Abstract
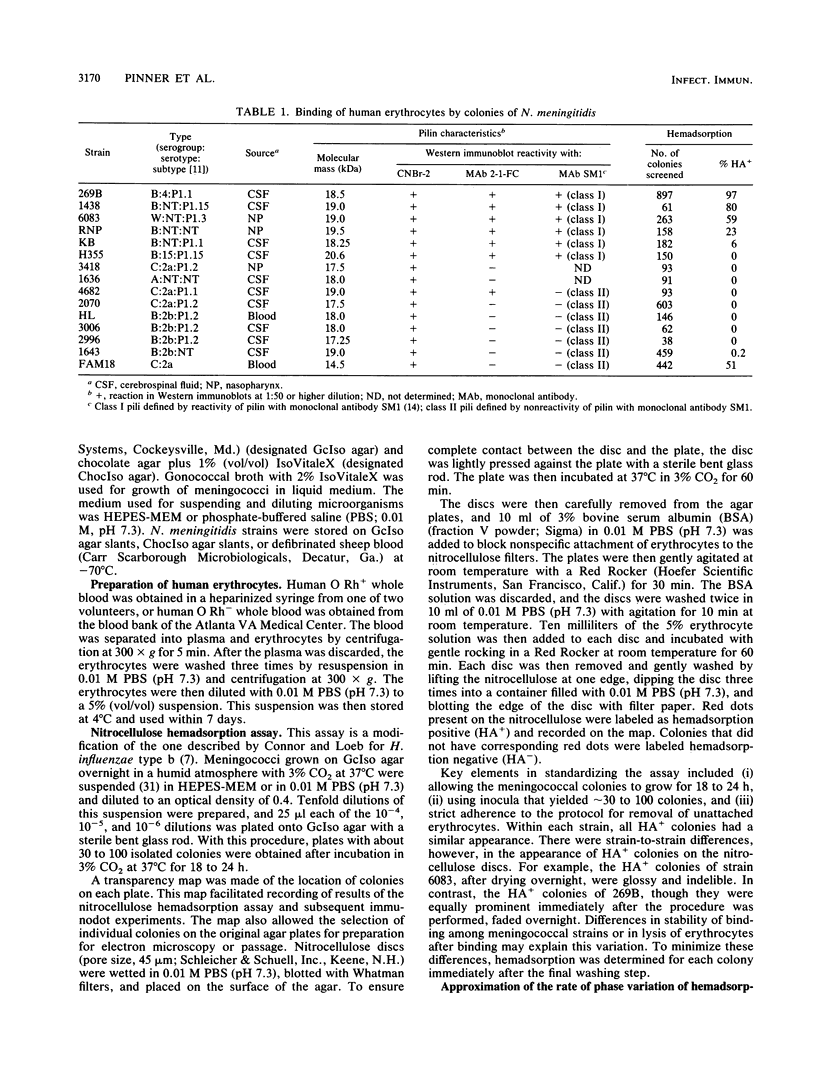
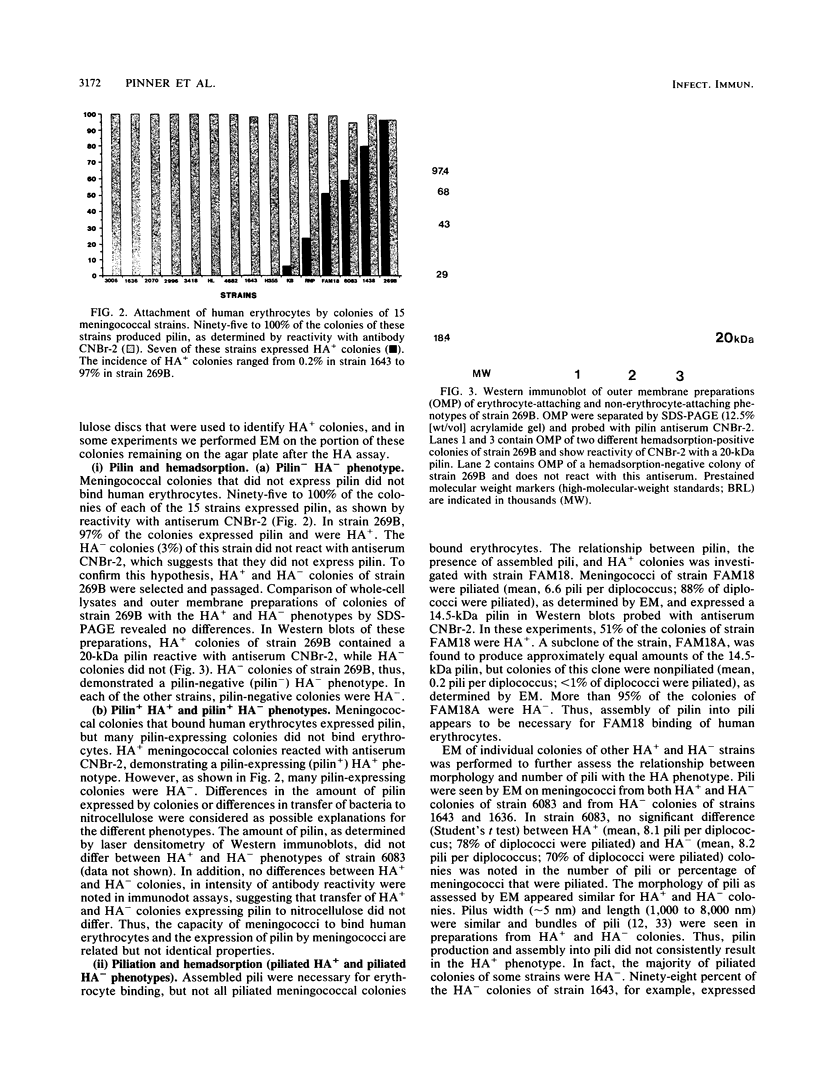
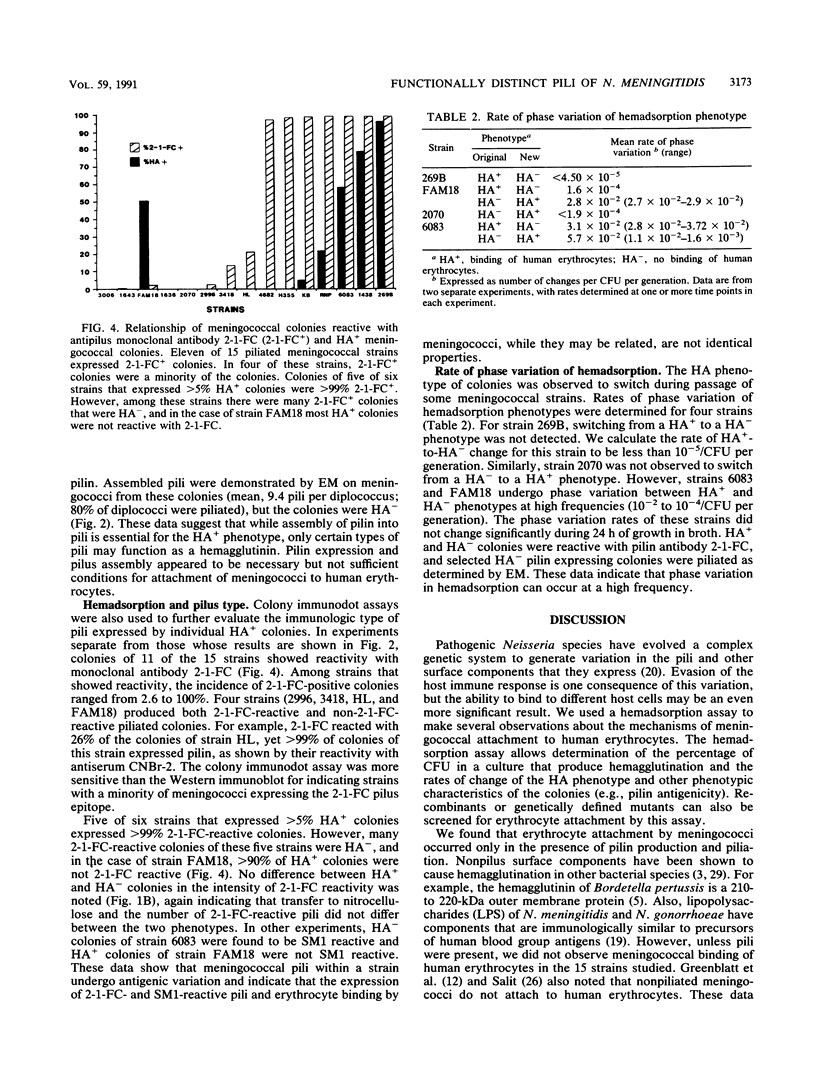
In order to investigate possible functional consequences of phase and antigenic variation of meningococci, the attachment of 15 strains of Neisseria meningitidis to human erythrocytes was studied by a nitrocellulose hemadsorption assay. This assay allows the study of individual meningococcal colonies with respect to erythrocyte attachment. Of the 15 strains studied, 7 demonstrated binding of human erythrocytes (HA+). Among these seven strains, the percentage of colonies that were HA+ ranged from 0.2 to 97%. Meningococcal colonies that did not produce pilin (the major structural subunit of pili) did not demonstrate erythrocyte binding (HA-). The HA+ colony phenotype was correlated with assembly of pilin into pili and expression of pili on the meningococcal surface. However, only some piliated colonies bound human erythrocytes. This could not be explained by differences between piliated HA+ and HA- colonies in the amount of pilin produced or by differences in number of pili expressed per diplococcus. Pili of five of the meningococcal strains with HA+ colonies were antigenically related to gonococcal pili (class I meningococcal pili), but HA+ colonies were also seen in two meningococcal strains expressing class II meningococcal pili. Changes from HA+ to HA- and from HA- to HA+, in the presence of continuing pilin production and pilus assembly, occurred at frequencies of up to 10(-2)/CFU per generation. Such frequencies resemble those of phase and antigenic variation described previously for Neisseria species pilin. These studies indicate that phase variation influences the ability of meningococci to attach to human cells and suggest that meningococci may express functionally different pili.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho E. L., Cannon J. G. Characterization of a silent pilin gene locus from Neisseria meningitidis strain FAM18. Microb Pathog. 1988 Nov;5(5):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Robbins K., Koomey J. M., Swanson J. Piliation control mechanisms in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3890–3894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. R., Parker C. D. Cloning of the filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis and its expression in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):154–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.154-161.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Pearce W. A. Pili as a mediator of the attachment of gonococci to human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1483–1489. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1483-1489.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor E. M., Loeb M. R. A hemadsorption method for detection of colonies of Haemophilus influenzae type b expressing fimbriae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Nov;148(5):855–860. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.5.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. Phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli is under transcriptional control. Science. 1981 Oct 16;214(4518):337–339. doi: 10.1126/science.6116279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto M., Stocker B. A. Integration, at hag or elsewhere, of H2 (phase-2 flagellin) genes transduced from Salmonella to Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1975 Dec;81(4):595–614. doi: 10.1093/genetics/81.