Abstract
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment of mice 1 to 5 days prior to administration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A (PA) induced full or partial protection against PA intoxication. The optimal LPS dose that induced resistance was 50 to 100 micrograms per mouse. Simultaneous administration of LPS and PA to mice, however, increased their sensitivity to PA two- to fourfold. Mice pretreated with LPS demonstrated a markedly enhanced clearance rate of 125I-labeled PA from peripheral blood, livers, and kidneys. In mice exposed to LPS and PA simultaneously, the rate of elimination of labeled PA was lower than that in control mice. While protein synthesis was inhibited significantly in livers and other organs of PA-exposed mice, in LPS-pretreated mice, PA-induced inhibition of protein synthesis was either diminished or totally prevented and elongation factor 2 (EF2) levels were normal. In mice treated only with LPS, enhanced protein synthesis and increased levels of EF2 were observed, suggesting that LPS protection against PA intoxication was perhaps a consequence of excessive amounts of EF2 induced by LPS.
Full text
PDF
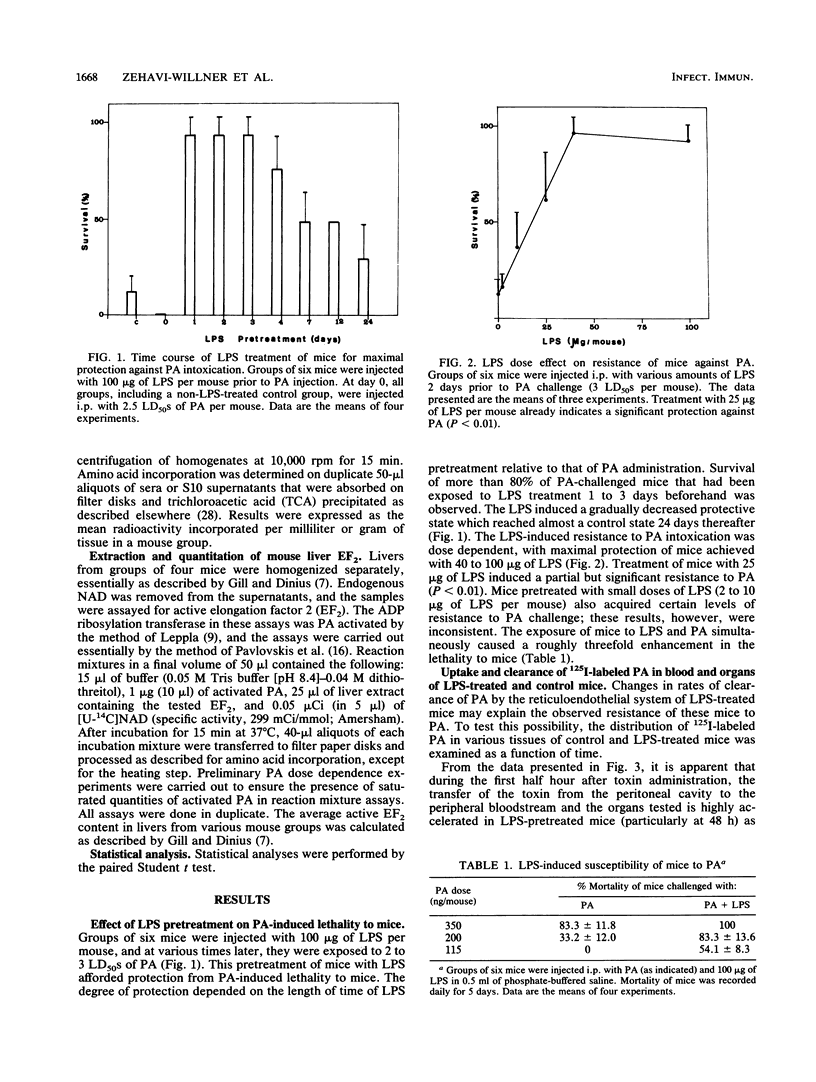
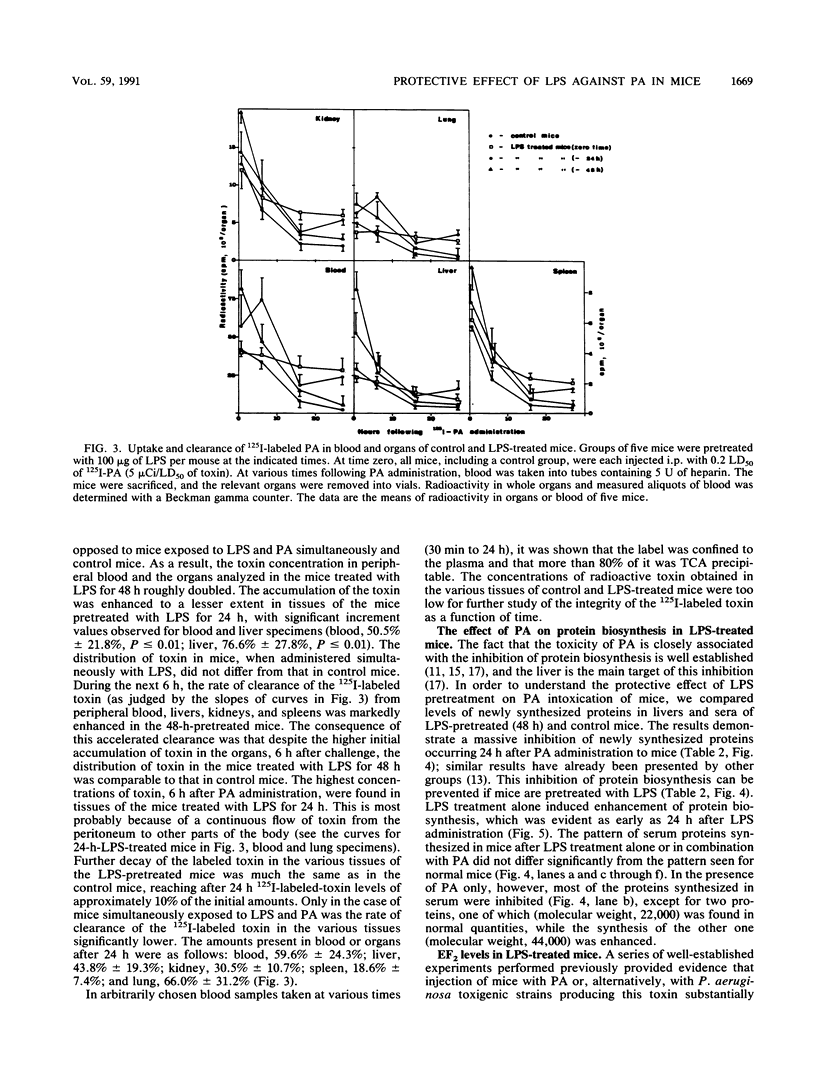
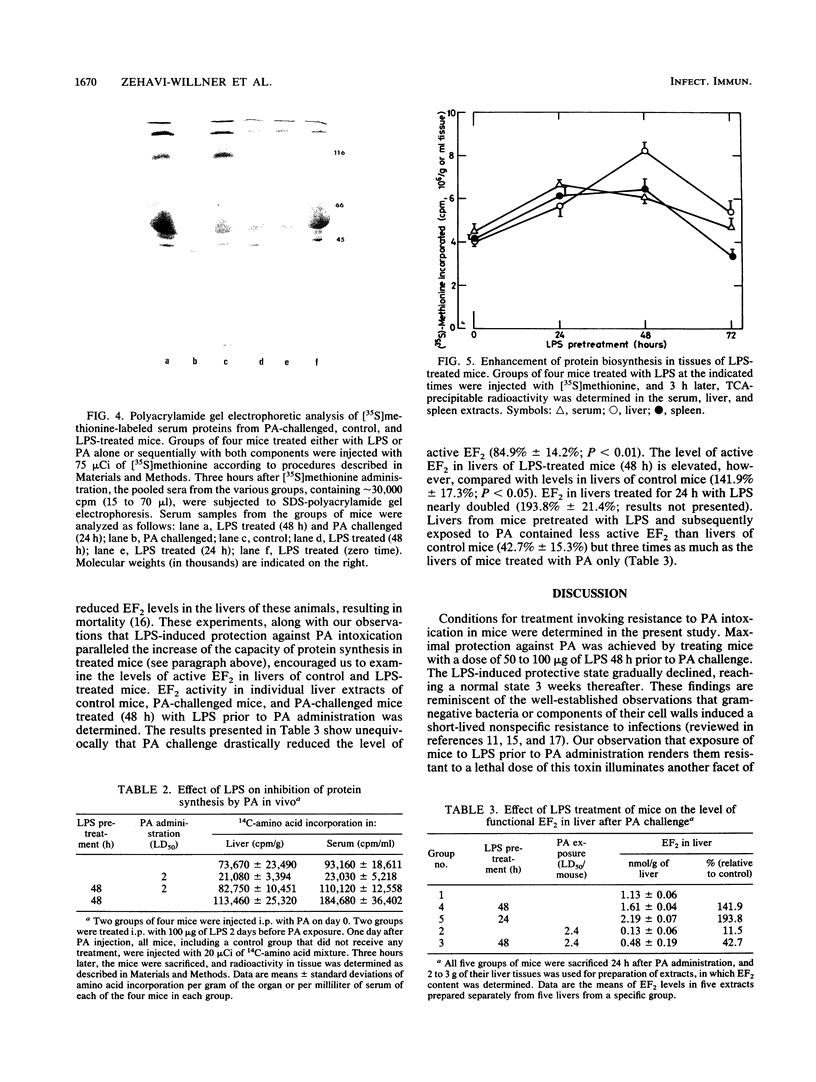


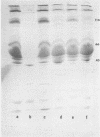
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cluff C. W., Ziegler H. K. An early response to lipopolysaccharide is the elicitation of macrophages specialized for antigen degradation with negative regulatory effects on the induction of specific immune responses. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1346–1354. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1346-1354.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans N. Bacterial toxins and diarrhoea. Trop Doct. 1979 Jan;9(1):10–15. doi: 10.1177/004947557900900105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwaka H., Igarashi H., Usami H., Tanaka S., Tamura H. Clearance of endotoxin from blood of rabbits injected with staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):134–137. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.134-137.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. The elongation factor 2 content of mammalian cells. Assay method and relation to ribosome number. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):654–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton J. P., Joisel F., Raoult J. P., Lannuzel B., Rogez J. P., Humbert G. Serum concentration of human alpha 2 HS glycoprotein during the inflammatory process: evidence that alpha 2 HS glycoprotein is a negative acute-phase reactant. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):1118–1129. doi: 10.1172/JCI109551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1139/m77-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Gordon F. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: effect on cell cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):631–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Iglewski B. H., Pollack M. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A in experimental mouse infections: adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of elongation factor 2. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.29-33.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Shackelford A. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in mice: localization and effect on protein synthesis. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.540-546.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogoff T. M., Lipsky P. E. Role of the Kupffer cells in local and systemic immune responses. Gastroenterology. 1981 Apr;80(4):854–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Watson D. W. Group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin: pyrogenicity, alteration of blood-brain barrier, and separation of sites for pyrogenicity and enhancement of lethal endotoxin shock. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):753–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.753-763.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä I. J., Mäkelä O. Adjuvant effect of bacterial LPS and/or alum precipitation in responses to polysaccharide and protein antigens. Immunology. 1984 Dec;53(4):827–836. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell K., Holder I. A., Leppla S. A., Saelinger C. B. Role of exotoxin and protease as possible virulence factors in experimental infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.839-845.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone R. L., Schlievert P. M. Evidence for the involvement of endotoxin in toxic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):682–689. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuopio-Varkila J., Nurminen M., Pyhälä L., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide-induced non-specific resistance to systemic Escherichia coli infection in mice. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Mar;25(3):197–203. doi: 10.1099/00222615-25-3-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. A., Keller G. A., Hyland B. J., Cerra F. B., Simmons R. L. Hepatocyte function in sepsis: Kupffer cells mediate a biphasic protein synthesis response in hepatocytes after exposure to endotoxin or killed Escherichia coli. Surgery. 1985 Sep;98(3):388–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehavi-Willner T. Induction of murine cytolytic T lymphocytes by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):213–218. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.213-218.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Azavedo J. C., Lucken R. N., Arbuthnott J. P. Effect of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 on chicken embryos. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):710–712. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.710-712.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]