Abstract
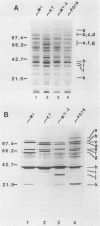
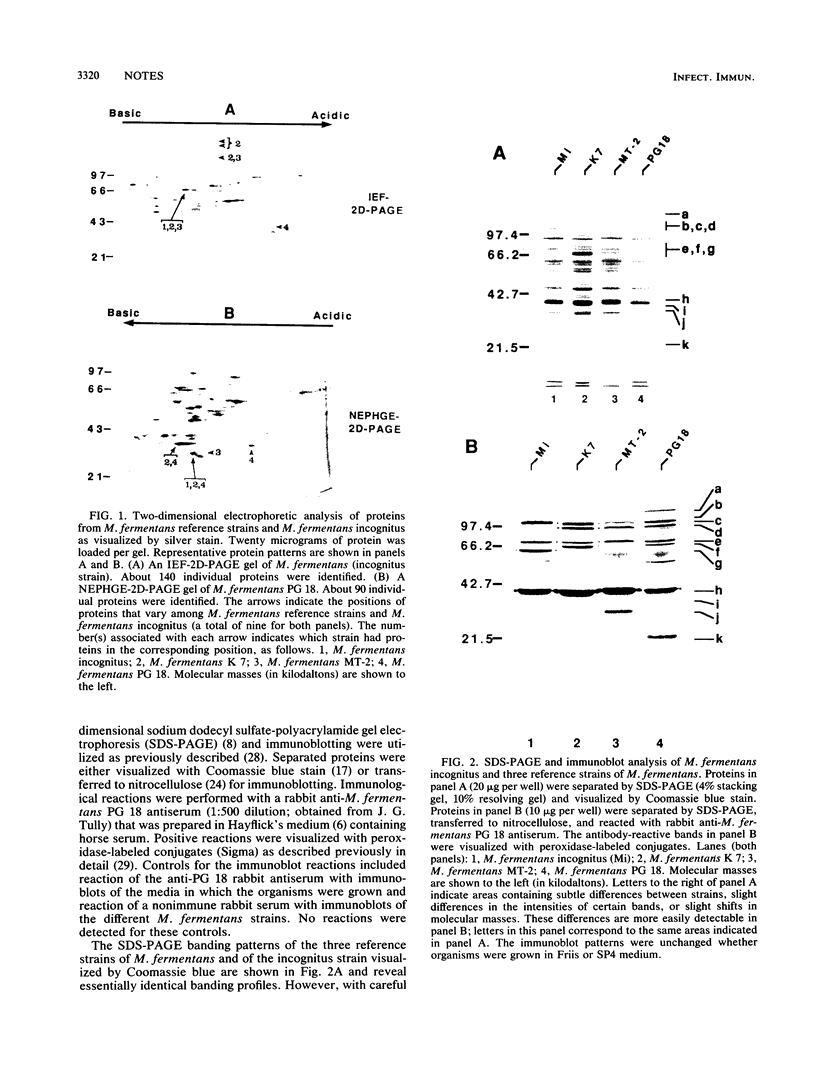
The proteins and antigens of three strains of Mycoplasma fermentans were compared with those of a mycoplasma, designated "Mycoplasma incognitus," recently identified in tissues of AIDS patients. Previous studies have shown that "M. incognitus" is most likely not a new species but rather a strain of M. fermentans. In the present study, one- and two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis demonstrated the expected similarity between these mycoplasmas, but it also demonstrated several distinct protein differences. Nine proteins were identified as strain variable by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Also, immunoblot analysis using rabbit antiserum against the type strain of M. fermentans (strain PG 18) documented the occurrence of size heterogeneity in at least one and possibly two other antigens.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer F. A., Wear D. J., Angritt P., Lo S. C. Mycoplasma fermentans (incognitus strain) infection in the kidneys of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and associated nephropathy: a light microscopic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study. Hum Pathol. 1991 Jan;22(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(91)90063-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Cole B. C. Mycoplasmas as agents of human disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 8;304(2):80–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101083040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dybvig K., Alderete J., Watson H. L., Cassell G. H. Adsorption of mycoplasma virus P1 to host cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4373–4375. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4373-4375.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis N. F. Some recommendations concerning primary isolation of Mycoplasma suipneumoniae and Mycoplasma flocculare a survey. Nord Vet Med. 1975 Jun;27(6):337–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhoff H., Heitmann J., Ammar A., Hermanns W., Schulz L. C. Studies of polyarthritis caused by Mycoplasma arthritidis in rats. I. Detection of the persisting Mycoplasma antigen by the enzyme immune assay (EIA) and conventional culture technique. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Mar;254(1):129–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Dawson M. S., Newton P. B., 3rd, Sonoda M. A., Shih J. W., Engler W. F., Wang R. Y., Wear D. J. Association of the virus-like infectious agent originally reported in patients with AIDS with acute fatal disease in previously healthy non-AIDS patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Sep;41(3):364–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Dawson M. S., Wong D. M., Newton P. B., 3rd, Sonoda M. A., Engler W. F., Wang R. Y., Shih J. W., Alter H. J., Wear D. J. Identification of Mycoplasma incognitus infection in patients with AIDS: an immunohistochemical, in situ hybridization and ultrastructural study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Nov;41(5):601–616. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.41.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C. Isolation and identification of a novel virus from patients with AIDS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jul;35(4):675–676. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Shih J. W., Newton P. B., 3rd, Wong D. M., Hayes M. M., Benish J. R., Wear D. J., Wang R. Y. Virus-like infectious agent (VLIA) is a novel pathogenic mycoplasma: Mycoplasma incognitus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Nov;41(5):586–600. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.41.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Shih J. W., Yang N. Y., Ou C. Y., Wang R. Y. A novel virus-like infectious agent in patients with AIDS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Feb;40(2):213–226. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Wang R. Y., Newton P. B., 3rd, Yang N. Y., Sonoda M. A., Shih J. W. Fatal infection of silvered leaf monkeys with a virus-like infectious agent (VLIA) derived from a patient with AIDS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Apr;40(4):399–409. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Dunau M. L., Goldman D. A rapid sensitive silver stain for polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUITER M., WENTHOLT H. M. M. A pleuropneumonia-like organism in primary fusospirochetal gangrene of the penis. J Invest Dermatol. 1950 Oct;15(4):301–304. doi: 10.1038/jid.1950.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengarten R., Wise K. S. Phenotypic switching in mycoplasmas: phase variation of diverse surface lipoproteins. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):315–318. doi: 10.1126/science.1688663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saillard C., Carle P., Bové J. M., Bébéar C., Lo S. C., Shih J. W., Wang R. Y., Rose D. L., Tully J. G. Genetic and serologic relatedness between Mycoplasma fermentans strains and a mycoplasma recently identified in tissues of AIDS and non-AIDS patients. Res Virol. 1990 May-Jun;141(3):385–395. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(90)90010-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A colour test for the measurement of antibody to certain mycoplasma species based upon the inhibition of acid production. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Mar;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G. New laboratory techniques for isolation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):511–515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. L., Davidson M. K., Cox N. R., Davis J. K., Dybvig K., Cassell G. H. Protein variability among strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2838–2840. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2838-2840.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. L., Dybvig K., Blalock D. K., Cassell G. H. Subunit structure of the variable V-1 antigen of Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1684–1690. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1684-1690.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. L., McDaniel L. S., Blalock D. K., Fallon M. T., Cassell G. H. Heterogeneity among strains and a high rate of variation within strains of a major surface antigen of Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1358–1363. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1358-1363.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]