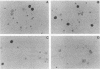
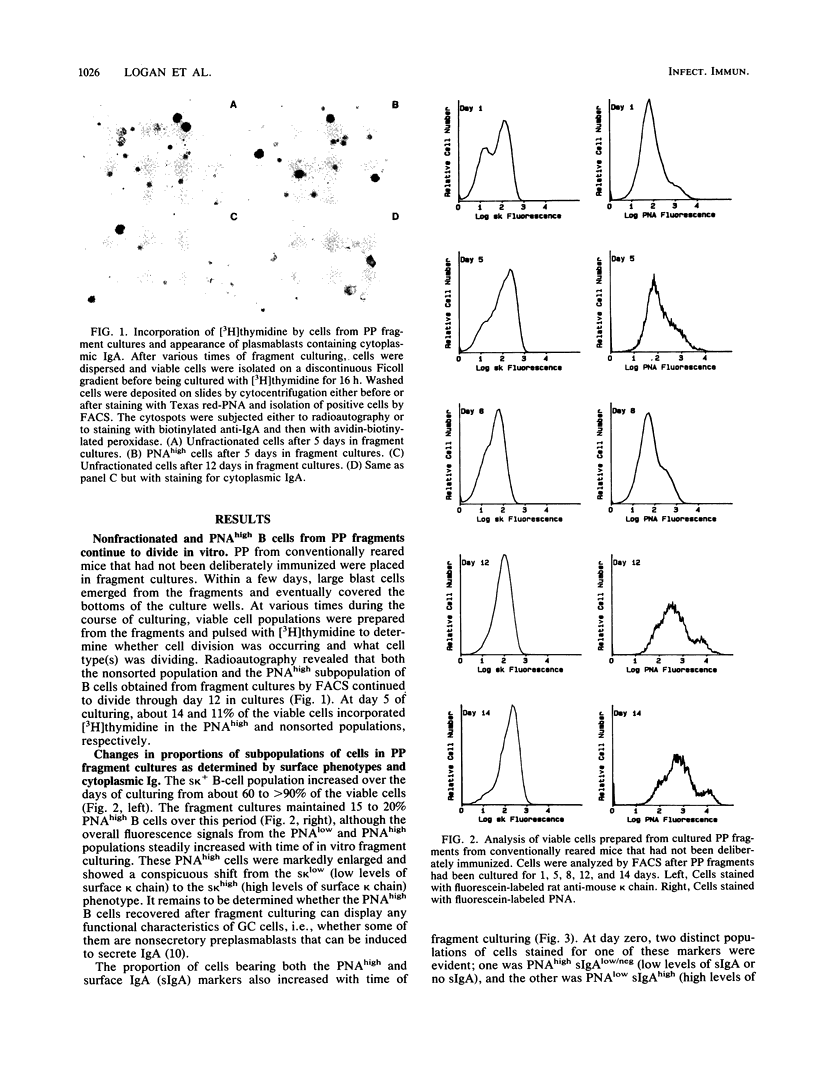
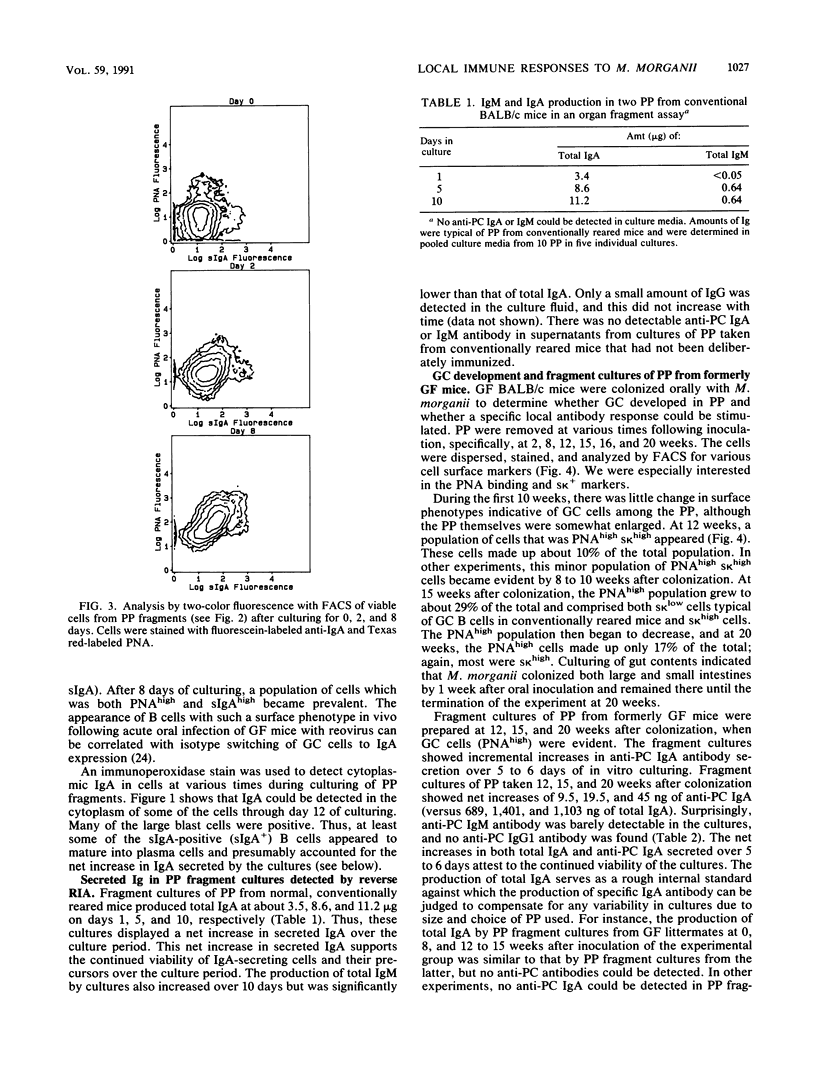
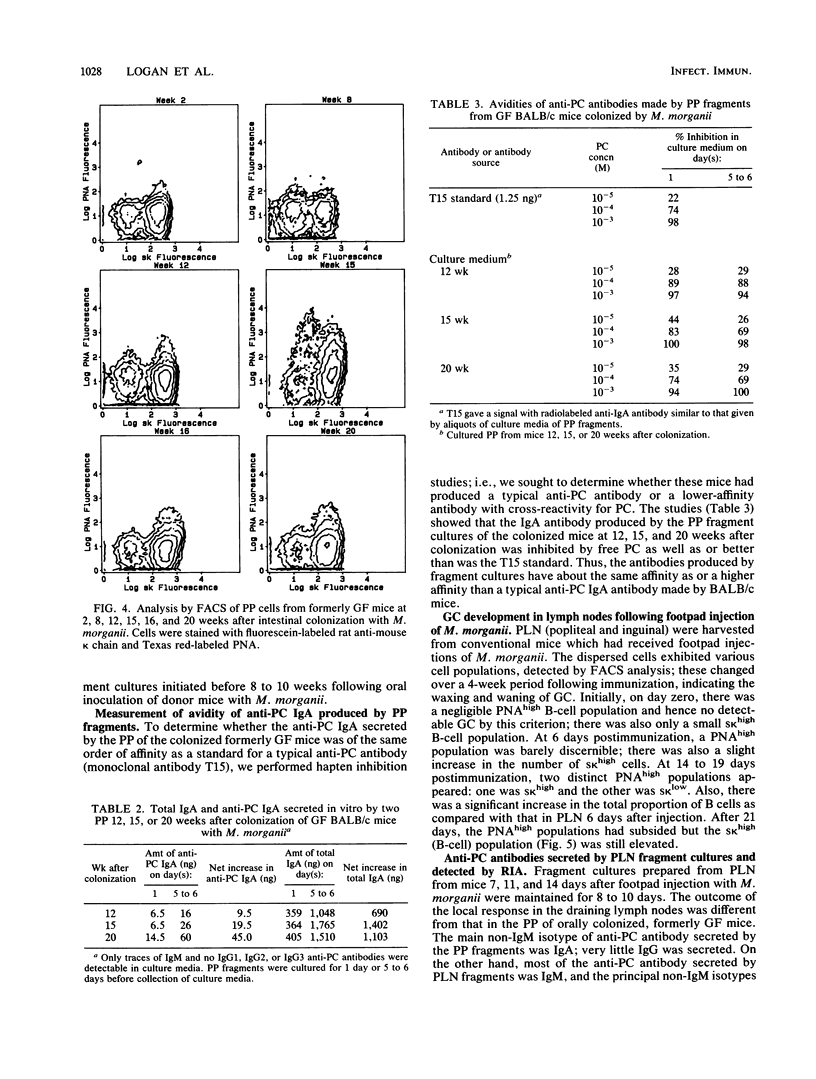
Abstract
Lymphoid tissue fragment cultures were established to analyze the differentiative processes among B cells in Peyer's patches (PP) and peripheral lymph nodes (PLN), especially those in germinal centers. PP cultures from both conventionally reared mice and formerly germ-free mice colonized with Morganella morganii could be maintained for greater than 12 days with continued B-cell division, especially among cells binding high levels of peanut agglutinin, a characteristic of germinal center cells. PLN cultures from conventionally reared mice injected with a heat-killed vaccine of M. morganii could be maintained for the same amount of time. Over this period, PP cultures continued to secrete immunoglobulin A (IgA) as well as smaller amounts of IgM. PP cultures from formerly germ-free mice colonized with M. morganii showed net increases of IgA antiphosphocholine (anti-PC) antibodies with avidities as high as those of the prototypic T15 monoclonal antibody. Similar PLN fragment cultures from conventionally reared mice given footpad injections of M. morganii showed net increases of IgM and IgG anti-PC antibodies in the culture fluid. Thus, although M. morganii stimulated lymphoid tissues in vivo to produce an anti-PC response in vitro when given by either the oral or the parenteral route, the antibody isotypes