Abstract
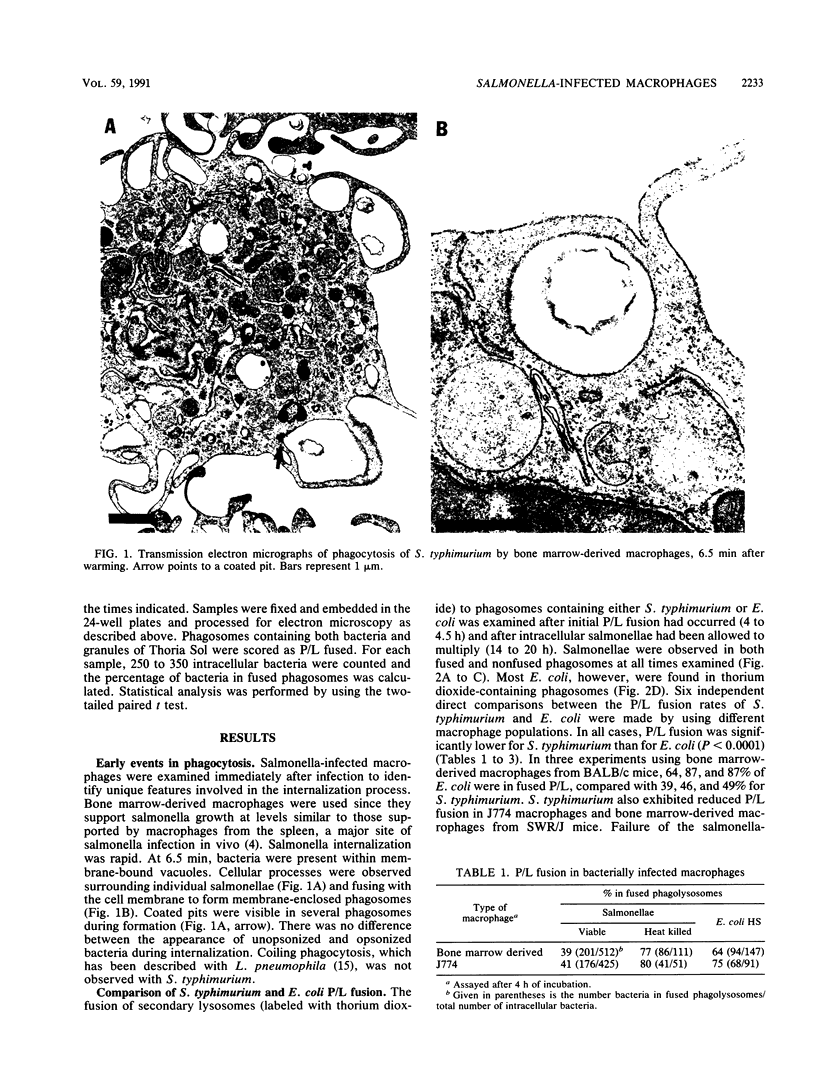
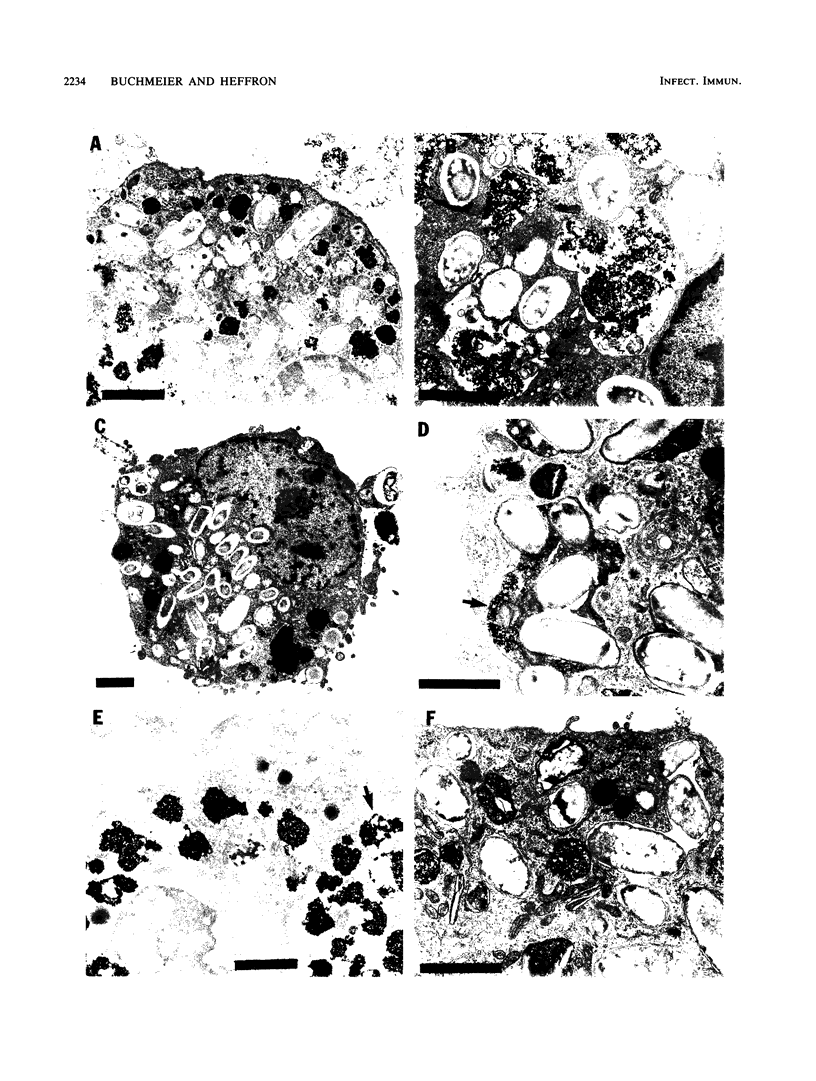
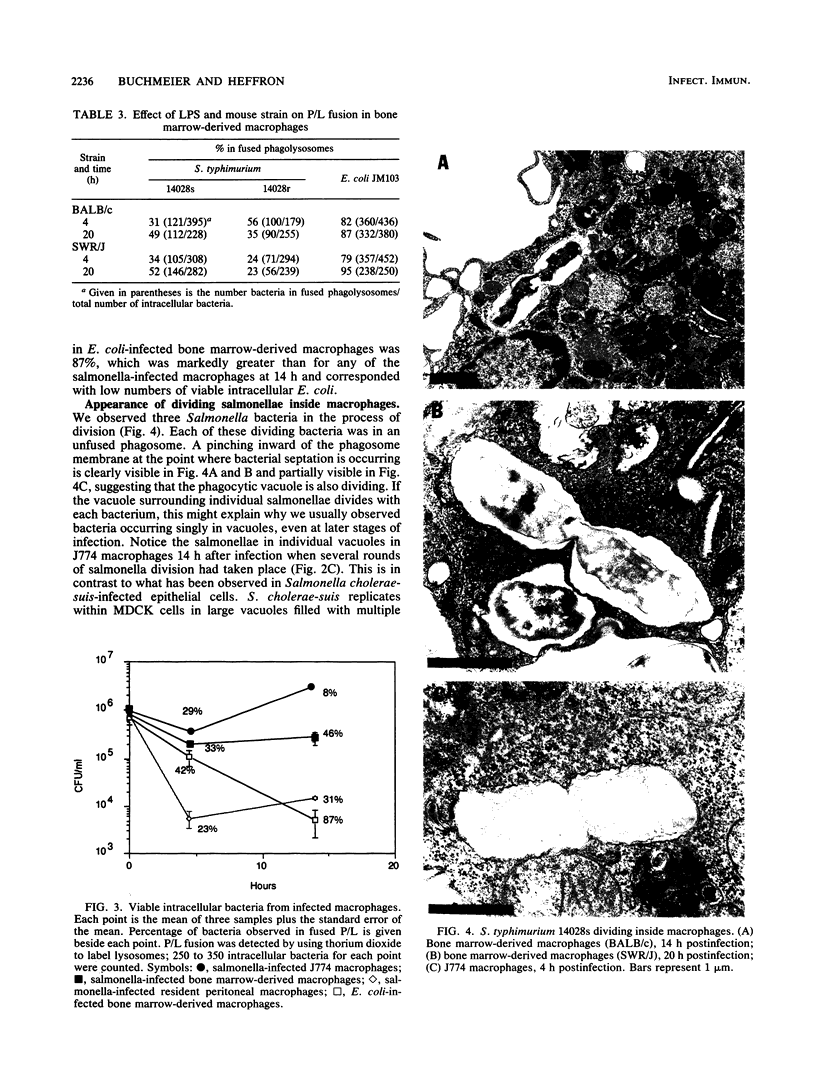
Salmonella typhimurium-infected macrophages were examined by electron microscopy to determine whether intracellular survival of S. typhimurium is associated with failure of bacteria containing phagosomes to fuse with secondary lysosomes. S. typhimurium 14028 actively inhibited phagosome-lysosome fusion and appeared to preferentially divide within unfused phagocytic vesicles. In comparison with Escherichia coli, S. typhimurium inhibited phagosome-lysosome fusion in peritoneal macrophages, J774 macrophages, and bone marrow-derived macrophages from both BALB/c (itys) and SWR/J (ityr) mice. The mechanism responsible for Salmonella inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion is unknown but requires viable salmonellae, is not blocked by opsonization with fresh normal mouse serum, and is not due to lipopolysaccharide. Inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion may play a critical role in survival of salmonellae within macrophages and in virulence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Phagosome-lysosome interactions in cultured macrophages infected with virulent tubercle bacilli. Reversal of the usual nonfusion pattern and observations on bacterial survival. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Response of cultured macrophages to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with observations on fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):713–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V. Modification of macrophage function. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1968 Jun;5(3):179–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Heffron F. Induction of Salmonella stress proteins upon infection of macrophages. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):730–732. doi: 10.1126/science.1970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Heffron F. Intracellular survival of wild-type Salmonella typhimurium and macrophage-sensitive mutants in diverse populations of macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.1-7.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrol M. E., Jackett P. S., Aber V. R., Lowrie D. B. Phagolysosome formation, cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and the fate of Salmonella typhimurium within mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):421–429. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P. L., Ryter A., Mounier J., Sansonetti P. J. Plasmid-mediated early killing of eucaryotic cells by Shigella flexneri as studied by infection of J774 macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):521–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.521-527.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis-Scibienski C., Beaman B. L. Interaction of Nocardia asteroides with rabbit alveolar macrophages: association of virulence, viability, ultrastructural damage, and phagosome-lysosome fusion. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):610–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.610-619.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehel C., Rastogi N. Mycobacterium leprae surface components intervene in the early phagosome-lysosome fusion inhibition event. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2916–2921. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2916-2921.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahring L. C., Heffron F., Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Invasion and replication of Salmonella typhimurium in animal cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):443–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.443-448.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., D'Arcy Hart P., Young M. R., Armstrong J. A. Prevention of phagosome-lysosome fusion in cultured macrophages by sulfatides of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2510–2514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R., Gordon A. H., Sullivan K. H. Inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion in macrophages by certain mycobacteria can be explained by inhibition of lysosomal movements observed after phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):933–946. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) occurs by a novel mechanism: engulfment within a pseudopod coil. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. The Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2108–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi Y., Arai T. Specific inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion in murine macrophages mediated by Salmonella typhimurium infection. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1990 May;2(1):35–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb03476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Fuhrman S. A., Miettinen H. M., Kasper L. H., Mellman I. Toxoplasma gondii: fusion competence of parasitophorous vacuoles in Fc receptor-transfected fibroblasts. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):641–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2200126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. II. The absence of lysosomal fusion with phagocytic vacuoles containing living parasites. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1173–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagaya K., Watanabe K., Fukazawa Y. Capacity of recombinant gamma interferon to activate macrophages for Salmonella-killing activity. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):609–615. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.609-615.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M. C., Cohn Z. A. Phagosome-lysosome fusion. Characterization of intracellular membrane fusion in mouse macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):754–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Falkow S. Recombinant DNA risk assessment studies in humans: efficacy of poorly mobilizable plasmids in biologic containment. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):699–709. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrie D. B., Aber V. R., Jackett P. S. Phagosome-lysosome fusion and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in macrophages infected with Mycobacterium microti, Mycobacterium bovis BCG or Mycobacterium lepraemurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):431–441. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: mechanism of entry and intracellular fate in mammalian cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1402–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Franzblau S. G., Krahenbuhl J. L. Intracellular fate of Mycobacterium leprae in normal and activated mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):680–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.680-685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spargo B. J., Crowe L. M., Ioneda T., Beaman B. L., Crowe J. H. Cord factor (alpha,alpha-trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate) inhibits fusion between phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):737–740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Harmon P. A. Yersinia pestis grows within phagolysosomes in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.655-659.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





