Abstract
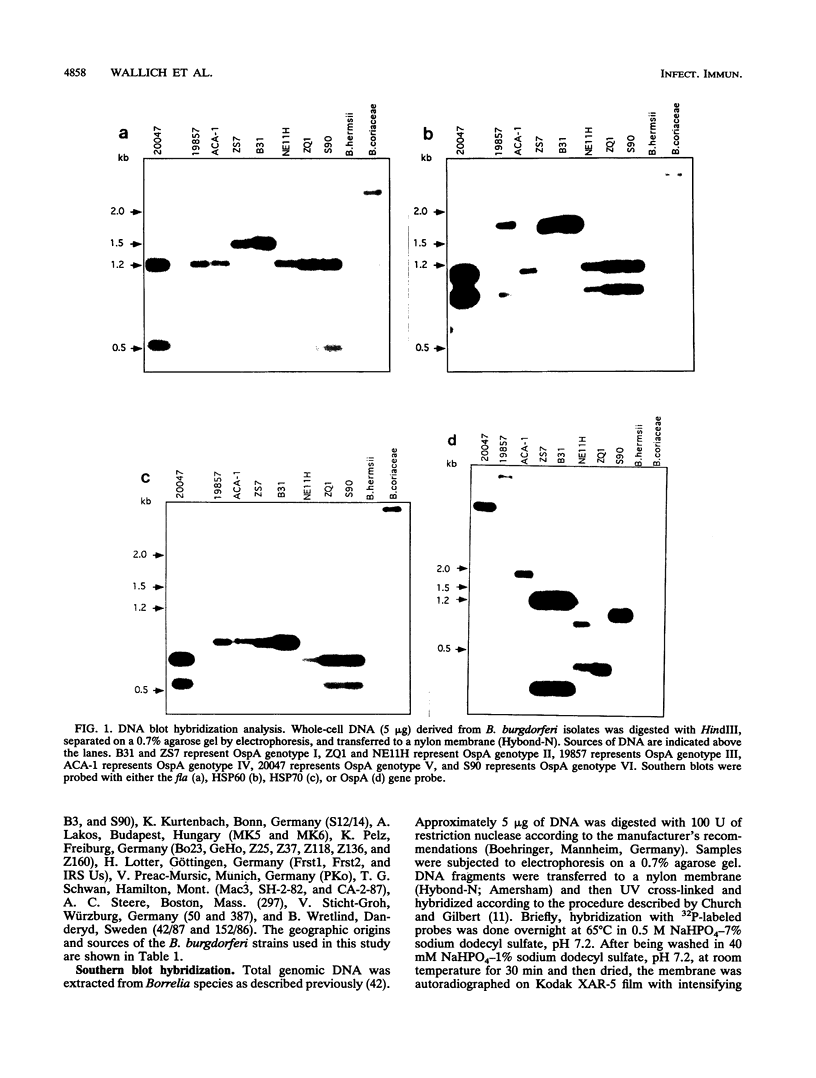
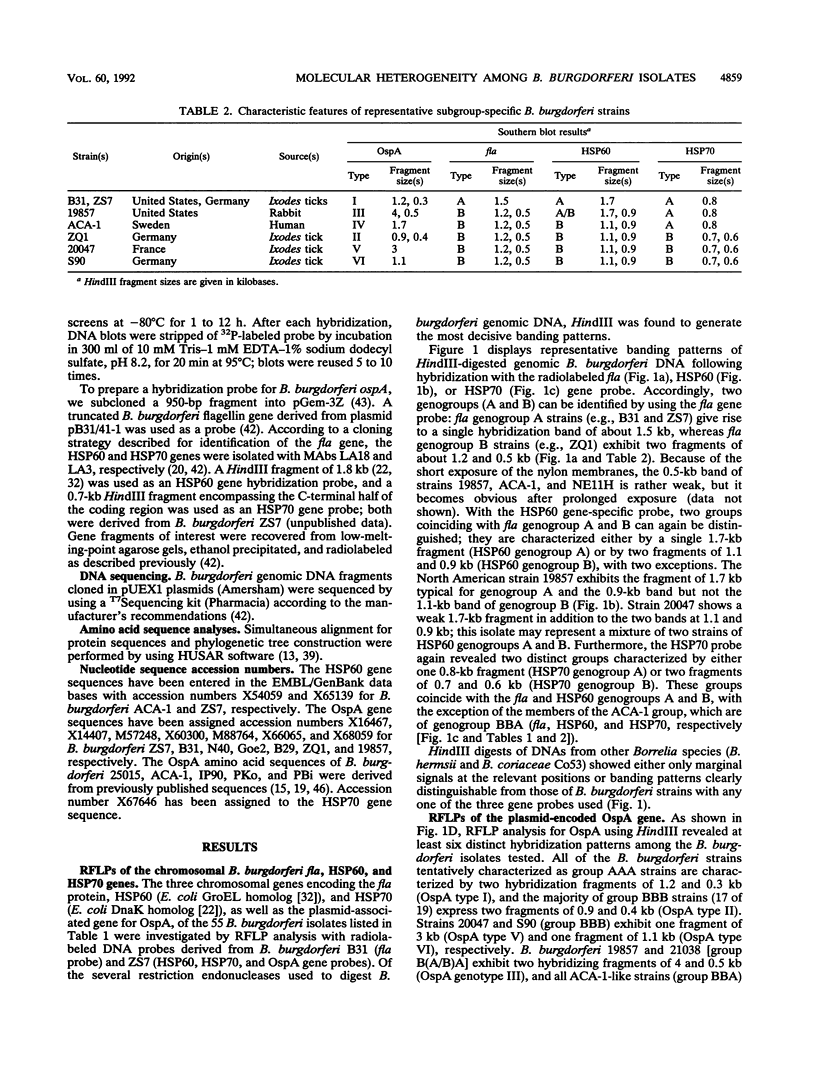
In order to assess the genetic variation of immunologically relevant structures among isolates of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, three chromosomal genes encoding flagellin (fla) and the heat shock proteins HSP60 and HSP70, as well as the plasmid gene encoding outer surface protein A (OspA), from 55 different European and North American strains obtained from ticks and mammal hosts have been investigated by restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). RFLPs of fla and the HSP60 and HSP70 genes revealed two distinct banding patterns (A and B) for each of the three genes and allowed the definition of four genomic groups [AAA, BBB, BBA, and B(A/B)A] for the three chromosomal genes. On the other hand, RFLPs of the OspA gene revealed six distinct banding patterns (types I to VI) making up six independent genomic groups for the plasmid-encoded gene. Furthermore, we have sequenced the chromosomal HSP60 gene from B. burgdorferi ZS7 and the plasmid-encoded OspA gene from two strains, ZQ1 and 19857. Alignment of the deduced HSP60 amino acid sequence from B. burgdorferi ZS7 (genomic group AAA) to a previously published HSP60 sequence derived from strain ACA-1, which according to the proposed classification is in a different genomic group (BBA), revealed a sequence identity of > 99%. Similar alignments of the OspA sequence of strain ZQ1 to those of other isolates that were published previously revealed sequence identities of between 70 and 94% among strains of distinct OspA genomic groups. These data indicate the existence of a restricted number of species-specific subgroups and clearly show that genotypic variation is much more pronounced for the OspA gene than for fla and the HSP60 and HSP70 genes. A phylogenetic tree constructed on the basis of distance matrix analyses of 12 OspA sequences supports the proposed classification of genomic groups of B. burgdorferi.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam T., Gassmann G. S., Rasiah C., Göbel U. B. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates from various sources. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2579–2585. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2579-2585.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzola J., Luft B. J., Gorgone G., Dattwyler R. J., Soderberg C., Lahesmaa R., Peltz G. Borrelia burgdorferi HSP70 homolog: characterization of an immunoreactive stress protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3704–3713. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3704-3713.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D., Abson K. G., Prose N. S. The laboratory diagnosis of Lyme disease. Arch Dermatol. 1991 Jun;127(6):866–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. N., Lane R. S. Lyme disease in California: a novel enzootic transmission cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1439–1442. doi: 10.1126/science.1604318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Clonal polymorphisms of outer membrane protein OspB of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2733–2741. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2733-2741.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputa A. C., Murtaugh M. P., Bey R. F., Loken K. I. 110-kilodalton recombinant protein which is immunoreactive with sera from humans, dogs, and horses with Lyme borreliosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2418–2423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2418-2423.