differed between PP and PLN fragment cultures. Fragment culturing may offer a complementary and simpler way to detect a local secretory IgA response than does either measuring IgA antibody in secretions or detecting IgA antibody in the cytoplasm of plasma cells in the lamina propria of gastrointestinal or respiratory tissue.
Full text
PDF

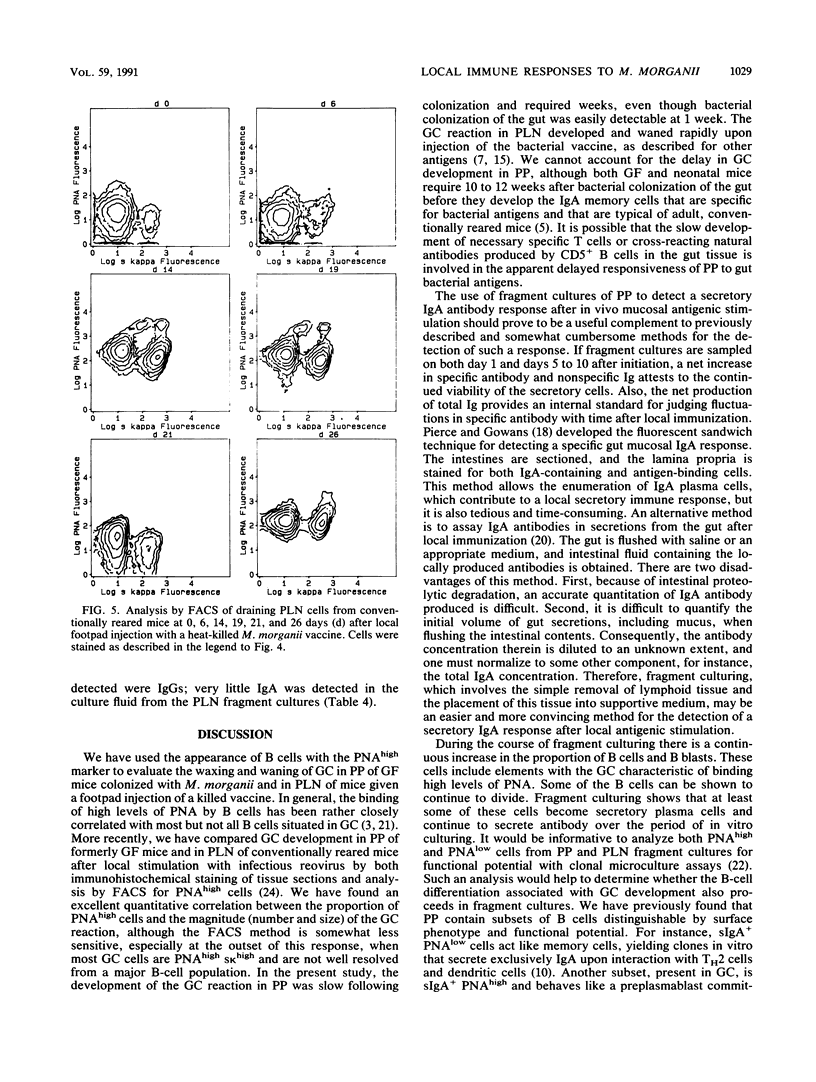
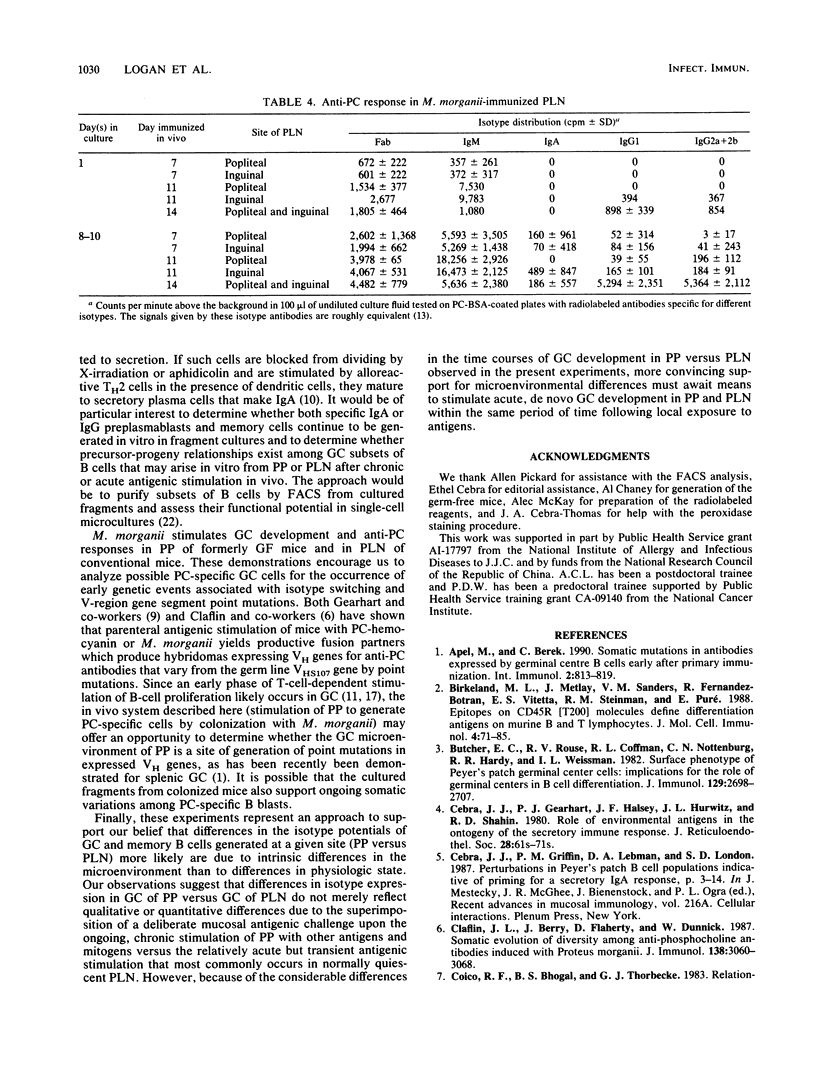

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apel M., Berek C. Somatic mutations in antibodies expressed by germinal centre B cells early after primary immunization. Int Immunol. 1990;2(9):813–819. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.9.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkeland M. L., Metlay J., Sanders V. M., Fernandez-Botran R., Vitetta E. S., Steinman R. M., Puré E. Epitopes on CD45R [T200] molecules define differentiation antigens on murine B and T lymphocytes. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1988;4(2):71–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Rouse R. V., Coffman R. L., Nottenburg C. N., Hardy R. R., Weissman I. L. Surface phenotype of Peyer's patch germinal center cells: implications for the role of germinal centers in B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2698–2707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Gearhart P. J., Halsey J. F., Hurwitz J. L., Shahin R. D. Role of environmental antigens in the ontogeny of the secretory immune response. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Dec;28(Suppl):61s–71s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Griffin P. M., Lebman D. A., London S. D. Perturbations in Peyer's patch B cell populations indicative of priming for a secretory IgA response. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;216A:3–14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5344-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claflin J. L., Berry J., Flaherty D., Dunnick W. Somatic evolution of diversity among anti-phosphocholine antibodies induced with Proteus morganii. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):3060–3068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coico R. F., Bhogal B. S., Thorbecke G. J. Relationship of germinal centers in lymphoid tissue to immunologic memory. VI. Transfer of B cell memory with lymph node cells fractionated according to their receptors for peanut agglutinin. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2254–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. G., Landolfi N. F., Mehta V., Leone J., Hoyland D. Interleukin 2 mediates an alteration in the T200 antigen expressed on activated B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):991–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J., Johnson N. D., Douglas R., Hood L. IgG antibodies to phosphorylcholine exhibit more diversity than their IgM counterparts. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):29–34. doi: 10.1038/291029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A., Cebra J. J. Responses of single germinal-center B cells in T-cell-dependent microculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinen E., Cormann N., Kinet-Denoël C. The lymph follicle: a hard nut to crack. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):240–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz J. L., Tagart V. B., Schweitzer P. A., Cebra J. J. Patterns of isotype expression by B cell clones responding to thymus-dependent and thymus-independent antigens in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Apr;12(4):342–348. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Kunkl A. The role of germinal centres in the generation of immunological memory. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;84:265–280. doi: 10.1002/9780470720660.ch14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraal G., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. Germinal centre B cells: antigen specificity and changes in heavy chain class expression. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):377–379. doi: 10.1038/298377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebman D. A., Griffin P. M., Cebra J. J. Relationship between expression of IgA by Peyer's patch cells and functional IgA memory cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1405–1418. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuis P., Opstelten D. Functional anatomy of germinal centers. Am J Anat. 1984 Jul;170(3):421–435. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001700315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Gowans J. L. Cellular kinetics of the intestinal immune response to cholera toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1550–1563. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Antigen-binding myeloma proteins in mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:306–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. L., Birbeck M. S., Wallis V. J., Forrester J. A., Davies A. J. Peanut lectin binding properties of germinal centres of mouse lymphoid tissue. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):364–366. doi: 10.1038/284364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader C. E., George A., Kerlin R. L., Cebra J. J. Dendritic cells support production of IgA and other non-IgM isotypes in clonal microculture. Int Immunol. 1990;2(6):563–570. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.6.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer P. A., Cebra J. J. Quality of antibodies secreted by clones in microcultures from B cells enriched on haptenated gelatin: isotypes and avidities. Mol Immunol. 1988 Mar;25(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. R., Claflin J. L. Clonotypes of anti-phosphocholine antibodies induced with Proteus morganii (Potter). I. Structural and idiotypic similarities in a diverse repertoire. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]