Abstract
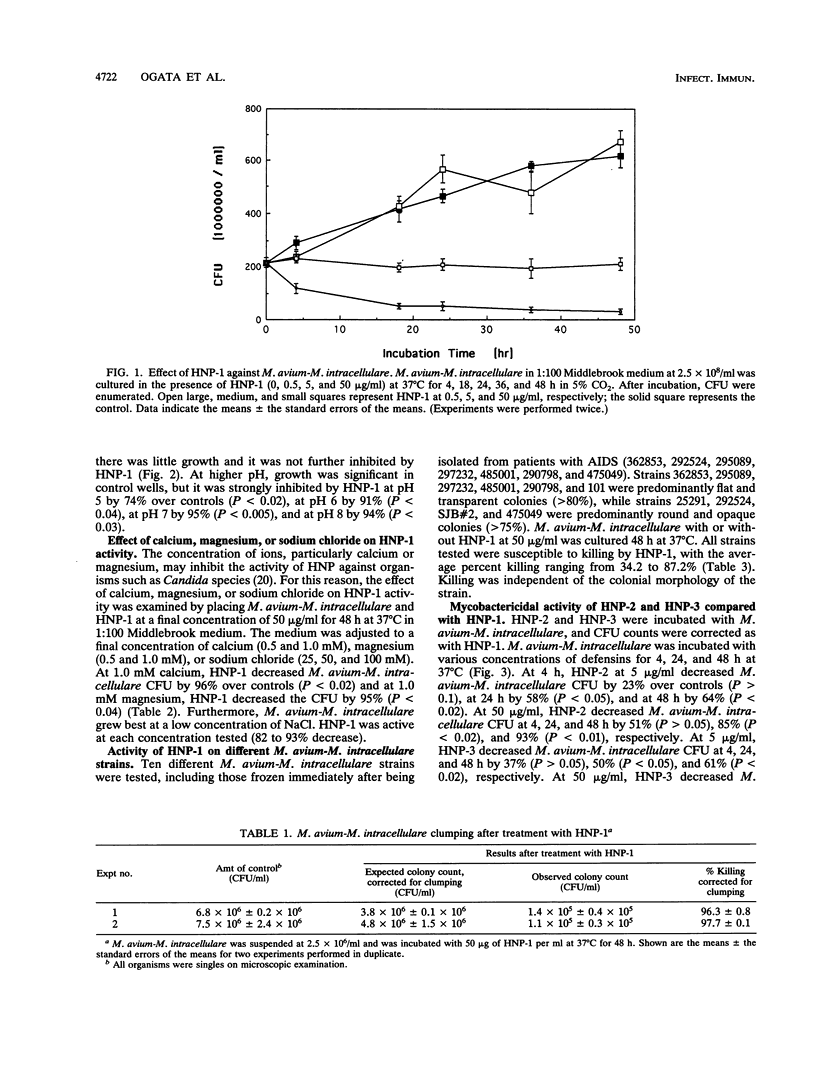
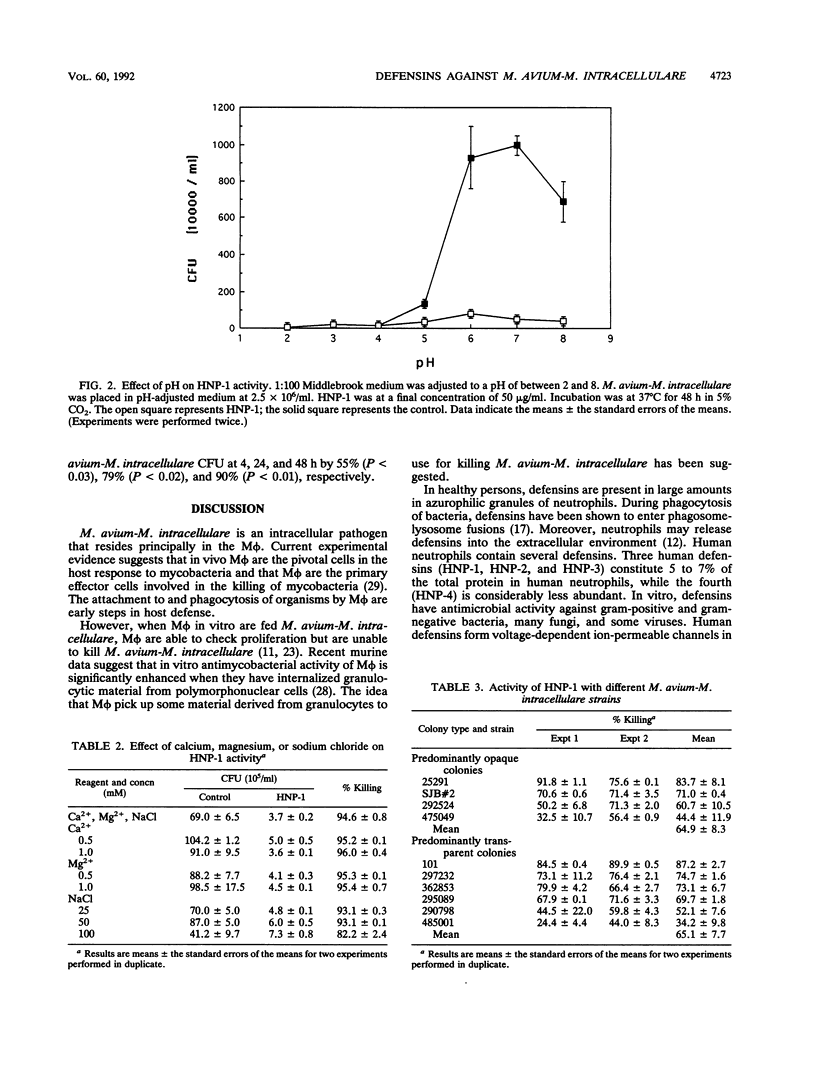
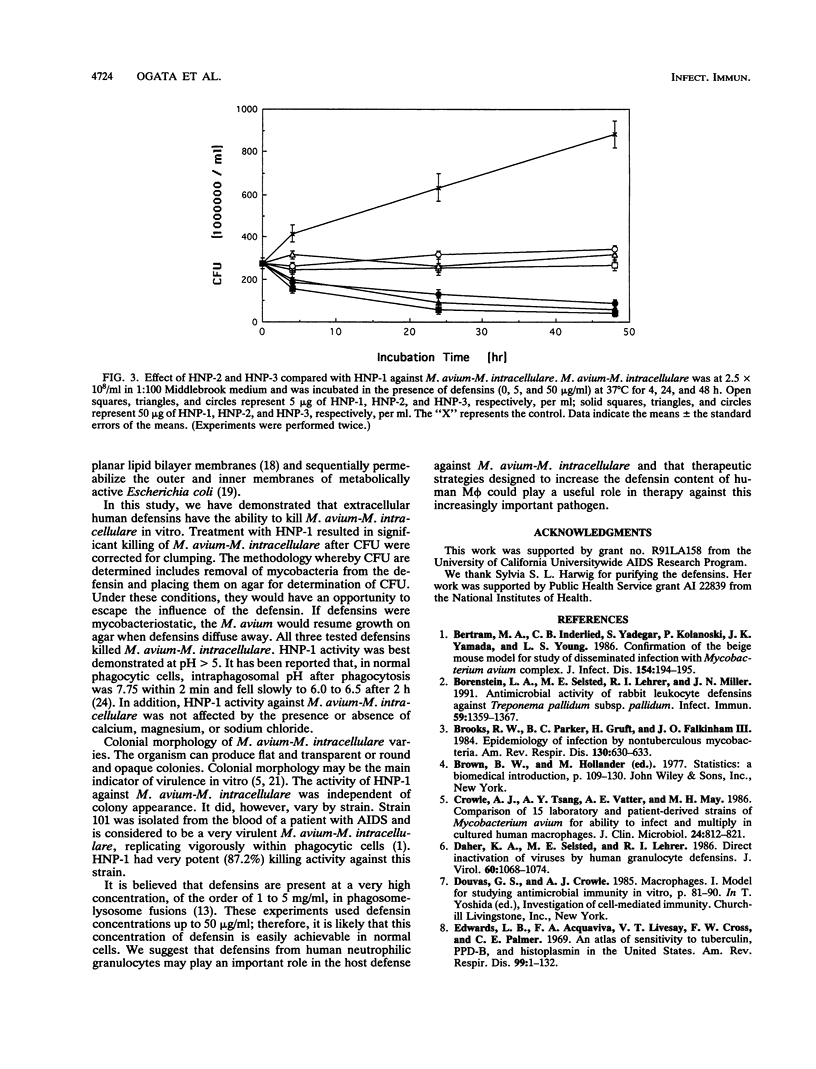
We have examined the activity of defensins from human neutrophilic granulocytes against Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare. M. avium-M. intracellulare at 2.5 x 10(6)/ml or 2.5 x 10(8)/ml was cultured in the presence of defensins at 37 degrees C from 4 to 48 h. After incubation, CFU were enumerated. Human neutrophil peptide 1 (HNP-1) at 5 micrograms/ml had the ability to kill M. avium-M. intracellulare. Treatment with HNP-1 resulted in significant (96.3 to 97.7%) killing of M. avium-M. intracellulare, even after taking clumping into consideration. This activity was not affected by the presence of calcium (0.5 and 1.0 mM), magnesium (0.5 and 1.0 mM), or sodium chloride (25, 50, and 100 mM). The optimal pH for bactericidal activity was higher than 5. We tested numerous M. avium-M. intracellulare strains, and HNP-1 was successful in killing every strain, although the degree of killing varied among them (34.2 to 87.2%). Additionally, this activity was independent of colonial morphology. We also examined the activity of HNP-2 and HNP-3 against M. avium-M. intracellulare and found that they were as effective in killing M. avium-M. intracellulare as HNP-1 was. These observations suggest that defensins may play an important role in the host defense against M. avium-M. intracellulare.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertram M. A., Inderlied C. B., Yadegar S., Kolanoski P., Yamada J. K., Young L. S. Confirmation of the beige mouse model for study of disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium complex. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):194–195. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein L. A., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I., Miller J. N. Antimicrobial activity of rabbit leukocyte defensins against Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1359–1367. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1359-1367.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. W., Parker B. C., Gruft H., Falkinham J. O., 3rd Epidemiology of infection by nontuberculous mycobacteria. V. Numbers in eastern United States soils and correlation with soil characteristics. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):630–633. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Tsang A. Y., Vatter A. E., May M. H. Comparison of 15 laboratory and patient-derived strains of Mycobacterium avium for ability to infect and multiply in cultured human macrophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):812–821. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.812-821.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daher K. A., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Direct inactivation of viruses by human granulocyte defensins. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1068-1074.