Abstract
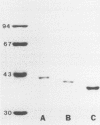
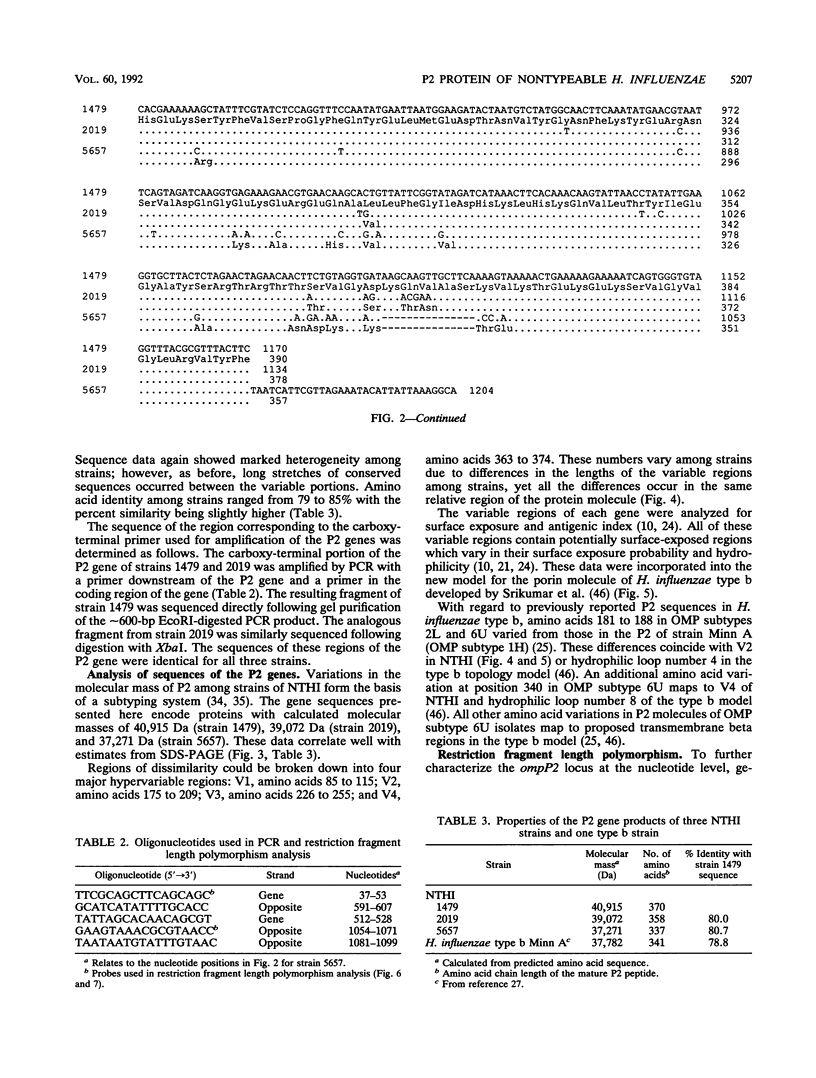
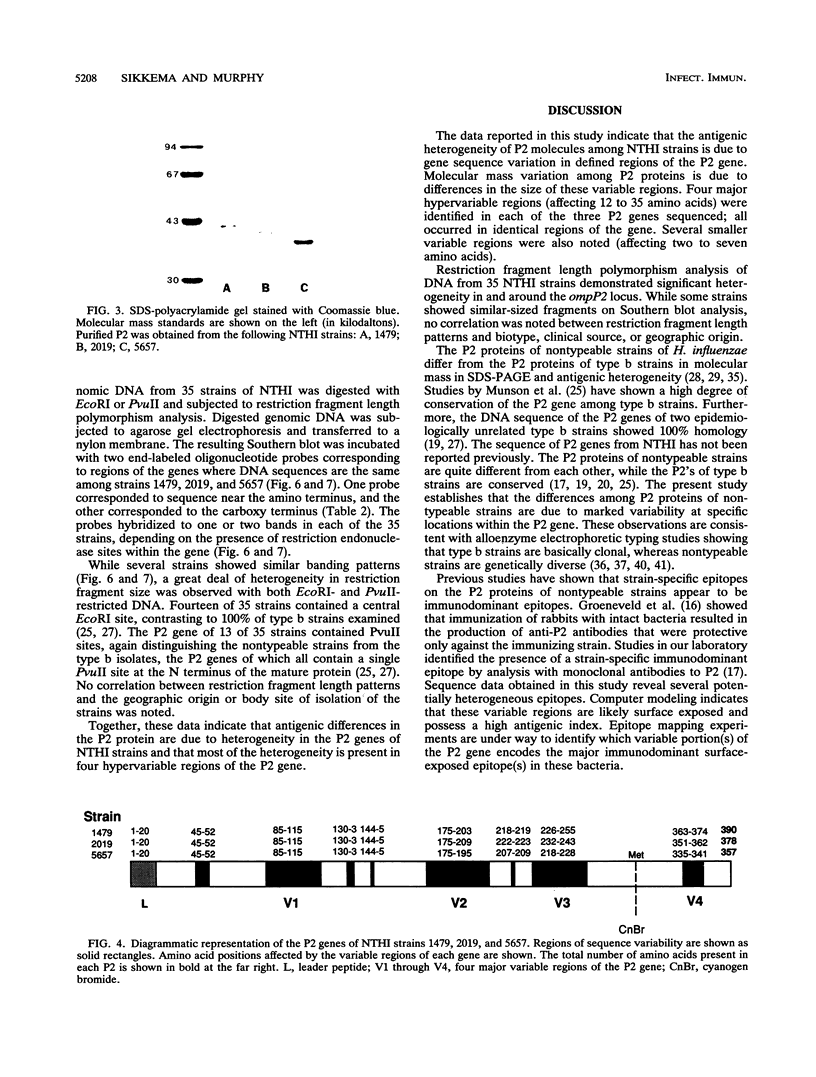
The P2 porin protein is the most abundant outer membrane protein (OMP) of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHI) and shows extensive antigenic heterogeneity among strains. To study the molecular basis of this heterogeneity, the DNA sequences of the genes encoding the P2 proteins of three unrelated strains of NTHI were determined, and restriction fragment length polymorphisms around the P2 genes of 35 strains were analyzed. The deduced amino acid sequences of the P2 genes from the three strains of NTHI revealed four major (12 to 35 amino acids long) and several smaller (2 to 7 amino acids) hypervariable regions in each protein. The major variations occurred in identical portions of the genes, and these regions showed a high antigenic index and surface exposure probability in computer modeling analysis. Differences in the molecular mass of the P2 protein correlate with differences in the size of the variable region in each strain. Oligonucleotide primers suitable for amplification of the P2 genes by polymerase chain reaction were developed. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis showed marked heterogeneity in and around the ompP2 locus of 35 NTHI strains. These results contrast with the high degree of conservation of the P2 genes in H. influenzae type b strains. We conclude that the molecular mass and antigenic heterogeneity of the P2 molecule of NTHI is due to variations in gene sequence that are clustered primarily in four large hypervariable regions of the gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Shurin P. A., Marchant C. D., Karasic R. B., Pelton S. I., Howie V. M., Granoff D. M. Do children with recurrent Haemophilus influenzae otitis media become infected with a new organism or reacquire the original strain? J Pediatr. 1984 Oct;105(4):533–537. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk S. L., Holtsclaw S. A., Wiener S. L., Smith J. K. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):537–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnari A. A., Gupta M. R., Dudas K. C., Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Antigenic diversity of lipooligosaccharides of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):882–887. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.882-887.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonetti N. H., Sparling P. F. Molecular cloning and characterization of the structural gene for protein I, the major outer membrane protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9084–9088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowson C. G., Hutchison A., Brannigan J. A., George R. C., Hansman D., Liñares J., Tomasz A., Smith J. M., Spratt B. G. Horizontal transfer of penicillin-binding protein genes in penicillin-resistant clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8842–8846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Hughes J. V., Perlow D. S., Boger J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):836–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.836-839.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A., Massalski A., Schindler H., Dorset D. L., Rosenbusch J. P. Porin channel triplets merge into single outlets in Escherichia coli outer membranes. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):643–645. doi: 10.1038/317643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Bernstein J., Brodsky L., Stanievich J., Krystofik D., Shuff C., Hong J. J., Ogra P. L. Otitis media in children. I. The systemic immune response to nontypable Hemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):999–1004. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feavers I. M., Heath A. B., Bygraves J. A., Maiden M. C. Role of horizontal genetic exchange in the antigenic variation of the class 1 outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):489–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Seiff M. E., Blake M. S., Koomey M. Porin protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: cloning and gene structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8135–8139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld K., Eijk P. P., van Alphen L., Jansen H. M., Zanen H. C. Haemophilus influenzae infections in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease despite specific antibodies in serum and sputum. