Abstract
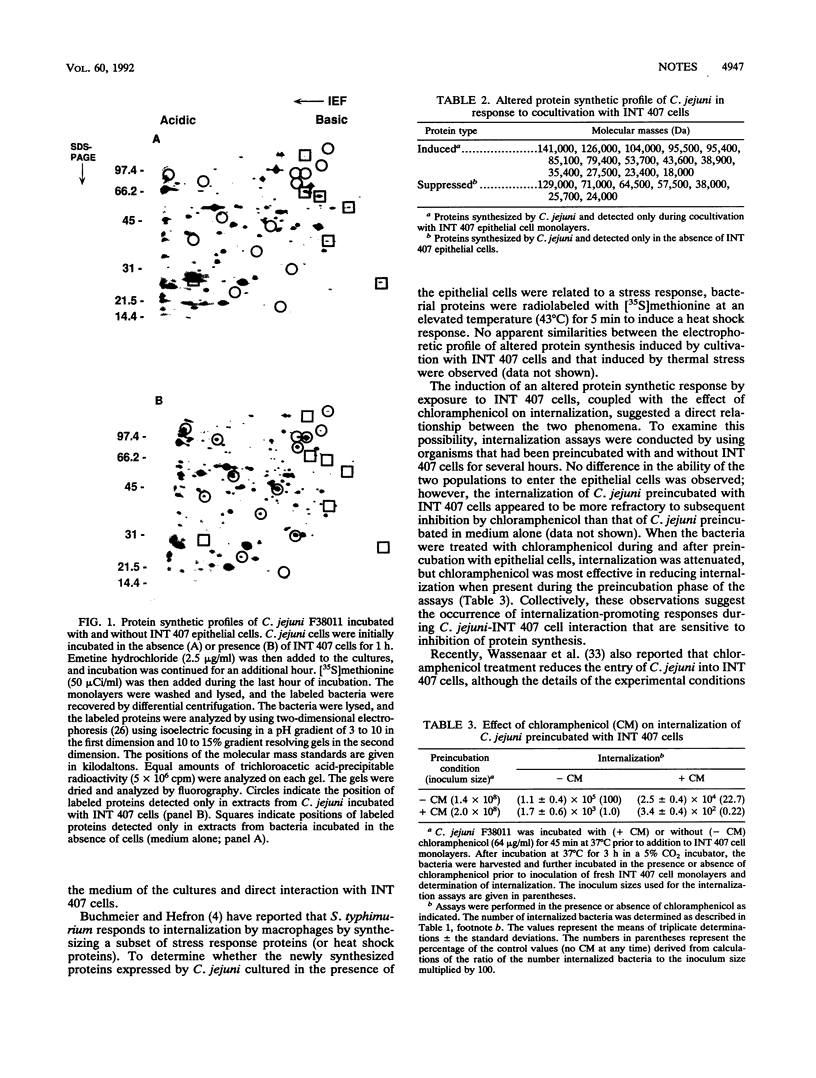
Campylobacter jejuni has been shown to bind to and enter epithelial cells in culture. The interaction of C. jejuni with INT 407 epithelial cells was examined to determine whether bacterial protein synthesis is required for either binding or internalization. Chloramphenicol, a selective inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis, significantly reduced the internalization, but not binding, of C. jejuni compared with untreated controls as determined by protection from gentamicin. Electrophoretic analysis of metabolically labeled proteins revealed that C. jejuni cultured with INT 407 cells synthesized 14 proteins that were not detected in organisms cultured in medium alone. The inhibitory effect of chloramphenicol on internalization was reduced by preincubation of C. jejuni with INT 407 cells. The results indicate that C. jejuni, like some other enteric pathogens, engages in a directed response to cocultivation with epithelial cells by synthesizing one or more proteins that facilitate internalization and suggest that this phenomenon is relevant to the pathogenesis of enteritis caused by C. jejuni.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black R. E., Levine M. M., Clements M. L., Hughes T. P., Blaser M. J. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Wells J. G., Feldman R. A., Pollard R. A., Allen J. R. Campylobacter enteritis in the United States. A multicenter study. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):360–365. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Heffron F. Induction of Salmonella stress proteins upon infection of macrophages. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):730–732. doi: 10.1126/science.1970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calva E., Torres J., Vázquez M., Angeles V., de la Vega H., Ruíz-Palacios G. M. Campylobacter jejuni chromosomal sequences that hybridize to Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli LT enterotoxin genes. Gene. 1989 Feb 20;75(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. C., Bavoil P., Clark V. L. Enhancement of the invasive ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by contact with HecIB, an adenocarcinoma endometrial cell line. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1531–1538. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. C., Benson J. B., Rubin S. J. Mucosal invasion in campylobacter enteritis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 May;73(5):706–708. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/73.5.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S. Bacterial entry into eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1099–1102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90003-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauchere J. L., Rosenau A., Veron M., Moyen E. N., Richard S., Pfister A. Association with HeLa cells of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from human feces. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):283–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.283-287.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Heffron F., Falkow S. Epithelial cell surfaces induce Salmonella proteins required for bacterial adherence and invasion. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):940–943. doi: 10.1126/science.2919285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAWALT P., SETLOW R. Effect of monochromatic ultraviolet light on macromolecular synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 1;41:283–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of Henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the bacterium. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):879–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.879-886.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Mammalian cell adhesion functions and cellular penetration of enteropathogenic Yersinia species. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1449–1453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilhström E. Interaction between Salmonella bacteria and mammalian nonprofessional phagocytes. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Nov;33(11 Suppl):2491–2501. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.11.2491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Short H., Schenk E. A. Pathogenic properties of Campylobacter jejuni: assay and correlation with clinical manifestations. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.43-49.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel M. E., Joens L. A. Adhesion to and invasion of HEp-2 cells by Campylobacter spp. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):2984–2990. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.2984-2990.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. E., Schofield P. F., Ironside A. G., Mandal B. K. Campylobacter colitis. Br Med J. 1979 Mar 31;1(6167):857–859. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6167.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Falkow S. The ability of Salmonella to enter mammalian cells is affected by bacterial growth state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4304–4308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSweegan E., Walker R. I. Identification and characterization of two Campylobacter jejuni adhesins for cellular and mucous substrates. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):141–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.141-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Environmental signals controlling expression of virulence determinants in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.1-7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miliotis M. D. Acridine orange stain for determining intracellular enteropathogens in HeLa cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):830–831. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.830-831.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Interaction of chlamydiae and host cells in vitro. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):143–190. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.143-190.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi P., Losonsky G., DeTolla L. J., Morris J. G., Jr Human immune response to Campylobacter jejuni proteins expressed in vivo. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4938–4944. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4938-4944.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. P., Sadoff J. C. Induced engulfment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by tissue culture cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2512–2514. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2512-2514.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Torres J., Torres N. I., Escamilla E., Ruiz-Palacios B. R., Tamayo J. Cholera-like enterotoxin produced by Campylobacter jejuni. Characterisation and clinical significance. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):250–253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Geme J. W., 3rd, Falkow S. Haemophilus influenzae adheres to and enters cultured human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4036–4044. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4036-4044.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I., Caldwell M. B., Lee E. C., Guerry P., Trust T. J., Ruiz-Palacios G. M. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter enteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):81–94. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.81-94.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Penetration of cultured mouse fibroblasts (L cells) by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassenaar T. M., Bleumink-Pluym N. M., van der Zeijst B. A. Inactivation of Campylobacter jejuni flagellin genes by homologous recombination demonstrates that flaA but not flaB is required for invasion. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2055–2061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]