Abstract
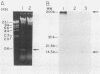
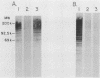
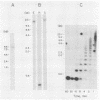
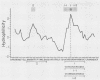
Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted protozoan parasite that undergoes phenotypic variation for numerous surface proteins. A monoclonal antibody (MAb) was used to isolate an approximately 400-bp cDNA encoding a fragment of an important phenotypically varying immunogen of T. vaginalis (Mr = 270 kDa; P270). The MAb completely inhibited the binding of P270 by antibody in sera of patients and by antibody in monospecific antiserum obtained toward purified P270, indicating that P270 contained only one immunodominant epitope. Hydrophilicity plot analysis of the deduced amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein predicted the hexapeptide sequence DREGRD as the antigenic determinant of P270. Synthetic peptides synthesized to this region demonstrated that the amino acid sequence DREGRD is important for antibody binding. Seven adjacent amino acids also contributed substantially to maximal recognition of the epitope by the MAb. A single transcript of approximately 9.5 kb, a size compatible with the reported Mr of the immunogen, hybridized to the cDNA in Northern blots of total RNA from T. vaginalis. DNA sequence and Southern blot analysis determined the epitope to be encoded by a 339-bp unit, which was found to be tandemly repeated at least 12 times within the single-copy gene. This 12-mer unit would only constitute approximately 50% of the protein, yet it is responsible for all of the serum antibody to the immunogen produced by animals and humans. The epitope sequence was found in all fresh and long-term-grown organisms examined to date, demonstrating the stability and conservation of this gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Demes P., Gombosová A., Valent M., Yánoska A., Fabusová H., Kasmala L., Garza G. E., Metcalfe E. C. Phenotypes and protein-epitope phenotypic variation among fresh isolates of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1037–1041. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1037-1041.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Kasmala L., Metcalfe E., Garza G. E. Phenotypic variation and diversity among Trichomonas vaginalis isolates and correlation of phenotype with trichomonal virulence determinants. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):285–293. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.285-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major glycoprotein immunogen mediates differential complement-independent lysis of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):697–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.697-699.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Neale K. A. Relatedness of structures of a major immunogen in Trichomonas vaginalis isolates. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1849–1853. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1849-1853.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Suprun-Brown L., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major surface glycoprotein immunogen differentiates isolates and subpopulations of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.70-75.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Suprun-Brown L., Kasmala L., Smith J., Spence M. Heterogeneity of Trichomonas vaginalis and discrimination among trichomonal isolates and subpopulations with sera of patients and experimentally infected mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):463–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.463-468.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND L. S. The establishment of various trichomonads of animals and man in axenic cultures. J Parasitol. 1957 Aug;43(4):488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoft D. F., Kim K. S., Otsu K., Moser D. R., Yost W. J., Blumin J. H., Donelson J. E., Kirchhoff L. V. Trypanosoma cruzi expresses diverse repetitive protein antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1959–1967. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1959-1967.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Cowman A. F., Walliker D. Genetic diversity in Plasmodium falciparum. Adv Parasitol. 1990;29:75–149. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Holmes K. K., Spence M. R., Rein M. F., McCormack W. M., Tam M. R. Geographic variation among isolates of Trichomonas vaginalis: demonstration of antigenic heterogeneity by using monoclonal antibodies and the indirect immunofluorescence technique. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):979–984. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafaille J. J., Linss J., Krieger M. A., Souto-Padrón T., de Souza W., Goldenberg S. Structure and expression of two Trypanosoma cruzi genes encoding antigenic proteins bearing repetitive epitopes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jun 15;35(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North M. J., Mottram J. C., Coombs G. H. Cysteine proteinases of parasitic protozoa. Parasitol Today. 1990 Aug;6(8):270–275. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90189-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Alderete J. F. Host plasma proteins on the surface of pathogenic Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.755-762.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A., Hemphill A., Wyler T., Seebeck T. Large microtubule-associated protein of T. brucei has tandemly repeated, near-identical sequences. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):459–462. doi: 10.1126/science.3393912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su-Lin K. E., Honigberg B. M. Antigenic analysis of Trichomonas vaginalis strains by quantitative fluorescent antibody methods. Z Parasitenkd. 1983;69(2):161–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00926952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. L., Wang C. C. Isolation and characterization of DNA from Tritrichomonas foetus and Trichomonas vaginalis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Mar;14(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavala F., Cochrane A. H., Nardin E. H., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. Circumsporozoite proteins of malaria parasites contain a single immunodominant region with two or more identical epitopes. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1947–1957. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]