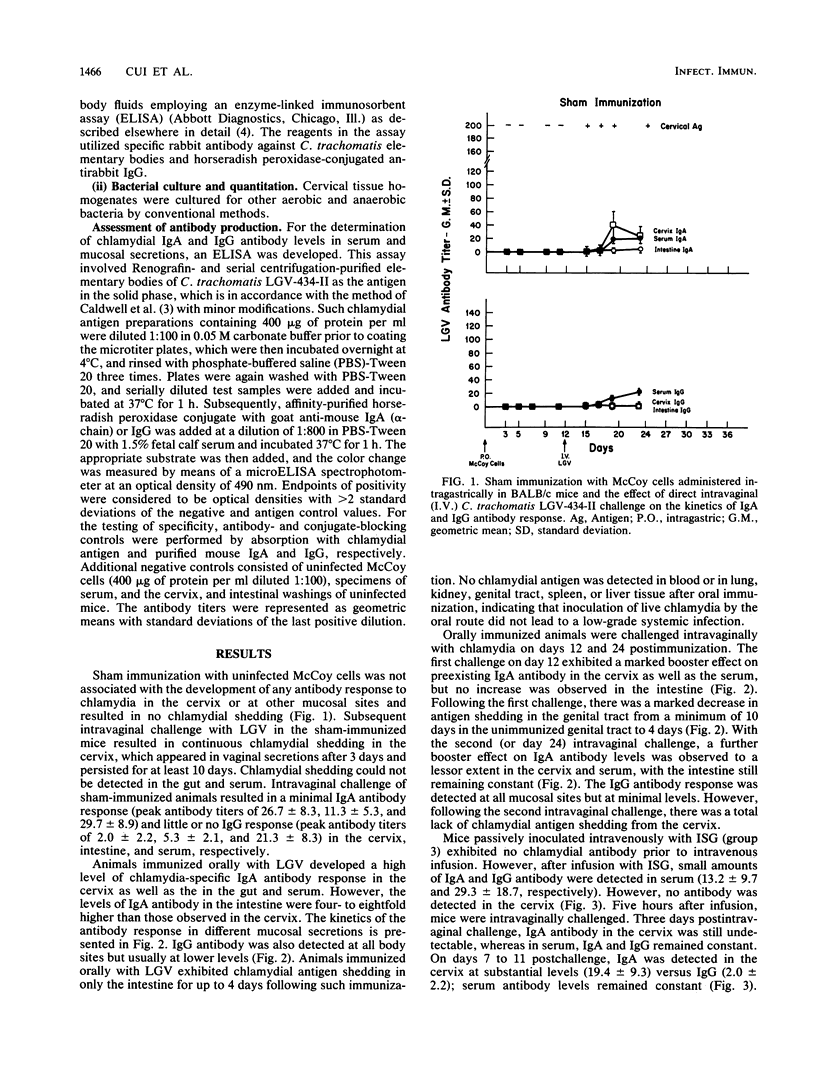
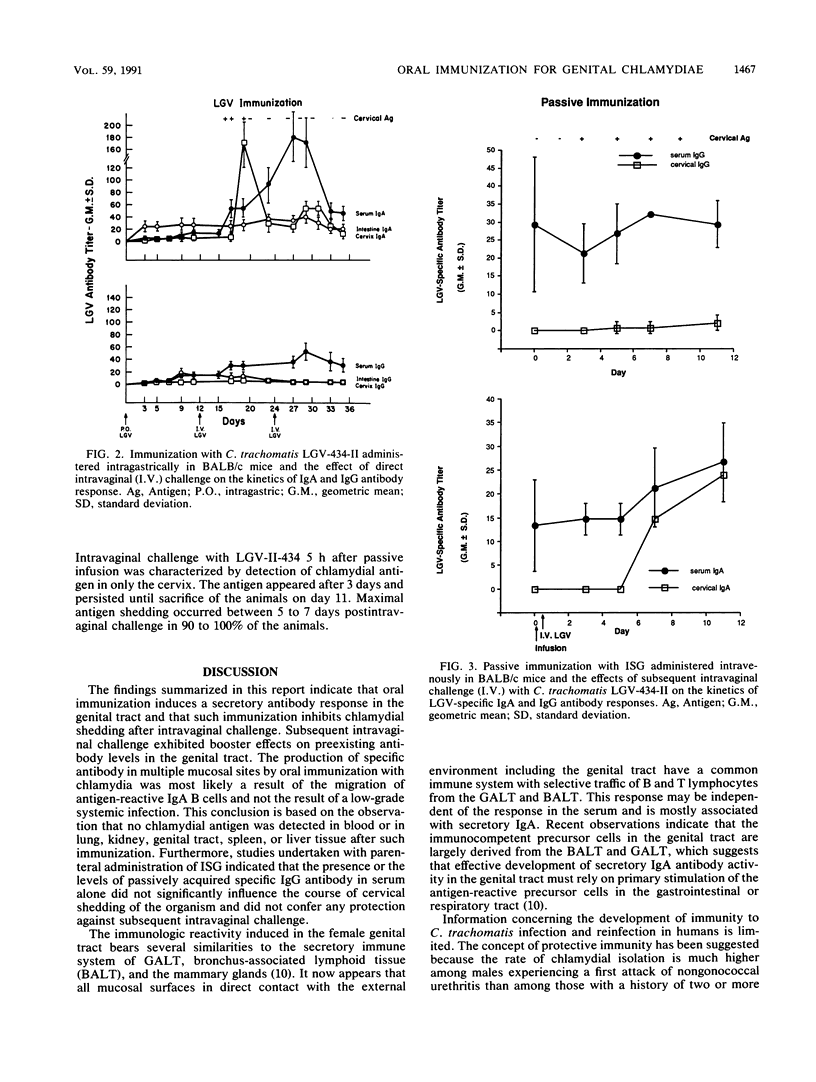
Abstract
Groups of BALB/c mice were orally immunized with Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2/434/Bu in order to characterize the nature and kinetics of the chlamydial antibody response in the cervix and other mucosal sites. These animals were subsequently challenged intravaginally to determine whether oral immunization offers protection against chlamydial antigen shedding in the genital tract. Following oral immunization, immunoglobulin A antibody activity was detected in the genital tract as well as other mucosal sites. Subsequent intravaginal challenges exhibited booster effects on preexisting antibody activity in the genital tract. Significant protection against challenge infection in the genital tract was observed by oral immunization. This was indicated by the absence of any chlamydial antigen shedding in cervical secretions. On the other hand, passively administered chlamydial-specific serum immunoglobulin G antibody did not significantly influence the course of cervical shedding of the organism and did not confer any protection against a subsequent intravaginal challenge. It is concluded that prior oral immunization can induce a secretory antibody response in the genital tract and provide protection against subsequent infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani M. D., Darougar S., Burns D. C., Thin R. N., Dunn H. Isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis from the male urethra. Br J Vener Dis. 1977 Apr;53(2):88–92. doi: 10.1136/sti.53.2.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Kuo C. C., Cles L., Holmes K. K. Correlation of host immune response with quantitative recovery of Chlamydia trachomatis from the human endocervix. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1491–1494. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1491-1494.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui Z. D., LaScolea L. J., Jr, Fisher J., Ogra P. L. Immunoprophylaxis of Chlamydia trachomatis lymphogranuloma venereum pneumonitis in mice by oral immunization. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):739–744. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.739-744.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison H. R., English M. G., Lee C. K., Alexander E. R. Chlamydia trachomatis infant pneumonitis: comparison with matched controls and other infant pneumonitis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 30;298(13):702–708. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803302981303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L. V., O'Leary M. P., Nichols R. L. Animal model studies of genital chlamydial infections. Immunity to re-infection with guinea-pig inclusion conjunctivitis agent in the urethra and eye of male guinea-pigs. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Aug;52(4):261–265. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.4.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. P. Pathogenesis and immunology of chlamydial infections of the genital tract. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Nov-Dec;7(6):741–745. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.6.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont H. C., Semine D. Z., Leveille C., Nichols R. L. Immunity to vaginal reinfection in female guinea pigs infected sexually with Chlamydia of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):807–813. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.807-813.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucero M. E., Kuo C. C. Neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis cell culture infection by serovar-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):595–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.595-597.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J. The common mucosal immune system and current strategies for induction of immune responses in external secretions. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Jul;7(4):265–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00915547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E. S., Charbonnet L. T., MacDonald A. B. Immunity to chlamydial infections of the eye. I. The role of circulatory and secretory antibodies in resistance to reinfection with guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1518–1525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. L., Murray E. S., Nisson P. E. Use of enteric vaccines in protection against chlamydial infections of the genital tract and the eye of guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):742–746. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. L., Oertley R. E., Fraser E. C., MacDonald A. B., McComb D. E. Immunity to chlamydial infections of the eye. VI. Homologous neutralization of trachoma infectivity for the owl monkey conjuctivae by eye secretions from humans with trachoma. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):429–432. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeling R., Maclean I. W., Brunham R. C. In vitro neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibody to an epitope on the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):484–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.484-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puolakkainen M., Vesterinen E., Purola E., Saikku P., Paavonen J. Persistence of chlamydial antibodies after pelvic inflammatory disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):924–928. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.924-928.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J. Chlamydial infections (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 9;298(10):540–549. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803092981005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Grossman M., Holt J., Sweet R., Goodner E., Mills J. Prospective study of chlamydial infection in neonates. Lancet. 1979 Aug 25;2(8139):377–380. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90400-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Grubbs B., Sumaya C. V. The role of antibody in host defense against the agent of mouse pneumonitis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):200–205. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. X., Stewart S. J., Caldwell H. D. Protective monoclonal antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis serovar- and serogroup-specific major outer membrane protein determinants. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):636–638. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.636-638.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


