetic diversity of Haemophilus influenzae (type b). Microb Pathog. 1987 Feb;2(2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Johnston R. B., Jr, Smith D. H. Human serum activities against Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI106793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw M. W., Schneerson R., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. Bacterial antigens cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1095–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91837-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler C. A., Fothergill L. D., Dingle J. H. The Pattern of Dissociation in Hemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1939 Apr;37(4):415–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.37.4.415-427.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor E. M., Loeb M. R. A hemadsorption method for detection of colonies of Haemophilus influenzae type b expressing fimbriae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Nov;148(5):855–860. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.5.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Peppler M. S., Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F., McGrath P. P., Washington G. Adherence of isolates of Neisseria meningitidis from patients and carriers to human buccal epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):556–568. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley M. M., Stephens D. S., Mulks M. H., Cooper M. D., Bricker J. V., Mirra S. S., Wright A. Pathogenesis of IgA1 protease-producing and -nonproducing Haemophilus influenzae in human nasopharyngeal organ cultures. J Infect Dis. 1986 Nov;154(5):752–759. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Langermann S., Clegg H. W., Kessler T. W., Goldman D. A., Gilsdorf J. R. Adherence of piliated Haemophilus influenzae type b to human oropharyngeal cells. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):564–564. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herriott R. M., Meyer E. M., Vogt M. Defined nongrowth media for stage II development of competence in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):517–524. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.517-524.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Connelly C. J., Moxon E. R. Genetics of spontaneous, high-frequency loss of b capsule expression in Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):389–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.389-395.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Gilsdorf J. R. The relationship between type b and nontypable Haemophilus influenzae isolated from the same patient. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):643–645. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Moxon E. R., Silver R. P. Genes involved in Haemophilus influenzae type b capsule expression are part of an 18-kilobase tandem duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. S., Hopkins I., Moxon E. R. Capsule loss in H. influenzae type b occurs by recombination-mediated disruption of a gene essential for polysaccharide export. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. S., Moxon E. R. Capsulation and gene copy number at the cap locus of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):859–864. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.859-864.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Gilsdorf J. R. Role of capsule in adherence of Haemophilus influenzae type b to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2308–2310. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2308-2310.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Connor E., Penney D. A comparison of the adherence of fimbriated and nonfimbriated Haemophilus influenzae type b to human adenoids in organ culture. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):484–489. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.484-489.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Vaughn K. A. The type b capsular polysaccharide as a virulence determinant of Haemophilus influenzae: studies using clinical isolates and laboratory transformants. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):517–524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Kroll J. S., Granoff D. M., Moxon E. R., Brodeur B. R., Campos J., Dabernat H., Frederiksen W., Hamel J., Hammond G. Global genetic structure and molecular epidemiology of encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12(1):75–111. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E. Adherence of Haemophilus influenzae to human buccal and pharyngeal epithelial cells: relationship to pilation. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):107–116. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E., Loeb M., Anderson, Smith D. H. Do pili play a role in pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type B? Lancet. 1982 Oct 30;2(8305):960–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runnels P. L., Moon H. W. Capsule reduces adherence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to isolated intestinal epithelial cells of pigs. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):737–740. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.737-740.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sable N. S., Connor E. M., Hall C. B., Loeb M. R. Variable adherence of fimbriated Haemophilus influenzae type b to human cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):119–123. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.119-123.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger D. S., Reed W. P. Pneumococcal adherence to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):545–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.545-548.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk D. C. The pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):1–16. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Kroll J. S., Rubin L. G., Moxon E. R. The molecular basis of pathogenicity in Haemophilus influenzae: comparative virulence of genetically-related capsular transformants and correlation with changes at the capsulation locus cap. Microb Pathog. 1989 Sep;7(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]