Abstract
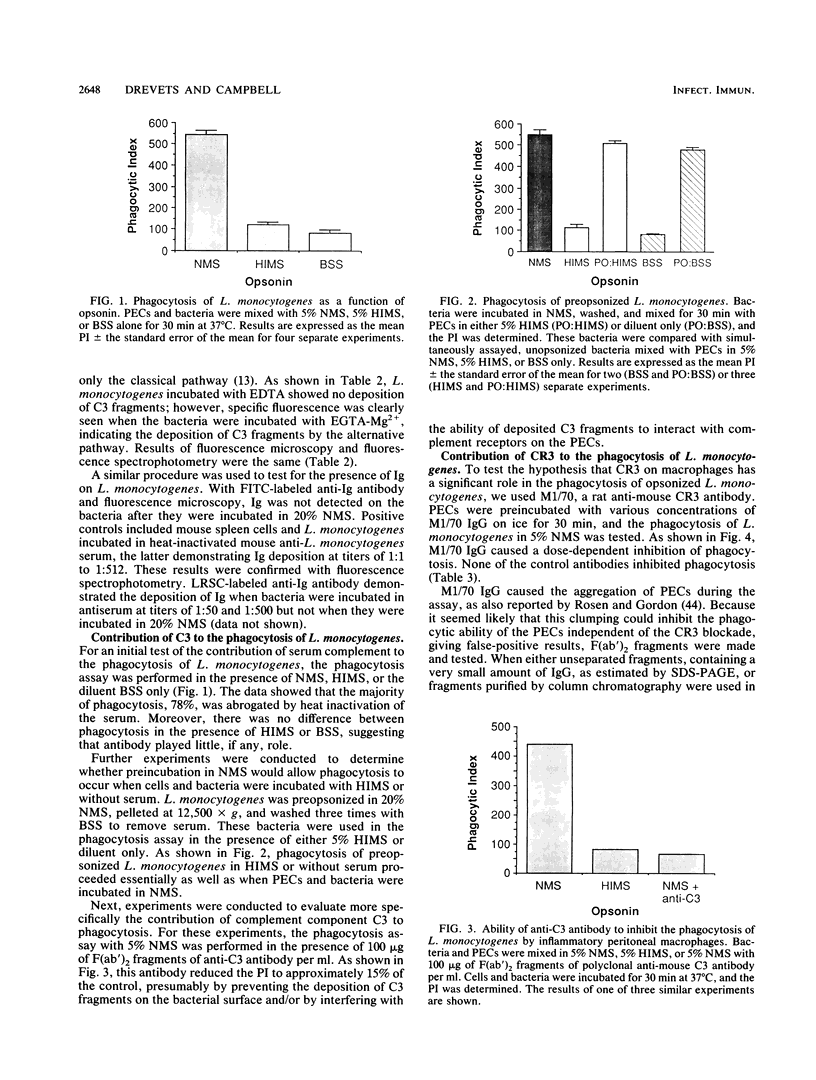
Listeria monocytogenes is a facultative intracellular bacterium that is phagocytosed by and can proliferate within cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system. However, the receptors used by macrophages to internalize this organism have not been identified. In the experiments described here, the contributions of serum complement component C3 and macrophage complement receptor type 3 (CR3) to opsonization and phagocytosis of L. monocytogenes by mouse inflammatory peritoneal macrophages were studied. An assay which allowed the distinction of adherent versus internalized bacteria was used to show that following mixing of L. monocytogenes with inflammatory macrophages, greater than 95% of the bacteria bound were internalized by these phagocytes. When immunofluorescent antibodies to C3 and immunoglobulin were used, C3 but not immunoglobulin was detected on L. monocytogenes following incubation in normal serum or ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetracetic acid-Mg(2+)-chelated serum. When macrophages were incubated with 5% serum and L. monocytogenes in a standard assay, approximately 80% of the phagocytosis was inhibited by heat-inactivated serum or by the addition of F(ab')2 anti-C3 antibody. The role of macrophage CR3 was demonstrated by the ability of anti-CR3 monoclonal antibody M1/70 to decrease phagocytosis to the same levels as those seen with heat-inactivated serum. These experiments indicated that in the presence of normal serum, L. monocytogenes is phagocytosed by inflammatory macrophages primarily because CR3 on these cells binds to C3 deposited on the bacterial surface.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. C., Springer T. A. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency: an inherited defect in the Mac-1, LFA-1, and p150,95 glycoproteins. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:175–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker L. A., Campbell P. A., Hollister J. R. Chemotaxigenesis and complement fixation by Listeria monocytogenes cell wall fractions. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1723–1726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Goldman R., Ofek I., Sharon N., Mirelman D. Mannose-binding activity of Escherichia coli: a determinant of attachment and ingestion of the bacteria by macrophages. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):417–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.417-424.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Springer T. A., Schreiber R. D. Anti-Mac-1 selectively inhibits the mouse and human type three complement receptor. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1000–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Griffin F. M., Jr, Silverstein S. C. Studies of the macrophage complement receptor. Alteration of receptor function upon macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1278–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Bohnsack J. F., Gresham H. D. Mechanism of inhibition of immunoglobulin G-mediated phagocytosis by monoclonal antibodies that recognize the Mac-1 antigen. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):365–375. doi: 10.1172/JCI113328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Wright S. D. Role of the adherence-promoting receptors, CR3, LFA-1, and p150,95, in binding of Histoplasma capsulatum by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):195–210. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canono B. P., Middleton M. H., Campbell P. A. Recombinant mouse interferon-gamma is not chemotactic for macrophages or neutrophils. J Interferon Res. 1989 Feb;9(1):79–86. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Baudry B., Sansonetti P. J. Molecular mechanisms of entry, intracellular multiplication and killing of host cells by shigellae. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:3–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Enhanced accumulation of inflammatory neutrophils and macrophages mediated by transfer of T cells from mice immunized with Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3449–3454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Killing of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory neutrophils and mononuclear phagocytes from immune and nonimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Feb;35(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Prez R. M., Bryan C. S., Hawiger J., Colley D. G. Function of the classical and alternate pathways of human complement in serum treated with ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid and MgCl2-ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1235–1243. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1235-1243.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattorossi A., Nisini R., Pizzolo J. G., D'Amelio R. New, simple flow cytometry technique to discriminate between internalized and membrane-bound particles in phagocytosis. Cytometry. 1989 May;10(3):320–325. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990100311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Fauci A. S., Green I., Frank M. M. A simple method for the determination of complement receptor-bearing mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):595–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Mullinax P. J. High concentrations of bacterial lipopolysaccharide, but not microbial infection-induced inflammation, activate macrophage C3 receptors for phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):697–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington-Fowler L., Henson P. M., Wilder M. S. Fate of Listeria monocytogenes in resident and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):11–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.11-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. K., Springer T. A. Mac-1 antigen: quantitative expression in macrophage populations and tissues, and immunofluorescent localization in spleen. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2281–2286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Brown E. J., Frank M. M. Complement and bacteria: chemistry and biology in host defense. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:461–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Ganz T., Albert J., Rotrosen D. The opsonizing ligand on Salmonella typhimurium influences incorporation of specific, but not azurophil, granule constituents into neutrophil phagosomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2771–2782. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Goebel W. Identification of an extracellular protein of Listeria monocytogenes possibly involved in intracellular uptake by mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.55-61.