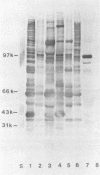
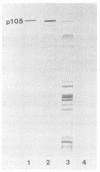
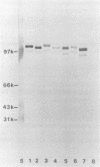
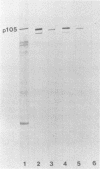
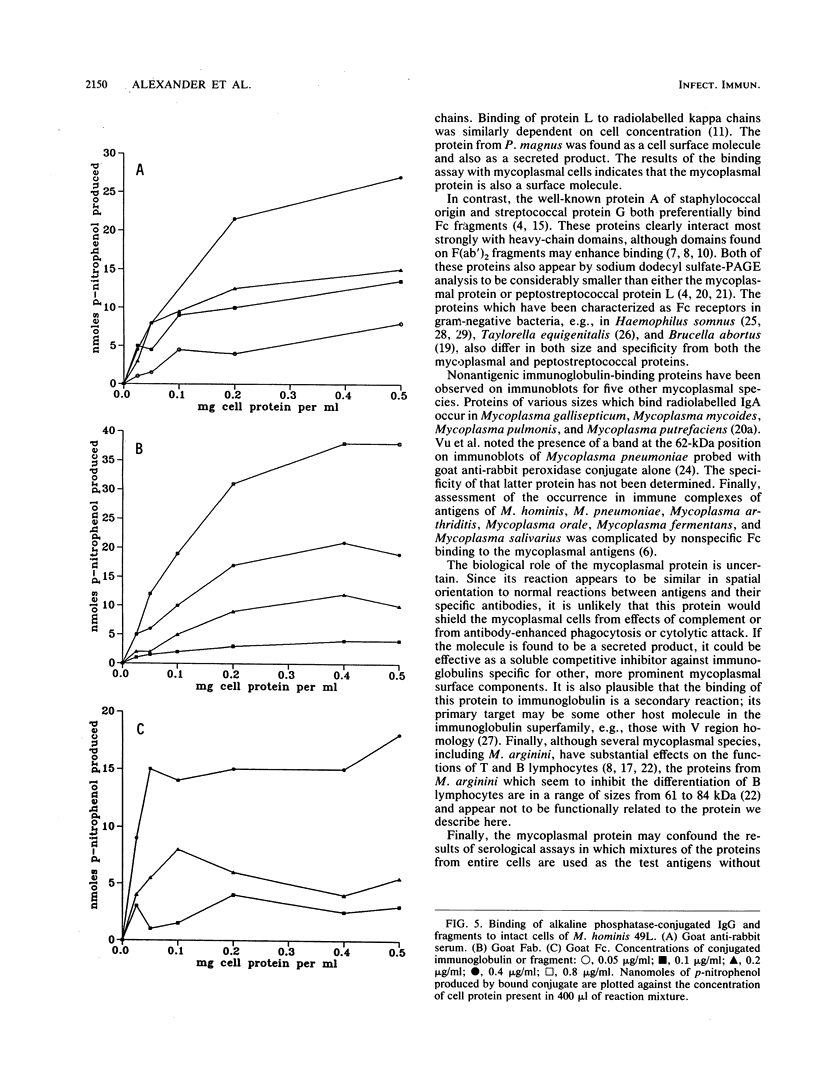
Abstract
Immunoblotted protein samples from several strains of Mycoplasma hominis and from one strain of Mycoplasma arginini each contain a polypeptide of a molecular mass of 95,000 to 105,000 Da which binds immunoglobulin nonimmunologically. Immunoblots from these organisms were probed with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin, conjugated goat immunoglobulin G (IgG) Fab fragments, and conjugated goat IgG Fc fragments. The polypeptide bound the goat anti-rabbit molecules and the Fab fragments but not the Fc fragments. These reactions could be blocked with nonimmune unconjugated goat IgG and unconjugated human IgM. Controls probed with alkaline phosphatase alone did not stain. Binding of the conjugated preparations to whole mycoplasmal cells was dependent on concentrations of both conjugate and cells for the goat anti-rabbit preparation and for Fab. The mycoplasmal polypeptide may be a light-chain-specific reactant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. G. Analysis of protein antigens of Mycoplasma hominis: detection of polypeptides involved in the human immune response. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 Jun;23(6):608–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Characterization of membrane and cytoplasmic antigens of Mycoplasma arginini by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.313-321.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Kronvall G. Purification and some properties of streptococcal protein G, a novel IgG-binding reagent. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):969–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L. Protein L. A novel bacterial cell wall protein with affinity for Ig L chains. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1194–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. W., Coker-Vann M. R., Bailey J. S., Brown T. M. Detection of mycoplasmal antigens in immune complexes from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluids. Ann Allergy. 1988 May;60(5):394–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson M., Andersson R., Olsson A., Wigzell H., Uhlén M. Differential IgG-binding characteristics of staphylococcal protein A, streptococcal protein G, and a chimeric protein AG. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erntell M., Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Non-immune IgG F(ab')2 binding to group C and G streptococci is mediated by structures on gamma chains. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Feb;21(2):151–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foresman M. D., Sheehan K. C., Swierkosz J. E. The regulation of murine B cell differentiation. I. Nonspecific suppression caused by Mycoplasma arginini. Cell Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;123(2):354–372. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inganäs M. Comparison of mechanisms of interaction between protein A from Staphylococcus aureus and human monoclonal IgG, IgA and IgM in relation to the classical FC gamma and the alternative F(ab')2 epsilon protein A interactions. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(4):343–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Cartwright F. D. Immunoblotting for determination of the antigenic specificities of antibodies to the Mycoplasmatales. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Oct;20(10):908–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):510–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.510-515.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke H., Krausse R., Lorenzen J., Havsteen B. Mycoplasma infection of cell lines can simulate the expression of Fc receptors by binding of the carbohydrate moiety of antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1985 May;15(5):442–447. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Erntell M. A non-immune interaction between the light chain of human immunoglobulin and a surface component of a Peptococcus magnus strain. Mol Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(8):879–885. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K., Stilwell K., Stemshorn B., Duncan R. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (disodium salt)-labile bovine immunoglobulin M Fc binding to Brucella abortus: a cause of nonspecific agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):32–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.32-38.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis K. J., Ayoub E. M., Boyle M. D. Streptococcal Fc receptors. I. Isolation and partial characterization of the receptor from a group C streptococcus. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3091–3097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis K. J., Hansen H. F., Björck L. Extraction and characterization of IgG Fc receptors from group C and group G streptococci. Mol Immunol. 1986 Apr;23(4):425–431. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruuth E., Praz F. Interactions between mycoplasmas and the immune system. Immunol Rev. 1989 Dec;112:133–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu A. C., Foy H. M., Cartwright F. D., Kenny G. E. The principal protein antigens of isolates of Mycoplasma pneumoniae as measured by levels of immunoglobulin G in human serum are stable in strains collected over a 10-year period. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1830–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1830-1836.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Smith J. W., Yarnall M., McGuire T. C., Corbeil L. B. Non-immune immunoglobulin binding by "Haemophilus somnus". J Med Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(4):307–311. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-4-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Stokes C. R., Newby T. J., Bourne F. J. Nonimmune binding of equine immunoglobulin by the causative organism of contagious equine metritis, Taylorella equigenitalis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):417–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.417-421.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Gogolewski R. P., Corbeil L. B. Characterization of two Haemophilus somnus Fc receptors. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jul;134(7):1993–1999. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-7-1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Widders P. R., Corbeil L. B. Isolation and characterization of Fc receptors from Haemophilus somnus. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Aug;28(2):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]