Abstract
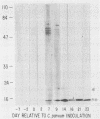
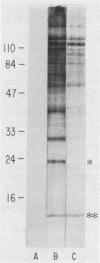
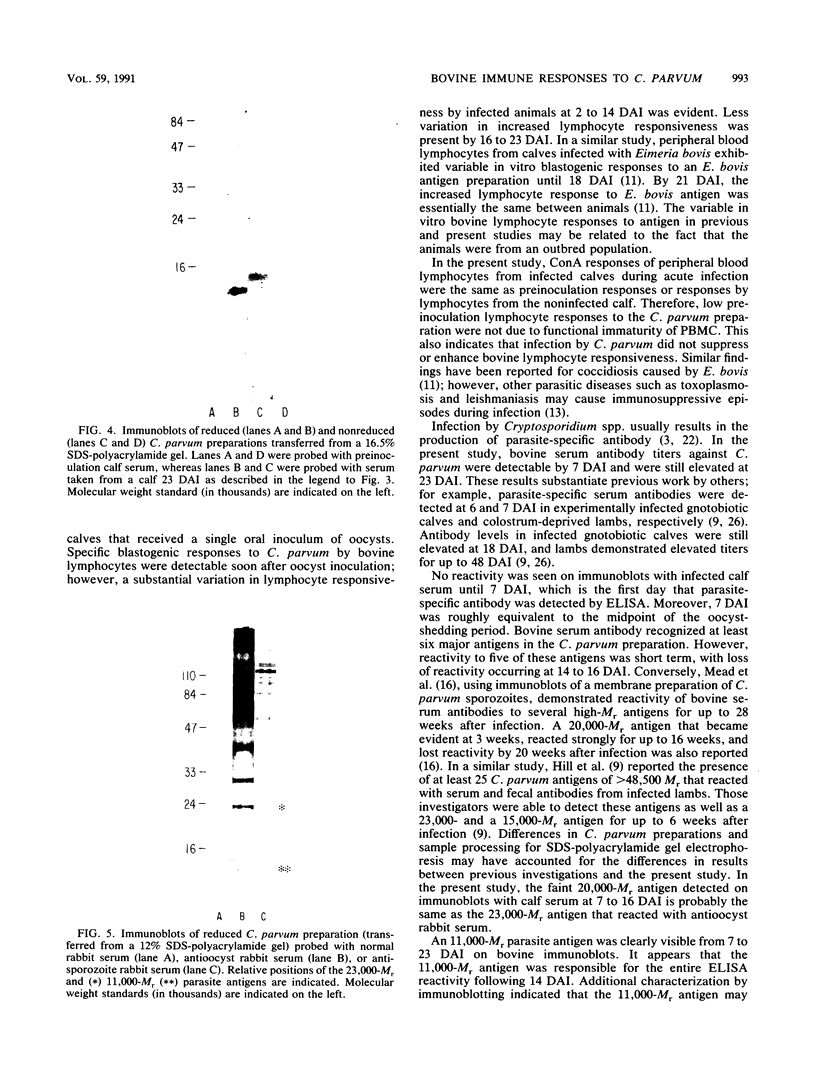
Cellular and serum antibody responses of calves were monitored for 23 days after oral inoculation of the calves with oocysts of Cryptosporidium parvum. In vitro blastogenic responses of peripheral blood lymphocytes were assessed after stimulation with a C. parvum preparation. Specific lymphocyte blastogenic responses to the parasite were detected 2 days after inoculation. Parasite-specific antibody titers were demonstrable 7 days after inoculation with oocysts and achieved peak levels 9 days after inoculation, coinciding with oocyst shedding at 5 to 10 days after inoculation. Both lymphocyte and antibody responses remained elevated until the termination of the experiment. Immunoblotting the C. parvum preparation with serum from an infected calf revealed six major parasite antigens. Five of these antigens reacted on immunoblots from 7 to 14 days after inoculation with oocysts. A parasite antigen of approximately 11,000 molecular weight demonstrated intense reactivity on immunoblots from 7 to 23 days after inoculation. The 11,000-molecular-weight antigen also reacted on immunoblots with parenterally raised antioocyst and antisporozoite rabbit sera. These results indicate that cell-mediated as well as humoral immune responses are initiated by cryptosporidial infection in calves and that the 11,000-molecular-weight parasite antigen is immunodominant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrowood M. J., Sterling C. R. Isolation of Cryptosporidium oocysts and sporozoites using discontinuous sucrose and isopycnic Percoll gradients. J Parasitol. 1987 Apr;73(2):314–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Current W. L., Bick P. H. Immunobiology of Cryptosporidium spp. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 1989;8(3-4):141–160. doi: 10.1159/000157146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Current W. L. Cryptosporidiosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1985 Dec 15;187(12):1334–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Current W. L., Reese N. C., Ernst J. V., Bailey W. S., Heyman M. B., Weinstein W. M. Human cryptosporidiosis in immunocompetent and immunodeficient persons. Studies of an outbreak and experimental transmission. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 26;308(21):1252–1257. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305263082102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Ungar B. L. Cryptosporidium spp. and cryptosporidiosis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):458–483. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.458-483.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harp J. A., Woodmansee D. B., Moon H. W. Effects of colostral antibody on susceptibility of calves to Cryptosporidium parvum infection. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Dec;50(12):2117–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J., Moon H. W., Woodmansee D. B. Persistent Cryptosporidium infection in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):856–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.856-859.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill B. D., Blewett D. A., Dawson A. M., Wright S. Analysis of the kinetics, isotype and specificity of serum and coproantibody in lambs infected with Cryptosporidium parvum. Res Vet Sci. 1990 Jan;48(1):76–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S. L., Cannon L. T., Sr, Berzofsky J. A., Majarian W. R., Young J. F., Maloy W. L., Hockmeyer W. T. Plasmodium falciparum: sporozoite boosting of immunity due to a T-cell epitope on a sporozoite vaccine. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Aug;64(1):64–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., Whitmire W. M., Speer C. A. Immunity patterns during acute infection by Eimeria bovis. J Parasitol. 1989 Feb;75(1):86–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Payne D., Woodmansee D., Kim C. W. Characterization of the Cryptosporidium antigens from sporulated oocysts of Cryptosporidium parvum. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2436–2441. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2436-2441.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumb R., Smith P. S., Davies R., O'Donoghue P. J., Atkinson H. M., Lanser J. A. Localization of a 23,000 MW antigen of Cryptosporidium by immunoelectron microscopy. Immunol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;67(Pt 4):267–270. doi: 10.1038/icb.1989.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J. R., Arrowood M. J., Sterling C. R. Antigens of Cryptosporidium sporozoites recognized by immune sera of infected animals and humans. J Parasitol. 1988 Feb;74(1):135–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Woodmansee D. B., Harp J. A., Abel S., Ungar B. L. Lacteal immunity to enteric cryptosporidiosis in mice: immune dams do not protect their suckling pups. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):649–653. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.649-653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soave R., Armstrong D. Cryptosporidium and cryptosporidiosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1012–1023. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley M., Fayer R., Guidry A., Upton S. J., Blagburn B. L. Cryptosporidium parvum (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) oocyst and sporozoite antigens recognized by bovine colostral antibodies. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2966–2971. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2966-2971.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Campbell I. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium antibodies in 10 animal species. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):455–456. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.455-456.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Burris J. A., Quinn C. A., Finkelman F. D. New mouse models for chronic Cryptosporidium infection in immunodeficient hosts. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):961–969. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.961-969.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Nash T. E. Quantification of specific antibody response to Cryptosporidium antigens by laser densitometry. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):124–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.124-128.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmire W. M., Harp J. A. In vitro murine lymphocyte blastogenic responses to Cryptosporidium parvum. J Parasitol. 1990 Jun;76(3):450–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Burden D. J. Measurement of class specific antibody against cryptosporidium in serum and faeces from experimentally infected calves. Res Vet Sci. 1987 Sep;43(2):264–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]