Abstract
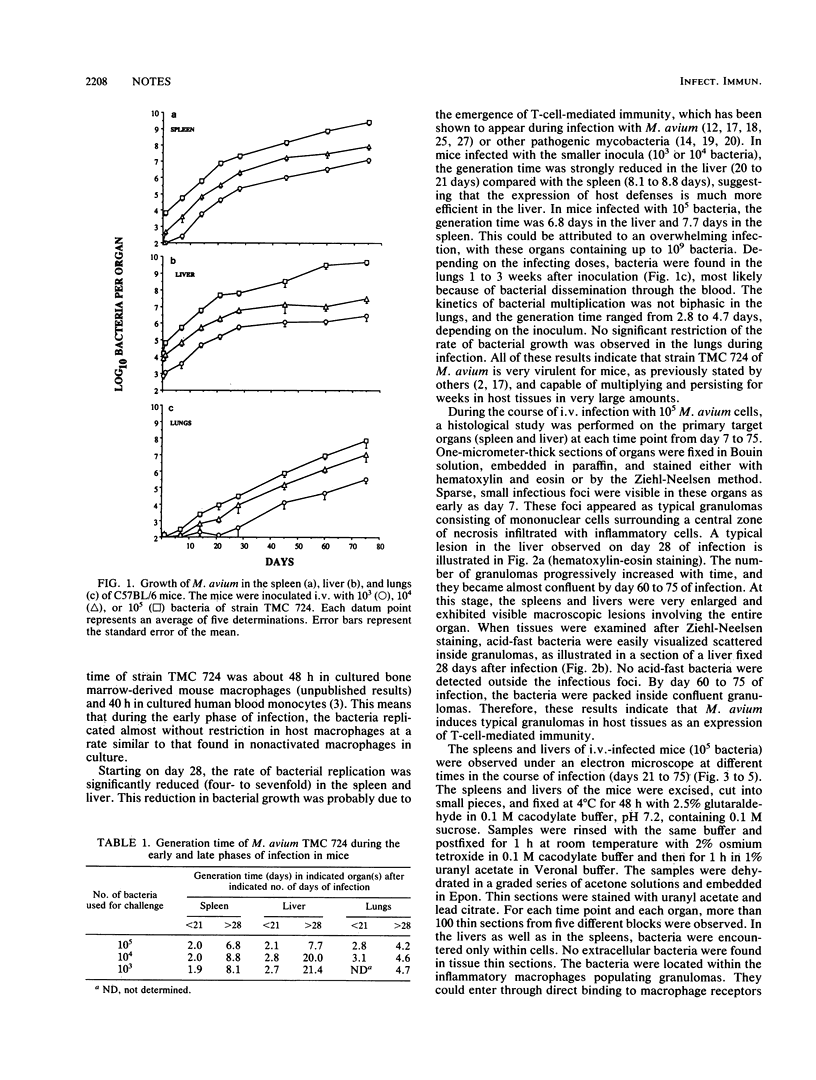
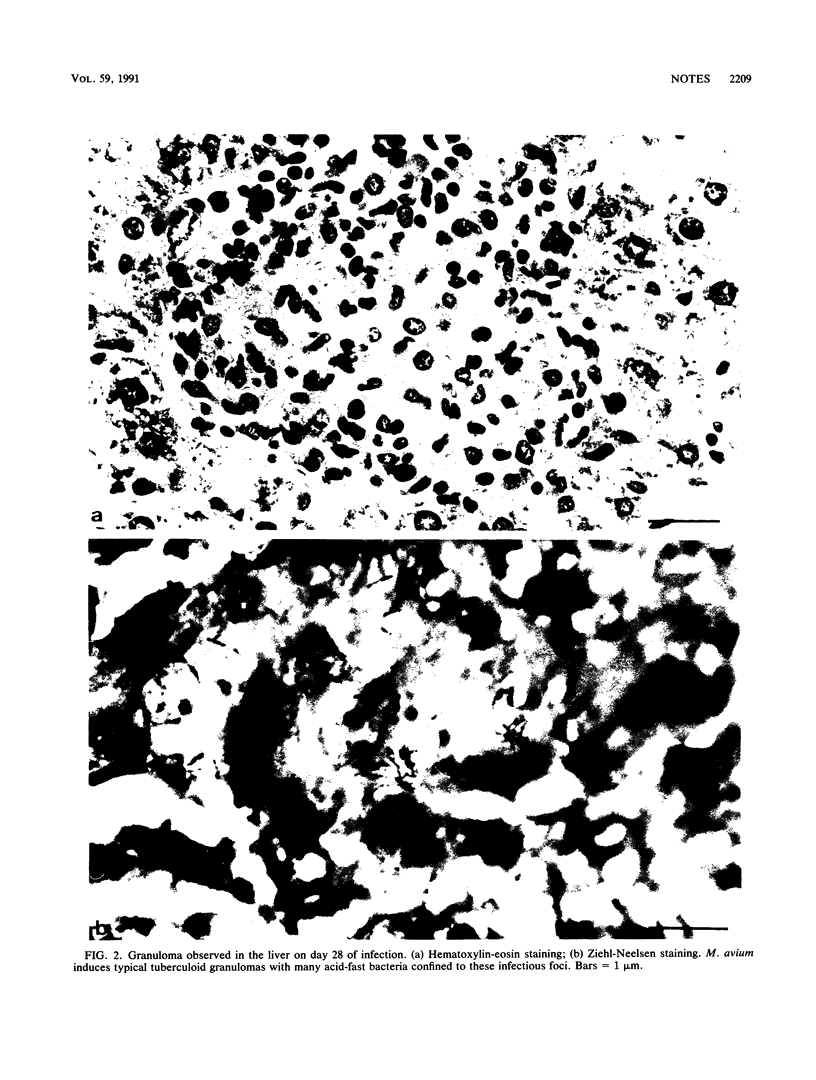
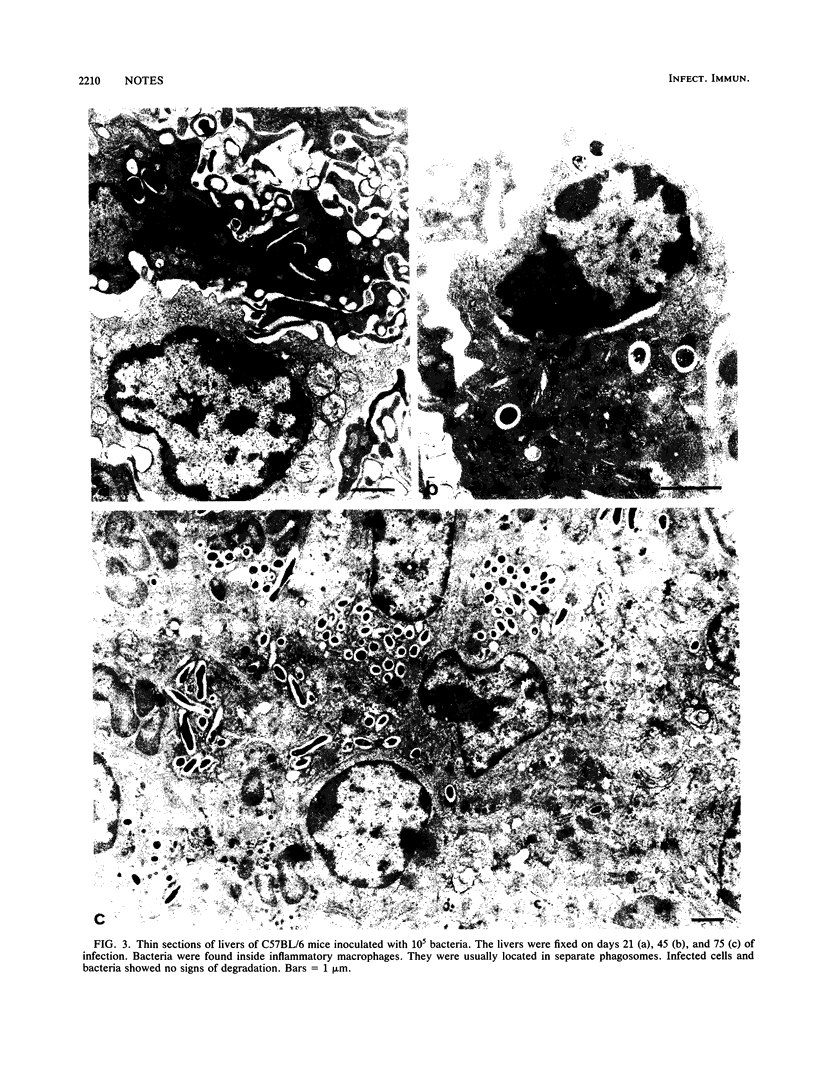
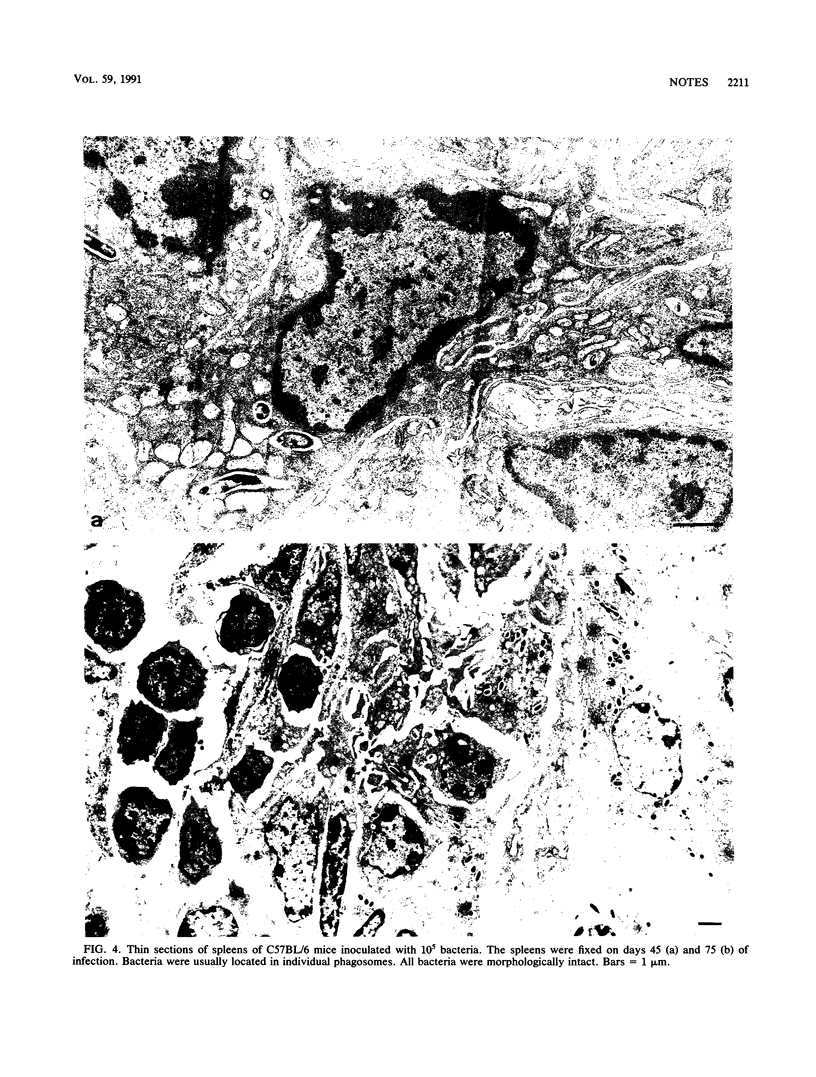
Growth of the virulent Mycobacterium avium strain TMC 724 in host tissues during persistent infection of mice was studied. Following intravenous infection of C57BL/6 mice, the kinetics of bacterial growth was biphasic in the spleen and liver, with a significant reduction of the multiplication rate after day 21 to 28 of infection. An electron-microscopic study of the liver and spleen of infected mice showed that the bacteria were strictly intracellular. They were observed within inflammatory macrophages populating granulomas disseminated in host tissues. The bacteria were confined to the phagosome compartment, and they were encapsulated. Phagosome-lysosome fusions were encountered, but the bacteria showed no visible signs of degradation and continued to multiply. These results are the first in vivo evidence that virulent M. avium multiplies exclusively intracellularly and that encapsulated bacteria resist the microbicidal mechanisms of macrophages inside the phagosomal compartment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Catanzaro A., Wright S. D. Binding of Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare to human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2951–2956. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2951-2956.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Tsang A. Y., Vatter A. E., May M. H. Comparison of 15 laboratory and patient-derived strains of Mycobacterium avium for ability to infect and multiply in cultured human macrophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):812–821. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.812-821.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper P., Rees R. J. Electron-transparent zone of mycobacteria may be a defence mechanism. Nature. 