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley J., Hyman R., Schulte R., Trotter J. Expression of transferrin receptor on murine hematopoietic progenitors. Cell Immunol. 1984 Jan;83(1):14–25. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Carter P. B. Cell-mediated immunity to intestinal infection. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):516–523. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.516-523.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel T. E., Cheers C. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: histopathology of listeriosis in resistant and susceptible strains. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):851–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.851-861.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani B. Phagocytosis of immune complexes mediated by IgM and C3 receptors by macrophages from mice treated with glycogen. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):127–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. M., Edelson P. J. The mouse macrophage receptor for C3bi (CR3) is a major mechanism in the phagocytosis of Leishmania promastigotes. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2785–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. L., Mikus L. K. Deposition of C3b and iC3b onto particulate activators of the human complement system. Quantitation with monoclonal antibodies to human C3. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1414–1431. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel G. J., Mosser D. M., Edelson P. J. Role of complement in mouse macrophage binding of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):208–218. doi: 10.1172/JCI114414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The relative importance of blood monocytes and fixed macrophages to the expression of cell-mediated immunity to infection. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):521–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Sharon N. Lectinophagocytosis: a molecular mechanism of recognition between cell surface sugars and lectins in the phagocytosis of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):539–547. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.539-547.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara J., Paul W. E. Production of a monoclonal antibody to and molecular characterization of B-cell stimulatory factor-1. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):333–336. doi: 10.1038/315333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Legionella pneumophila is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Gordon S. Monoclonal antibody to the murine type 3 complement receptor inhibits adhesion of myelomonocytic cells in vitro and inflammatory cell recruitment in vivo. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1685–1701. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Law S. K. The leukocyte cell surface receptor(s) for the iC3b product of complement. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;153:99–122. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74977-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Cain J. A., Lachmann P. J. Membrane complement receptor type three (CR3) has lectin-like properties analogous to bovine conglutinin as functions as a receptor for zymosan and rabbit erythrocytes as well as a receptor for iC3b. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3307–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Newman S. L., Lambris J. D., Devery-Pocius J. E., Cain J. A., Lachmann P. J. Generation of three different fragments of bound C3 with purified factor I or serum. II. Location of binding sites in the C3 fragments for factors B and H, complement receptors, and bovine conglutinin. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):334–352. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. C., Densen P. Complement deficiency states and infection: epidemiology, pathogenesis and consequences of neisserial and other infections in an immune deficiency. Medicine (Baltimore) 1984 Sep;63(5):243–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Complement receptor type three-dependent degradation of opsonized erythrocytes by mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2668–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Goodwin J. D., Vann J. M., Selvaraj M. P., Hart M. A. Role of C1q in phagocytosis of Salmonella minnesota by pulmonary endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1356–1362. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1356-1362.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger L. S., Bellinger-Kawahara C. G., Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors and complement component C3. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2771–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger L. S., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of leprosy bacilli is mediated by complement receptors CR1 and CR3 on human monocytes and complement component C3 in serum. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1304–1314. doi: 10.1172/JCI114568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P. P., Gervais F., Skamene E., Mortensen R. F. Serum amyloid P-component-induced enhancement of macrophage listericidal activity. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):688–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.688-694.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Gordon S. Expression of a mannosyl-fucosyl receptor for endocytosis on cultured primary macrophages and their hybrids. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):49–56. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. S., Unanue E. R. Antigen-presenting function of alveolar macrophages: uptake and presentation of Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):794–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Pearson R. D. Roles of CR3 and mannose receptors in the attachment and ingestion of Leishmania donovani by human mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):363–369. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.363-369.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Silverstein S. C. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters stimulate C3b and C3b' receptor-mediated phagocytosis in cultured human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1149–1164. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kessel K. P., Antonissen A. C., van Dijk H., Rademaker P. M., Willers J. M. Interactions of killed Listeria monocytogenes with the mouse complement system. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):16–19. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.16-19.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


