Abstract
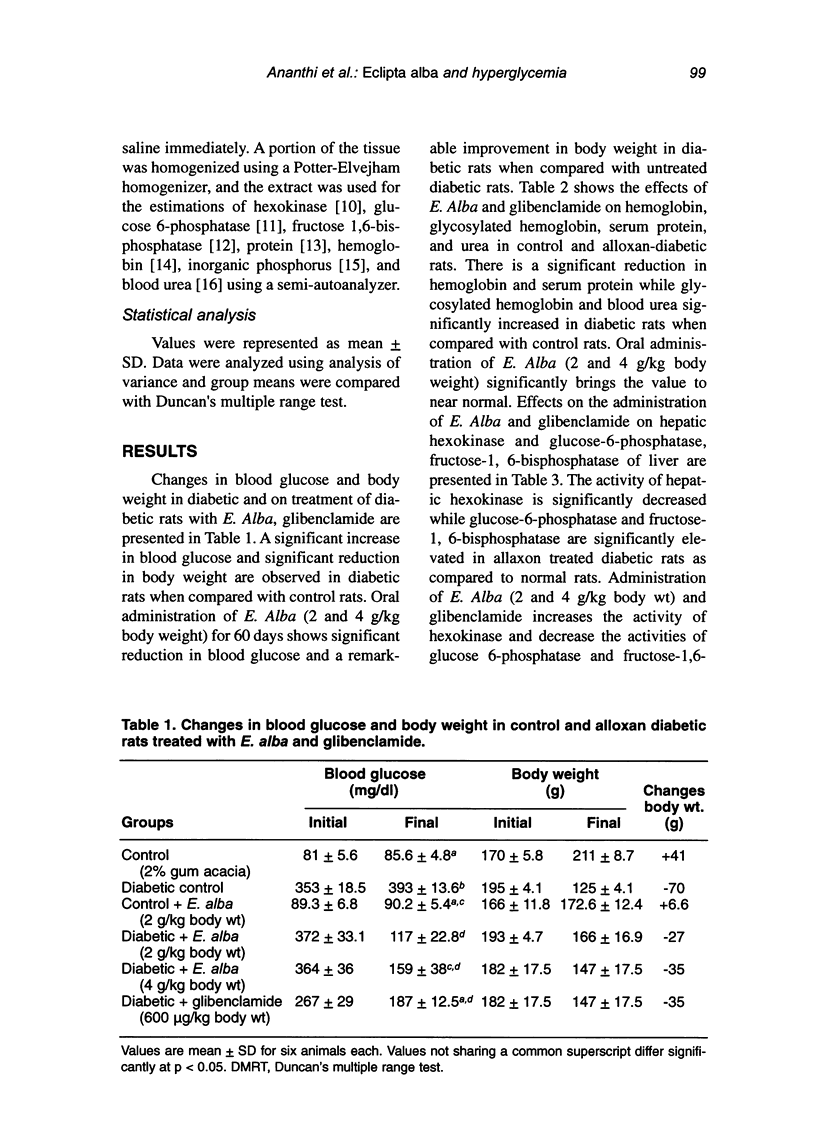
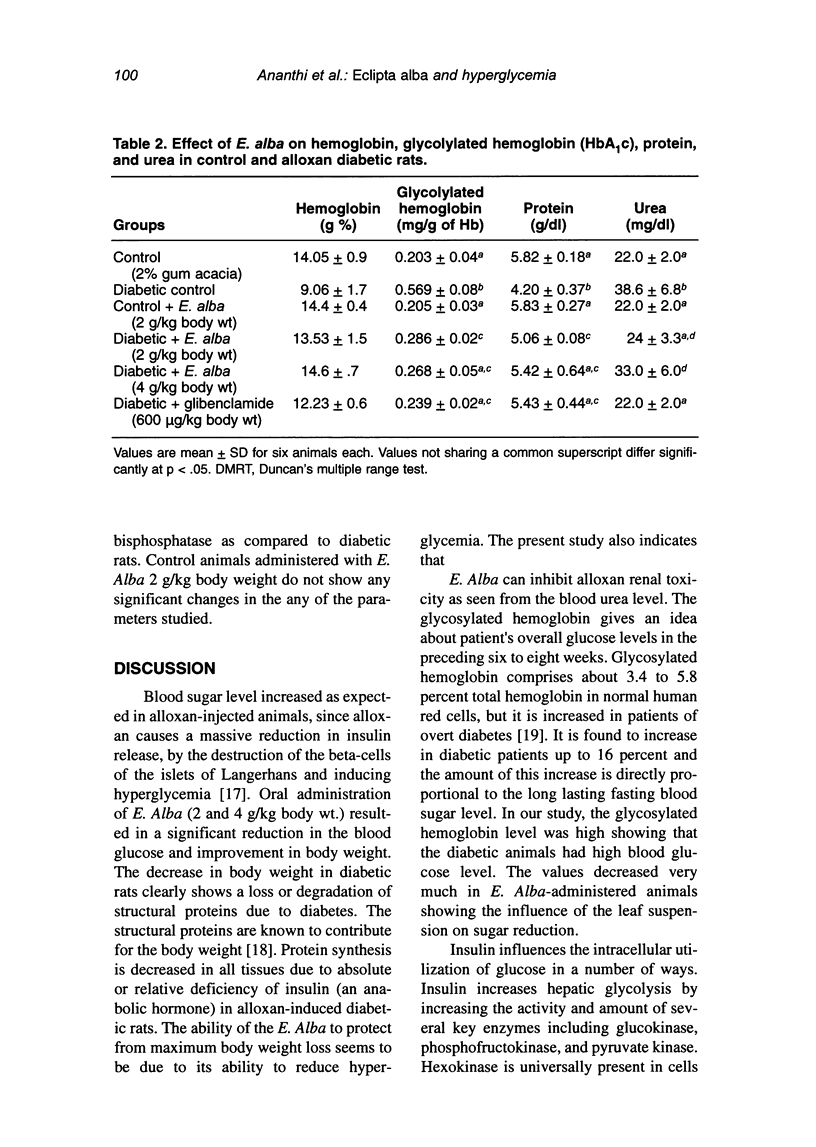
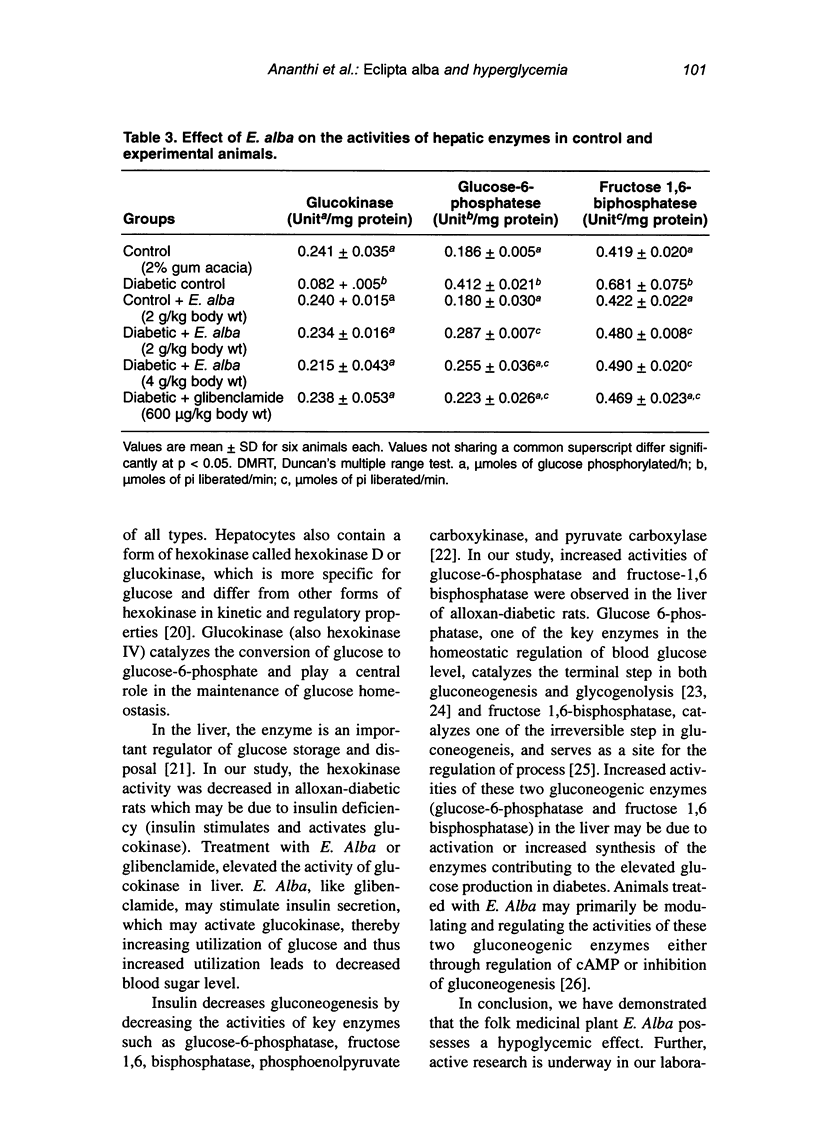
Eclipta alba, an indigenous medicinal plant, has a folk (Siddha and Ayurvedha) reputation in rural southern India as a hypoglycemic agent. In order to confirm this claim, the present study was carried out to evaluate the antihyperglycemic effect of E. alba and to study the activities of liver hexokinase and gluconeogenic enzymes such as glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase in the liver of control and alloxan-diabetic rats. Oral administration of leaf suspension of E. alba (2 and 4 g/kg body weight) for 60 days resulted in significant reduction in blood glucose (from 372.0 +/- 33.2 to 117.0 +/- 22.8), glycosylated hemoglobin HbA(1)c, a decrease in the activities of glucose-6 phosphatase and fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase, and an increase in the activity of liver hexokinase. E. alba at dose of 2 g/kg body weight exhibited better sugar reduction than 4 g/kg body weight. Thus, the