Abstract
The major pathogen implicated in footrot, a highly contagious disease of sheep, is the strict anaerobe Dichelobacter nodosus (formerly Bacteroides nodosus). Sequence analysis of a 2,262-bp segment of the D. nodosus genome which is more prevalent in virulent isolates than in other isolates showed the presence of four open reading frames which appeared to have consensus transcriptional and translational start signals. These virulence-associated genes have been designated vapABCD. Two of the three copies of the vap region in the genome of the reference strain D. nodosus A198 were shown to carry all of the vap genes, whereas one copy contained only the vapD gene. The VapD protein was gel purified, shown to contain the predicted amino-terminal sequence, and used to raise rabbit antibodies. Western blots (immunoblots) showed that all of the D. nodosus strains tested that contained the vap region produced the VapD protein. The VapD protein had significant amino acid sequence identity with open reading frame 5 from the cryptic plasmid of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and the vapBC operon had sequence similarity with the trbH region of the Escherichia coli F plasmid. It is proposed that these gene regions evolved from the integration of a conjugative plasmid from another bacterial species into the D. nodosus chromosome.
Full text
PDF



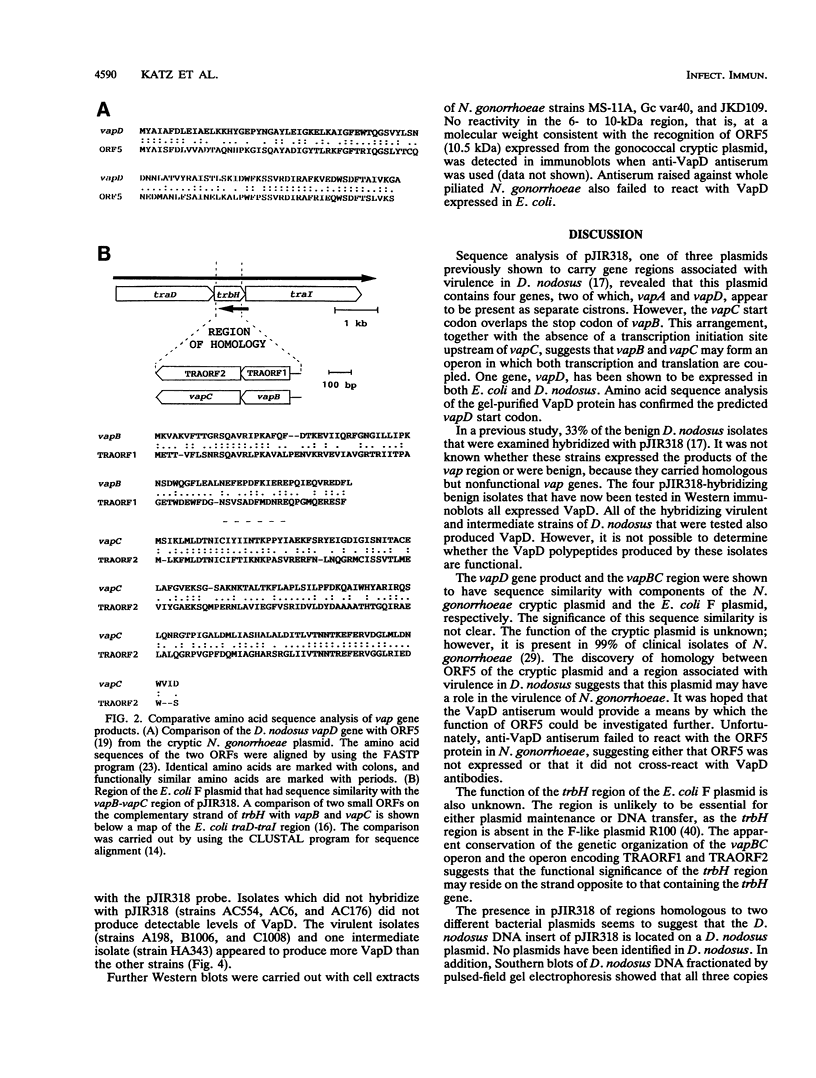


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. J., Bills M. M., Egerton J. R., Mattick J. S. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene encoding the structural subunit of Bacteroides nodosus fimbriae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):748–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.748-754.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey M. J., Cockayne A., Penn C. W. Monoclonal antibodies directed against surface-associated polypeptides of Treponema pallidum define a biologically active antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1793–1803. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Traxler B. A., Minkley E. G., Jr, Nester E. W., Gordon M. P. Nucleotide sequence of the traI (helicase I) gene from the sex factor F. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4127–4131. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4127-4131.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarco de Hormaeche R., Thornley M. J., Holmes A. Surface antigens of gonococci: correlation with virulence and serum resistance. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1559–1567. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depiazzi L. J., Richards R. B. A degrading proteinase test to distinguish benign and virulent ovine isolates of Bacteroides nodosus. Aust Vet J. 1979 Jan;55(1):25–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1979.tb09541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depiazzi L. J., Richards R. B., Henderson J., Rood J. I., Palmer M., Penhale W. J. Characterisation of virulent and benign strains of Bacteroides nodosus. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Jan;26(1-2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90051-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depiazzi L. J., Richards R. B. Motility in relation to virulence of Bacteroides nodosus. Vet Microbiol. 1985 Jan;10(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(85)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depiazzi L. J., Rood J. I. The thermostability of proteases from virulent and benign strains of Bacteroides nodosus. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Jul;9(3):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C. Pilins of Bacteroides nodosus: molecular basis of serotypic variation and relationships to other bacterial pilins. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):233–247. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.233-247.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Every D. Proteinase isoenzyme patterns of Bacteroides nodosus: distinction between ovine virulent isolates, ovine benign isolates and bovine isolates. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Apr;128(4):809–812. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-4-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. S. A method to differentiate between virulent and benign isolated of Bacteroides nodosus based on the thermal stability of their extracellular proteinases. N Z Vet J. 1985 Jan-Feb;33(1-2):11–13. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1985.35135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalajakumari M. B., Manning P. A. Nucleotide sequence of the traD region in the Escherichia coli F sex factor. Gene. 1989 Sep 30;81(2):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. E., Howarth P. M., Yong W. K., Riffkin G. G., Depiazzi L. J., Rood J. I. Identification of three gene regions associated with virulence in Dichelobacter nodosus, the causative agent of ovine footrot. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Sep;137(9):2117–2124. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-9-2117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korch C., Hagblom P., Ohman H., Göransson M., Normark S. Cryptic plasmid of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: complete nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):430–438. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.430-438.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortt A. A., Burns J. E., Stewart D. J. Detection of the extracellular proteases of Bacteroides nodosus in polyacrylamide gels: a rapid method of distinguishing virulent and benign ovine isolates. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Sep;35(2):171–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Morelli G., Fisseau C. RNA-polymerase binding sites within the tra region of the F factor of Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Mlawer N., So M. Pilus expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae involves chromosomal rearrangement. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Piot P., Falkow S. The ecology of gonococcal plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):491–494. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerman T. M. Determination of some in vitro growth requirements of Bacteroides nodosus. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Mar;87(1):107–119. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Peterson J. E., Vaughan J. A., Clark B. L., Emery D. L., Caldwell J. B., Kortt A. A. The pathogenicity and cultural characteristics of virulent, intermediate and benign strains of Bacteroides nodosus causing ovine foot-rot. Aust Vet J. 1986 Oct;63(10):317–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1986.tb02875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. The role of elastase in the differentiation of Bacteroides nodosus infections in sheep and cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Jul;27(1):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka Y., Fujita Y., Ohtsubo E. Nucleotide sequence of the promoter-distal region of the tra operon of plasmid R100, including traI (DNA helicase I) and traD genes. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):39–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90145-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




