Abstract
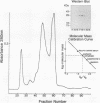
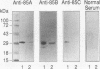
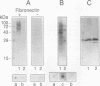
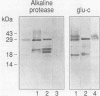
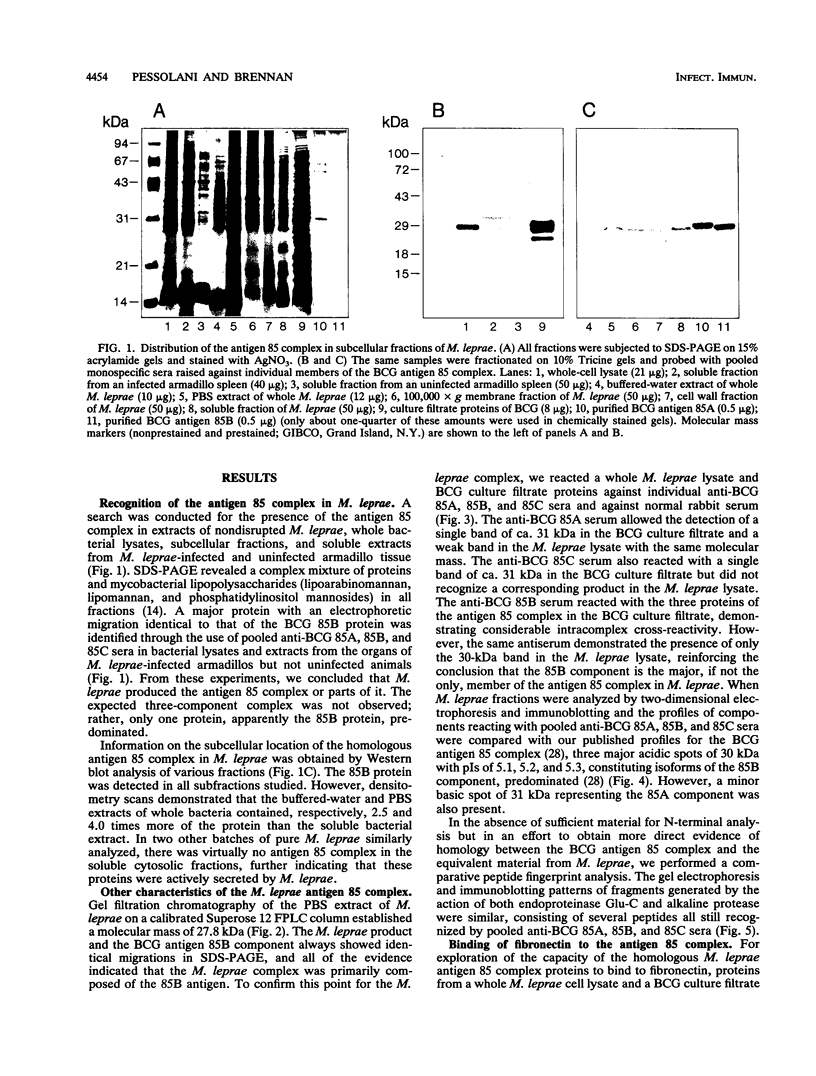
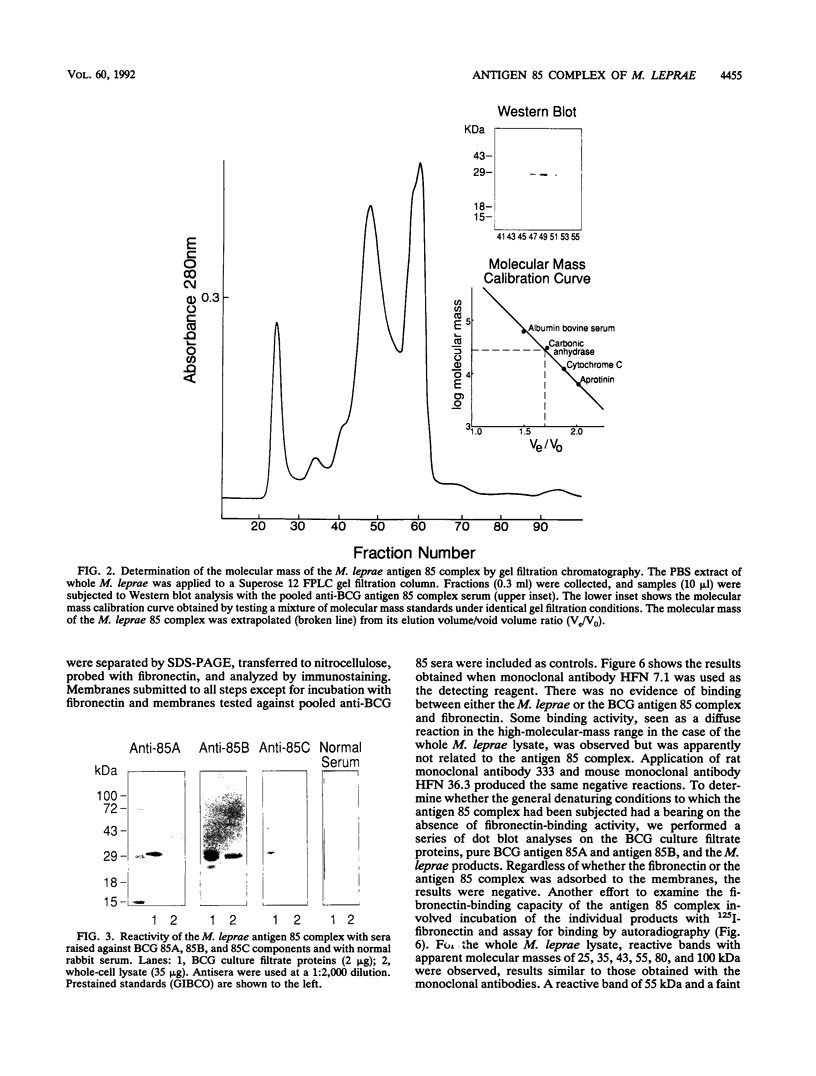
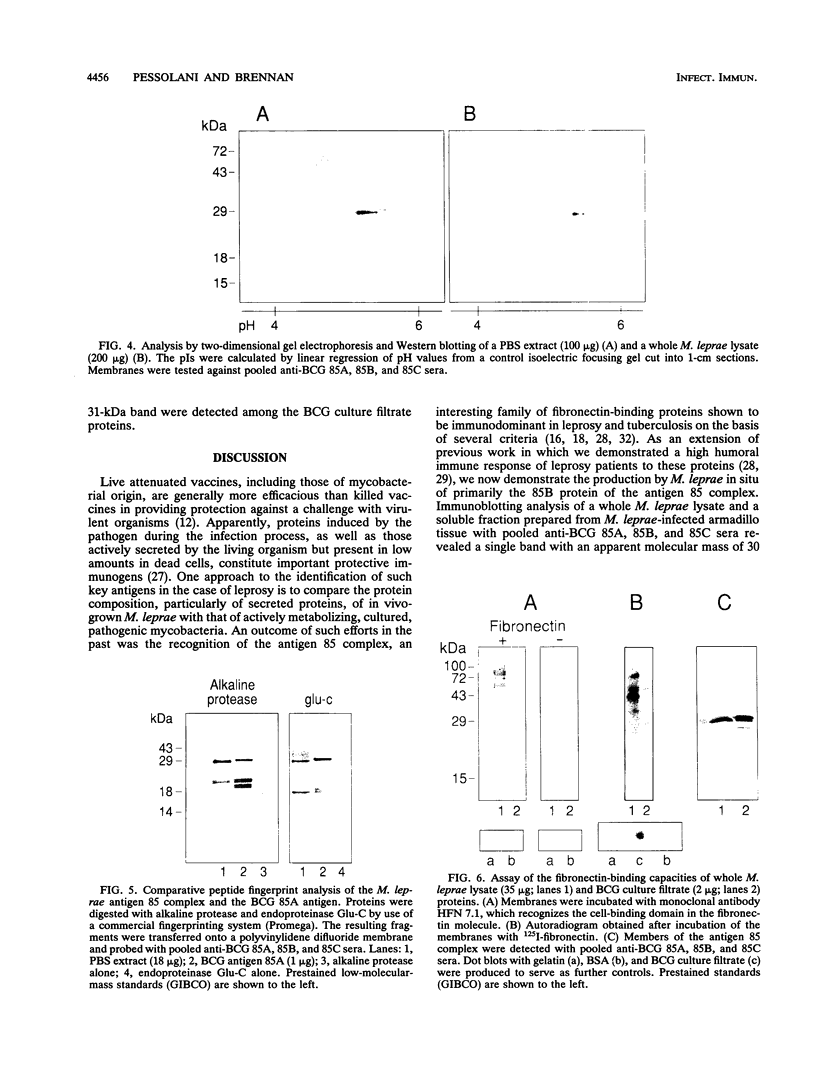
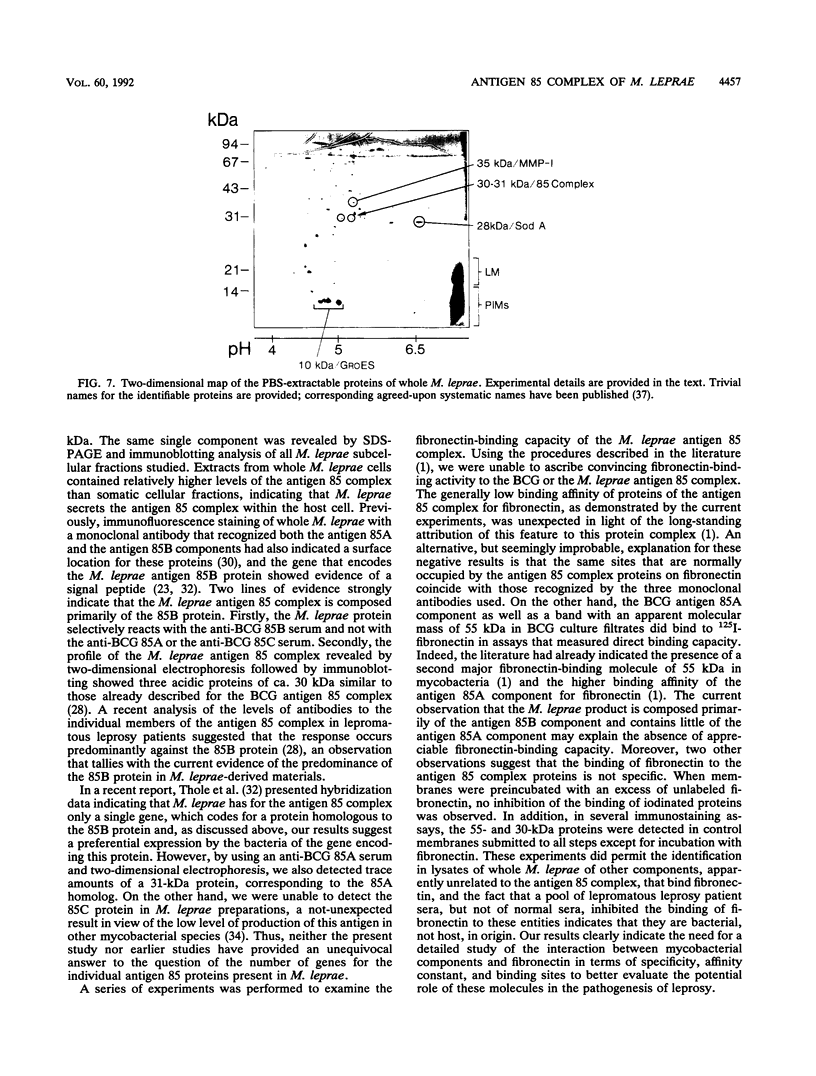
The antigen 85 complex is a set of at least three closely related secreted proteins (85A, 85B, and 85C) of 30 to 32 kDa produced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacteria. Their prominence in Mycobacterium leprae, the one obligate intracellular pathogen of the genus, had been assumed on the basis of immunological evidence and proof of the existence of the gene encoding the 85B protein of the complex. We have now observed the production of this family of proteins by M. leprae through analysis of various fractions by Western blotting (immunoblotting) with monospecific rabbit antisera raised against the individual Mycobacterium bovis BCG 85A, 85B, and 85C proteins. A predominant cross-reactive band with an apparent molecular mass of 30 kDa was detected in extracts of nondisrupted whole M. leprae and in soluble fractions prepared from the tissues of M. leprae-infected armadillos. Further studies of the subcellular distribution of this protein within the bacterium confirmed that it is secreted by the organism, an observation that explains past difficulties in detecting the antigen 85 complex in M. leprae. Confirmation that the M. leprae product is a member of the antigen 85 complex was obtained by comparison of peptide fingerprints with those from the BCG product. The pattern of reactivity of the M. leprae antigen 85 complex with anti-M. bovis BCG 85B serum, as well as two-dimensional electrophoresis, established that the 85B component was the predominant member of the complex in M. leprae. The fibronectin-binding capacity of the M. leprae and BCG 85 complexes was reinvestigated by new approaches and is questioned. Nevertheless, the results obtained with the native proteins reinforce previous reports, derived primarily from the use of homologous proteins, that the antigen 85 complex is one of the dominant protein immunogens of the leprosy bacillus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zeid C., Ratliff T. L., Wiker H. G., Harboe M., Bennedsen J., Rook G. A. Characterization of fibronectin-binding antigens released by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3046–3051. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3046-3051.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama S. K., Hasegawa E., Hasegawa T., Yamada K. M. The interaction of fibronectin fragments with fibroblastic cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13256–13260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borremans M., de Wit L., Volckaert G., Ooms J., de Bruyn J., Huygen K., van Vooren J. P., Stelandre M., Verhofstadt R., Content J. Cloning, sequence determination, and expression of a 32-kilodalton-protein gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3123–3130. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3123-3130.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs O., Harboe M., Axelsen N. H., Bunch-Christensen K., Magnusson M. The antigens of Mycobacterium bovis, strain BCG, studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: a reference system. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(3):249–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., de la Cuvellerie A., De Wit L., Vincent-Levy-Frébault V., Ooms J., De Bruyn J. The genes coding for the antigen 85 complexes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG are members of a gene family: cloning, sequence determination, and genomic organization of the gene coding for antigen 85-C of M. tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3205–3212. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3205-3212.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. M., Ferguson L. E. Purification and Characterization of Two Proteins from Culture Filtrates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H(37)Ra Strain. Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):164–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.164-168.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das P. K., Rambukkana A., Baas J. G., Groothuis D. G., Halperin M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for distinguishing serological responses of lepromatous and tuberculoid leprosies to the 29/33-kilodalton doublet and 64-kilodalton antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):379–382. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.379-382.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wit L., de la Cuvellerie A., Ooms J., Content J. Nucleotide sequence of the 32 kDa-protein gene (antigen 85 A) of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3995–3995. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drowart A., Launois P., De Cock M., Huygen K., De Bruyn J., Yernault J. C., Van Vooren J. P. An isoelectric focusing method for the study of the humoral response against the antigen 85 complex of Mycobacterium bovis BCG in the different forms of leprosy. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Dec 15;145(1-2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90330-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R. Immunity in experimental salmonellosis. 3. Comparative immunization with viable and heat-inactivated cells of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):792–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.792-797.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Fujiwara T., Brennan P. J. Structure and antigenicity of the major specific glycolipid antigen of Mycobacterium leprae. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15072–15078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Rivoire B., Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Brennan P. J. The major native proteins of the leprosy bacillus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14065–14068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huygen K., Van Vooren J. P., Turneer M., Bosmans R., Dierckx P., De Bruyn J. Specific lymphoproliferation, gamma interferon production, and serum immunoglobulin G directed against a purified 32 kDa mycobacterial protein antigen (P32) in patients with active tuberculosis. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Feb;27(2):187–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Launois P., Huygen K., De Bruyn J., N'Diaye M., Diouf B., Sarthouj L., Grimaud J., Millan J. T cell response to purified filtrate antigen 85 from Mycobacterium bovis Bacilli Calmette-Guérin (BCG) in leprosy patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Nov;86(2):286–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima L. de M., Content J., van Heuverswyn H., Degrave W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the 85-B antigen of Mycobacterium leprae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5789–5789. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo K., Yamaguchi R., Yamazaki A., Tasaka H., Terasaka K., Yamada T. Cloning and expression of the gene for the cross-reactive alpha antigen of Mycobacterium kansasii. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.550-556.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo K., Yamaguchi R., Yamazaki A., Tasaka H., Yamada T. Cloning and expression of the Mycobacterium bovis BCG gene for extracellular alpha antigen. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3847–3854. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3847-3854.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Bajardi A. C., Grisso C. L., Sieling P. A., Alland D., Convit J., Fan X. D., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. A major T cell antigen of Mycobacterium leprae is a 10-kD heat-shock cognate protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):275–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. J., Styblo K., Rouillon A. Tuberculosis in developing countries: burden, intervention and cost. Bull Int Union Tuberc Lung Dis. 1990 Mar;65(1):6–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordeen S. K., Lopez Bravo L., Sundaresan T. K. Estimated number of leprosy cases in the world. Bull World Health Organ. 1992;70(1):7–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Miller E. S., Roberts A. D., Furney S. K., Griffin J. P., Dobos K. M., Chi D., Rivoire B., Brennan P. J. T lymphocytes mediating protection and cellular cytolysis during the course of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Evidence for different kinetics and recognition of a wide spectrum of protein antigens. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessolani M. C., Peralta J. M., Rumjanek F. D., Gomes H. M., Marques M. A., Almeida E. C., Saad M. H., Sarno E. N. Serology and leprosy: immunoassays comparing immunoglobulin G antibody responses to 28- and 30-kilodalton proteins purified from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2285–2290. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2285-2290.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambukkana A., Das P. K., Chand A., Baas J. G., Groothuis D. G., Kolk A. H. Subcellular distribution of monoclonal antibody defined epitopes on immunodominant Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins in the 30-kDa region: identification and localization of 29/33-kDa doublet proteins on mycobacterial cell wall. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Jun;33(6):763–775. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb02551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Schöningh R., Janson A. A., Garbe T., Cornelisse Y. E., Clark-Curtiss J. E., Kolk A. H., Ottenhoff T. H., De Vries R. R., Abou-Zeid C. Molecular and immunological analysis of a fibronectin-binding protein antigen secreted by Mycobacterium leprae. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(2):153–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiker H. G., Harboe M., Lea T. E. Purification and characterization of two protein antigens from the heterogeneous BCG85 complex in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;81(4):298–306. doi: 10.1159/000234153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiker H. G., Harboe M., Nagai S., Patarroyo M. E., Ramirez C., Cruz N. MPB59, a widely cross-reacting protein of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;81(4):307–314. doi: 10.1159/000234154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiker H. G., Sletten K., Nagai S., Harboe M. Evidence for three separate genes encoding the proteins of the mycobacterial antigen 85 complex. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):272–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.272-274.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Kaufmann S. H., Hermans P. W., Thole J. E. Mycobacterial protein antigens: a compilation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(2):133–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]