present study clearly shows that the oral administration of E. alba possess potent antihyperglycemic activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRANDSTRUP N., KIRK J. E., BRUNI C. The hexokinase and phosphoglucoisomerase activities of aortic and pulmonary artery tissue in individuals of various ages. J Gerontol. 1957 Apr;12(2):166–171. doi: 10.1093/geronj/12.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya S. K., Satyan K. S., Chakrabarti A. Effect of Trasina, an Ayurvedic herbal formulation, on pancreatic islet superoxide dismutase activity in hyperglycaemic rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 1997 Mar;35(3):297–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancedo J. M., Gancedo C. Fructose-1,6-diphosphatase, phosphofructokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from fermenting and non fermenting yeasts. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;76(2):132–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00411787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta D., Raju J., Baquer N. Z. Modulation of some gluconeogenic enzyme activities in diabetic rat liver and kidney: effect of antidiabetic compounds. Indian J Exp Biol. 1999 Feb;37(2):196–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOIDE H., ODA T. Pathological occurrence of glucose-6-phosphatase in serum in liver diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 Jul;4:554–561. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak S. S., Pattabiraman T. N. A new colorimetric method for the estimation of glycosylated hemoglobin. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Feb 5;109(3):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen E. P. Experiences in sulfonylurea therapy. Metabolism. 1973 Feb;22(2):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90195-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumar L., Srinivasan N., Balasubramanian K., Govindarajulu P. Increased degradation of dermal collagen in diabetic rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 1991 Nov;29(11):1081–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