1970 Nov 28;228(5274):860–861. doi: 10.1038/228860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Bishburg E., Smith S. M., Mangia A. Diagnosis of Mycobacterium bacteremia in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome by direct examination of blood films. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):768–769. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.768-769.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehel C., Rastogi N. Mycobacterium leprae surface components intervene in the early phagosome-lysosome fusion inhibition event. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2916–2921. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2916-2921.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehel C., Ryter A., Rastogi N., David H. The electron-transparent zone in phagocytized Mycobacterium avium and other mycobacteria: formation, persistence and role in bacterial survival. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Nov-Dec;137B(3):239–257. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehel C., de Chastellier C., Lang T., Rastogi N. Evidence for inhibition of fusion of lysosomal and prelysosomal compartments with phagosomes in macrophages infected with pathogenic Mycobacterium avium. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):252–262. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.252-262.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangadharam P. R., Pratt P. F. In vitro response of murine alveolar and peritoneal macrophages to Mycobacterium intracellulare. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Dec;128(6):1044–1047. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.6.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good R. C. Opportunistic pathogens in the genus Mycobacterium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:347–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveton C., Barnass S., Champion B., Lucas S., De Souza B., Nicol M., Banerjee D., Rook G. T-cell-mediated protection of mice against virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):390–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.390-395.