Abstract
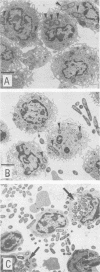
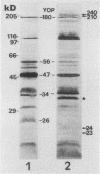
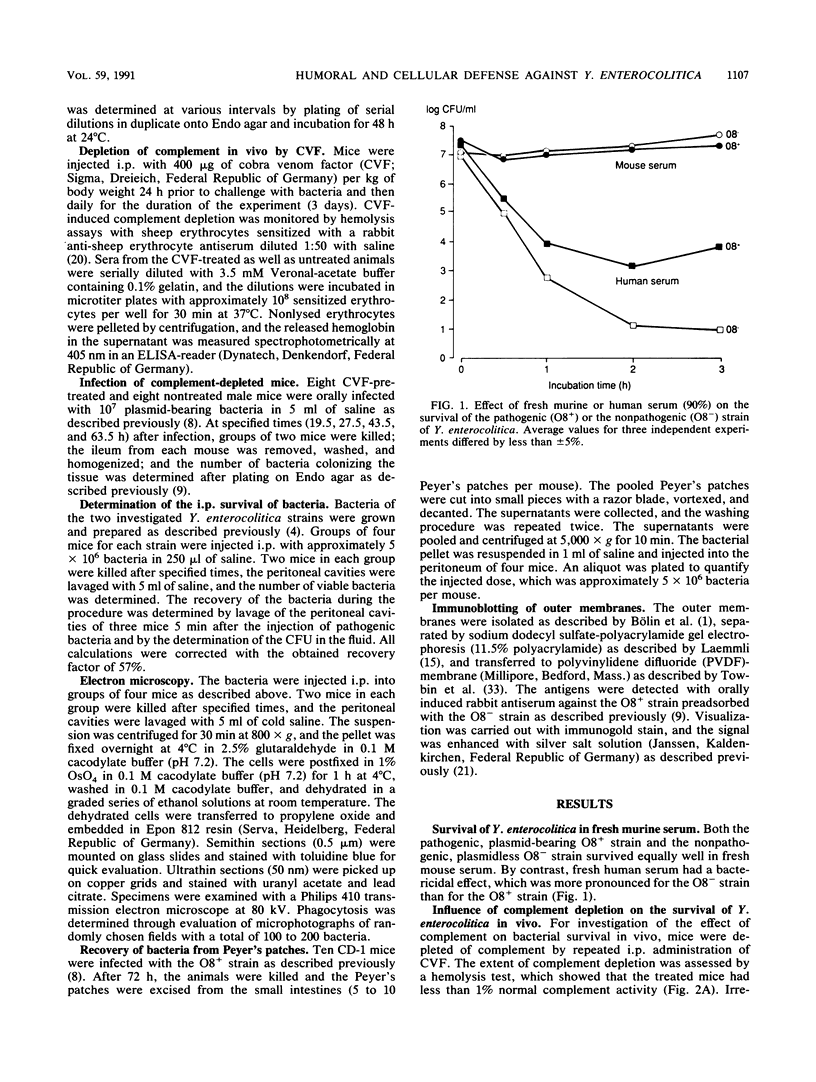
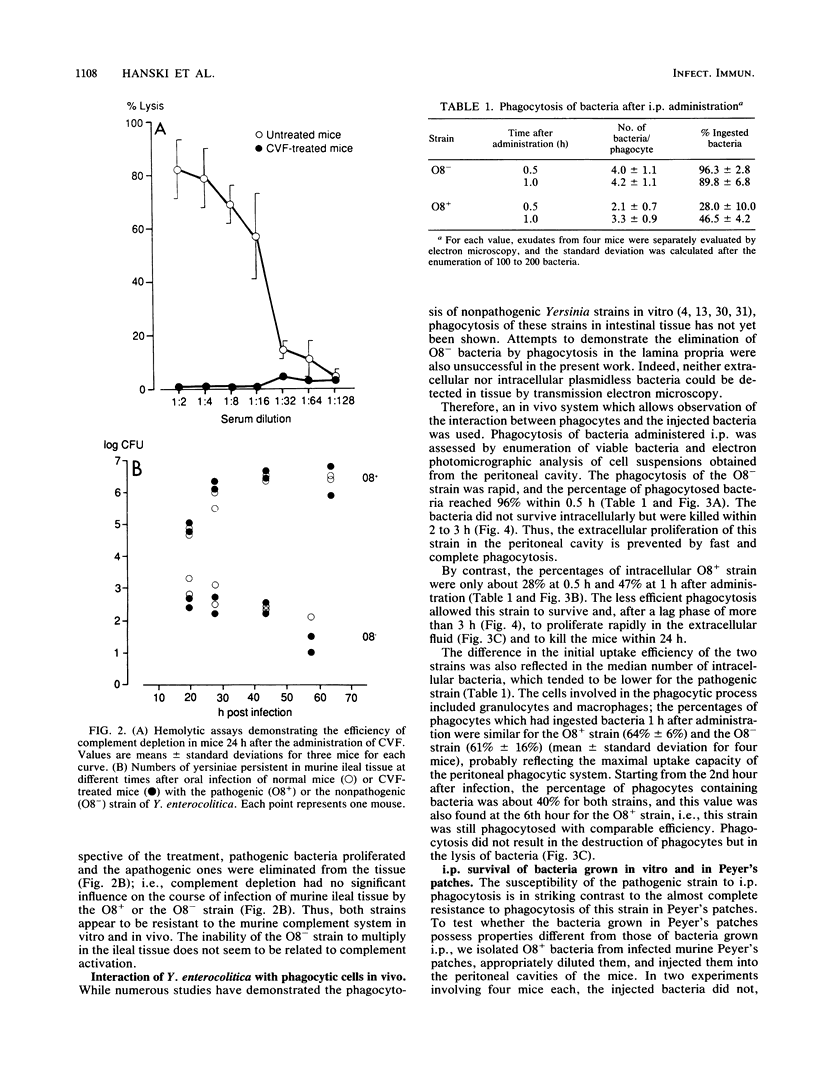
The role of phagocytes and the complement system as potential host defense mechanisms against bacterial infection were studied in mice with two isogenic strains of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O8 differing in pathogenicity because of differences in plasmid content. Complement depletion in mice by intraperitoneal injection of cobra venom factor did not affect the course of colonization of the intestinal tissue by each strain, indicating that in mice complement is not essential for the elimination of these bacteria. This conclusion is supported by the fact that fresh murine serum had no bactericidal effect in vitro either on the pathogenic or on the nonpathogenic strain. However, in the intestinal tissue as well as in the peritoneal cavity, only the pathogenic, plasmid-bearing Y. enterocolitica strain survived, while the nonpathogenic, plasmidless strain was rapidly eliminated. Since elimination from the peritoneal cavity is due to phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages, resistance to phagocytosis in vivo seems to be the decisive factor determining the virulence of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica strains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. The plasmid-encoded Yop2b protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is a virulence determinant regulated by calcium and temperature at the level of transcription. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):237–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B. Pathogenecity of Yersinia enterocolitica for mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):164–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.164-170.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnetzky W. T., Shuford W. W. Survival and growth of Yersinia pestis within macrophages and an effect of the loss of the 47-megadalton plasmid on growth in macrophages. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):234–241. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.234-241.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Simple model for the study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in leukopenic mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1067–1071. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1067-1071.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grützkau A., Hanski C., Hahn H., Riecken E. O. Involvement of M cells in the bacterial invasion of Peyer's patches: a common mechanism shared by Yersinia enterocolitica and other enteroinvasive bacteria. Gut. 1990 Sep;31(9):1011–1015. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.9.