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreiro M. M., Laux D. C., Nelson D. R. Characterization of the heat shock response and identification of heat shock protein antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2186–2191. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2186-2191.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Sun X., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Borrelia burgdorferi strain 25015: characterization of outer surface protein A and vaccination against infection. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2256–2260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Bangsborg J. M., Fjordvang H., Pedersen N. S., Hindersson P. Immunochemical characterization of and isolation of the gene for a Borrelia burgdorferi immunodominant 60-kilodalton antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2047–2053. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2047-2053.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Hindersson P., Pedersen N. S. Measurement of antibodies to the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum improves serodiagnosis in Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.338-346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., LaQuier F. W., Barbour A. G. Organization of genes encoding two outer membrane proteins of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi within a single transcriptional unit. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):207–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.207-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson M., Noppa L., Barbour A. G., Bergström S. Heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins in Borrelia burgdorferi: comparison of osp operons of three isolates of different geographic origins. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1845–1853. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1845-1853.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Schaible U. E., Wallich R., Moter S. E., Petzoldt D., Simon M. M. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi associated antigens by monoclonal antibodies. Immunobiology. 1990 Nov;181(4-5):357–366. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B., Perng G. C., Johnson R. C. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):636–639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.636-639.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Gorevic P. D., Jiang W., Munoz P., Dattwyler R. J. Immunologic and structural characterization of the dominant 66- to 73-kDa antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2776–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Garon C. F. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Borrelia: a comparison of North American and European isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):241–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.241-244.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensi N., Webb D. R., Turck C. W., Peltz G. A. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi proteins reactive with antibodies in synovial fluid of a patient with Lyme arthritis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2404–2407. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2404-2407.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postic D., Edlinger C., Richaud C., Grimont F., Dufresne Y., Perolat P., Baranton G., Grimont P. A. Two genomic species in Borrelia burgdorferi. Res Microbiol. 1990 May;141(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn D. W., Malawista S. E. Lyme disease: recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Mar 15;114(6):472–481. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-6-472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Hogan D., Schwan T. G. Polymerase chain reaction analyses identify two distinct classes of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):524–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.524-532.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eichmann K., Modolell M., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi prevent Lyme borreliosis in severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3768–3772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. S., Goldstein M. D., Ribeiro J. M., Schulze T. L., Shahied S. I. Antibody testing in Lyme disease. A comparison of results in four laboratories. JAMA. 1989 Dec 22;262(24):3431–3434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt M. C., Anzola J., Soderberg C., Yssel H., Turck C. W., Peltz G. Epitopes on the outer surface protein A of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized by antibodies and T cells of patients with Lyme disease. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):218–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt M. C., Hindersson P., Soderberg C., Mensi N., Turck C. W., Webb D., Yssel H., Peltz G. T cell and antibody reactivity with the Borrelia burgdorferi 60-kDa heat shock protein in Lyme arthritis. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3985–3992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eckerskorn C., Museteanu C., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Wallich R. Recombinant outer surface protein a from Borrelia burgdorferi induces antibodies protective against spirochetal infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):123–132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Schaible U. E., Wallich R., Kramer M. D. A mouse model for Borrelia burgdorferi infection: approach to a vaccine against Lyme disease. Immunol Today. 1991 Jan;12(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Schrumpf M. E., Hayes S. F., Schwan T. G. Molecular and immunological analysis of a polymorphic periplasmic protein of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):1940–1948. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.1940-1948.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Schrumpf M. E., Schwan T. G. Reactivity of human Lyme borreliosis sera with a 39-kilodalton antigen specific to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1329–1337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1329-1337.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Moter S. E., Simon M. M., Ebnet K., Heiberger A., Kramer M. D. The Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum-associated 41-kilodalton antigen (flagellin): molecular cloning, expression, and amplification of the gene. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1711-1719.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Schaible U. E., Simon M. M., Heiberger A., Kramer M. D. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the outer surface protein A (OspA) of a European Borrelia burgdorferi isolate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8864–8864. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumstein G., Fuchs R., Hofmann A., Preac-Mursic V., Soutschek E., Wilske B. Genetic polymorphism of the gene encoding the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181(2):57–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00189424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