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffie B. G., Krulder J. W., de Knijff J. C. Direct visualization of mycobacteria in blood culture. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 5;320(1):61–62. doi: 10.1056/nejm198901053200115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. J., Geiter L. J., Snider D. E., Jr The epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases in the United States. Results from a national survey. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1007–1014. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Crossprotection against nontuberculous mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis memory immune T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1986 Jan 1;163(1):203–208. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Immune response to atypical mycobacteria: immunocompetence of heavily infected mice measured in vivo fails to substantiate immunosuppression data obtained in vitro. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):32–37. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.32-37.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Resistance of various strains of mycobacteria to killing by activated macrophages in vivo. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1452–1454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. S., Peterson D. D., Steiner R. M., Gottlieb J. E., Scott R., Israel H. L., Figueroa W. G., Fish J. E. Infection with Mycobacterium avium complex in patients without predisposing conditions. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):863–868. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichert C. M., O'Leary T. J., Levens D. L., Simrell C. R., Macher A. M. Autopsy pathology in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1983 Sep;112(3):357–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Franzblau S. G., Krahenbuhl J. L. Intracellular fate of Mycobacterium leprae in normal and activated mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):680–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.680-685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes R. W., Collins F. M. Growth of Mycobacterium avium in activated macrophages harvested from inbred mice with differing innate susceptibilities to mycobacterial infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2250–2254. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2250-2254.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes R. W., Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Role of mononuclear phagocytes in expression of resistance and susceptibility to Mycobacterium avium infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.811-819.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz R. P., Naai D., Vogel C. W., Yeager H., Jr Differences in uptake of mycobacteria by human monocytes: a role for complement. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2223–2227. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2223-2227.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima T., Collins F. M. T-cell-mediated immunity in persistent Mycobacterium intracellulare infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2782–2787. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2782-2787.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakrus M. A., Good R. C. Geographic distribution, frequency, and specimen source of Mycobacterium avium complex serotypes isolated from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):926–929. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.926-929.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Mycobacterium avium complex infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):863–867. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski P., Fligiel S., Berlin G. W., Johnson L., Jr Disseminated Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection in homosexual men dying of acquired immunodeficiency. JAMA. 1982 Dec 10;248(22):2980–2982. doi: 10.1001/jama.1982.03330220024029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]