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diagnosis and treatment of disease caused by nontuberculous mycobacteria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Oct;142(4):940–953. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.4.940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards L. B., Acquaviva F. A., Livesay V. T., Cross F. W., Palmer C. E. An atlas of sensitivity to tuberculin, PPD-B, and histoplasmin in the United States. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Apr;99(4 Suppl):1–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhauer P. B., Harwig S. S., Szklarek D., Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antimicrobial properties of three defensins from rat neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2021–2027. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2021-2027.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner J. J., Goldberger M. J., Parenti D. M. Mycobacterium avium infection and AIDS: a therapeutic dilemma in rapid evolution. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1326–1335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangadharam P. R., Pratt P. F. In vitro response of murine alveolar and peritoneal macrophages to Mycobacterium intracellulare. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Dec;128(6):1044–1047. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.6.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T. Extracellular release of antimicrobial defensins by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):568–571. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.568-571.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Eur J Haematol. 1990 Jan;44(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1990.tb00339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goslee S., Wolinsky E. Water as a source of potentially pathogenic mycobacteria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Mar;113(3):287–292. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.3.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald G. I., Ganz T. Defensins mediate the microbicidal activity of human neutrophil granule extract against Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1365–1368. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1365-1368.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Ganz T., Albert J., Rotrosen D. The opsonizing ligand on Salmonella typhimurium influences incorporation of specific, but not azurophil, granule constituents into neutrophil phagosomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2771–2782. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Selsted M. E., Ganz T., Lehrer R. I. Antimicrobial defensin peptides form voltage-dependent ion-permeable channels in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Barton A., Daher K. A., Harwig S. S., Ganz T., Selsted M. E. Interaction of human defensins with Escherichia coli. Mechanism of bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):553–561. doi: 10.1172/JCI114198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Szklarek D., Selsted M. E. Modulation of the in vitro candidacidal activity of human neutrophil defensins by target cell metabolism and divalent cations. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1829–1835. doi: 10.1172/JCI113527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meylan P. R., Richman D. D., Kornbluth R. S. Characterization and growth in human macrophages of Mycobacterium avium complex strains isolated from the blood of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2564–2568. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2564-2568.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson-Delafield J., Martinez R. J., Lehrer R. I. Microbicidal cationic proteins in rabbit alveolar macrophages: a potential host defense mechanism. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):180–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.180-192.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S., Lane H. C., Witebsky F. G., Gosey L. L., Hoggan M. D., Fauci A. S. Host defense against Mycobacterium-avium complex. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Jul;8(4):234–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00916551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Geisow M., Garcia R., Harper A., Miller R. The respiratory burst of phagocytic cells is associated with a rise in vacuolar pH. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):406–409. doi: 10.1038/290406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal G. P., Lehrer R. I., Selsted M. E. In vitro effect of phagocyte cationic peptides on Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):890–894. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S. Purification, primary structure, and antimicrobial activities of a guinea pig neutrophil defensin. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2281–2286. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2281-2286.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antibacterial activity of antimicrobial peptides of rabbit granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):150–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.150-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Silva M. N., Appelberg R. Neutrophil-macrophage cooperation in the host defence against mycobacterial infections. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes R. W., Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Role of mononuclear phagocytes in expression of resistance and susceptibility to Mycobacterium avium infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.811-819.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Mycobacterium avium complex infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):863–867. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