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 May;141(5 Pt 1):1316–1321. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.5_Pt_1.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld K., van Alphen L., Voorter C., Eijk P. P., Jansen H. M., Zanen H. C. Antigenic drift of Haemophilus influenzae in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3038–3044. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3038-3044.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase E. M., Campagnari A. A., Sarwar J., Shero M., Wirth M., Cumming C. U., Murphy T. F. Strain-specific and immunodominant surface epitopes of the P2 porin protein of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1278–1284. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1278-1284.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Hasemann C., Clausell A., Capra J. D., Orth K., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C. A., Latimer J. L., Miller E. E. Primary structure of the porin protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b determined by nucleotide sequence analysis. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1100–1107. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1100-1107.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Pelzel S. E., Orth K., Moomaw C. R., Radolf J. D., Slaughter C. A. Structural and antigenic conservation of the P2 porin protein among strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3270–3275. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3270-3275.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiden M. C., Suker J., McKenna A. J., Bygraves J. A., Feavers I. M. Comparison of the class 1 outer membrane proteins of eight serological reference strains of Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):727–736. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrow S., Wolf H. Characterization of two related Epstein-Barr virus-encoded membrane proteins that are differentially expressed in Burkitt lymphoma and in vitro-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Shenep J. L., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Purification and comparison of outer membrane protein P2 from Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Bailey C., Grass S. Diversity of the outer membrane protein P2 gene from major clones of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1797–1803. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Grass S. Purification, cloning, and sequence of outer membrane protein P1 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2235–2242. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2235-2242.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Tolan R. W., Jr Molecular cloning, expression, and primary sequence of outer membrane protein P2 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.88-94.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Antigenic heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae is a basis for a serotyping system. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.15-21.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Human bactericidal antibody response to outer membrane protein P2 of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2673–2679. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2673-2679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Purification and analysis with monoclonal antibodies of P2, the major outer membrane protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1084–1089. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1084-1089.