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Zollinger W. D., Poolman J. T. Serotype antigens of Neisseria meningitidis and a proposed scheme for designation of serotypes. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):504–510. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. J., Floyd K., Philipps M. E., Frasch C. E. Morphological differences in Neisseria meningitidis pili. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2356–2362. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2356-2362.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagblom P., Segal E., Billyard E., So M. Intragenic recombination leads to pilus antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):156–158. doi: 10.1038/315156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. Structure and function of pili of pathogenic Neisseria species. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S66–S73. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Doig P., Lee K. K., Sastry P. A., Paranchych W., Todd T., Hodges R. S. Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilus adhesin: confirmation that the pilin structural protein subunit contains a human epithelial cell-binding domain. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3720–3726. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3720-3726.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koransky J. R., Scales R. W., Kraus S. J. Bacterial hemagglutination by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):495–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.495-498.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lund B., Johansson L., Normark S. Localization of the receptor-binding protein adhesin at the tip of the bacterial pilus. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):84–87. doi: 10.1038/328084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B., Lindberg F., Normark S. Structure and antigenic properties of the tip-located P pilus proteins of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1887–1894. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1887-1894.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M., Macher B. A. Lipooligosaccharides (LOS) of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis have components that are immunochemically similar to precursors of human blood group antigens. Carbohydrate sequence specificity of the mouse monoclonal antibodies that recognize crossreacting antigens on LOS and human erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):107–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Street C. H., Chappell C. L., Cousar E. S., Morris F., Horn R. G. Pili of Neisseria meningitidis: effect of media on maintenance of piliation, characteristics of Pili, and colonial morphology. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):194–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.194-201.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Gibbs C. P., Haas R. Variation and control of protein expression in Neisseria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:451–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minion F. C., Abraham S. N., Beachey E. H., Goguen J. D. The genetic determinant of adhesive function in type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli is distinct from the gene encoding the fimbrial subunit. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):1033–1036. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.1033-1036.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren M., Normark S., Lark D., O'Hanley P., Schoolnik G., Falkow S., Svanborg-Edén C., Båga M., Uhlin B. E. Mutations in E coli cistrons affecting adhesion to human cells do not abolish Pap pili fiber formation. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01945.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Sharon N. Lectinophagocytosis: a molecular mechanism of recognition between cell surface sugars and lectins in the phagocytosis of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):539–547. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.539-547.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Organization and expression of genes responsible for type 1 piliation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):736–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.736-744.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E. Hemagglutination by Neisseria meningitidis. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jun;27(6):586–593. doi: 10.1139/m81-089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Morton G. Adherence of Neisseria meningitidis to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):430–435. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.430-435.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Hoffman L. H., McGee Z. A. Interaction of Neisseria meningitidis with human nasopharyngeal mucosa: attachment and entry into columnar epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):369–376. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., McGee Z. A. Attachment of Neisseria meningitidis to human mucosal surfaces: influence of pili and type of receptor cell. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):525–532. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Whitney A. M., Rothbard J., Schoolnik G. K. Pili of Neisseria meningitidis. Analysis of structure and investigation of structural and antigenic relationships to gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1539–1553. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Whitney A. M., Schoolnik G. K., Zollinger W. D. Common epitopes of pilin of Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):332–342. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinsley C. R., Heckels J. E. Variation in the expression of pili and outer membrane protein by Neisseria meningitidis during the course of meningococcal infection. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Sep;132(9):2483–2490. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-9-2483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J., Gillespie R. M., Bhatti A. R., White L. A. Differences in the adhesive properties of Neisseria meningitidis for human buccal epithelial cells and erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.106-113.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitkins S. A. Fimbrial haemagglutination by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Aug;50(4):272–278. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.4.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