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Rice P. A., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Apicella M. A. Identification of a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein on nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a target for human serum bactericidal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bernstein J. M., Dryja D. M., Campagnari A. A., Apicella M. A. Outer membrane protein and lipooligosaccharide analysis of paired nasopharyngeal and middle ear isolates in otitis media due to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenetic and epidemiological observations. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):723–731. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Selander R. K. Genetic relationships of serologically nontypable and serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):183–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.183-191.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Granoff D. M., Pattison P. E., Selander R. K. A population genetic framework for the study of invasive diseases caused by serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5078–5082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. B., Munson R. S., Jr, Apicella M. A., Sikkema D. J., Molleston J. P., Murphy T. F. Molecular conservation of the P6 outer membrane protein among strains of Haemophilus influenzae: analysis of antigenic determinants, gene sequences, and restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2658–2663. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2658-2663.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka E., Matsuki S., Ikehara M., Takahashi Y., Matsubara K. An alternative approach to deoxyoligonucleotides as hybridization probes by insertion of deoxyinosine at ambiguous codon positions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2605–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras O., Caugant D. A., Gray B., Lagergård T., Levin B. R., Svanborg-Edén C. Difference in structure between type b and nontypable Haemophilus influenzae populations. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):79–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.79-89.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras O., Caugant D. A., Lagergård T., Svanborg-Edén C. Application of multilocus enzyme gel electrophoresis to Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.71-78.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H. S., Ajioka R. S., Marchal C., Sparling P. F., So M. DNA transformation leads to pilin antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):392–395. doi: 10.1038/336392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikumar R., Chin A. C., Vachon V., Richardson C. D., Ratcliffe M. J., Saarinen L., Käyhty H., Mäkelä P. H., Coulton J. W. Monoclonal antibodies specific to porin of Haemophilus influenzae type b: localization of their cognate epitopes and tests of their biological activities. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(5):665–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikumar R., Dahan D., Gras M. F., Ratcliffe M. J., van Alphen L., Coulton J. W. Antigenic sites on porin of Haemophilus influenzae type b: mapping with synthetic peptides and evaluation of structure predictions. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4007–4016. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4007-4016.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon V., Kristjanson D. N., Coulton J. W. Outer membrane porin protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b: pore size and subunit structure. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):134–140. doi: 10.1139/m88-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon V., Lyew D. J., Coulton J. W. Transmembrane permeability channels across the outer membrane of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.918-924.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Jähnig F. Models for the structure of outer-membrane proteins of Escherichia coli derived from raman spectroscopy and prediction methods. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Eijk P., Geelen-van den Broek L., Dankert J. Immunochemical characterization of variable epitopes of outer membrane protein P2 of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):247–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.247-252.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]