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H. Effects of Dextran Sulfate 500 on Cell-Mediated Resistance to Infection with Listeria monocytogenes in Mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1105–1109. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1105-1109.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski C., Kutschka U., Schmoranzer H. P., Naumann M., Stallmach A., Hahn H., Menge H., Riecken E. O. Immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study of interaction of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O8 with intestinal mucosa during experimental enteritis. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):673–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.673-678.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski C., Naumann M., Hahn H., Riecken E. O. Determinants of invasion and survival of Yersinia enterocolitica in intestinal tissue. An in vivo study. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1989;178(5):289–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00191063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartiala K. T., Granberg I., Toivanen A., Viljanen M. Inhibition of polymorphonuclear leucocyte functions in vivo by Yersinia enterocolitica lipopolysaccharide. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Jan;48(1):42–47. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Keller C., Morawa R., Schmidt N., Siemens H. J., Laufs R. Plasmids of human strains of Yersinia enterocolitica: molecular relatedness and possible importance for pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):107–115. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Laufs R. Double immunofluorescence microscopic technique for accurate differentiation of extracellularly and intracellularly located bacteria in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):168–175. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.168-175.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Intralysosomal accumulation of polyanions. I. Fusion of pinocytic and phagocytic vacuoles with secondary lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):866–874. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Hwang W. S., Kelly J. K., Pai C. H. Invasiveness of Yersinia enterocolitica lacking the virulence plasmid: an in-vivo study. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Nov;24(3):219–226. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-3-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Hwang W. S., Pai C. H. Plasmid-mediated resistance to phagocytosis in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1176–1183. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1176-1183.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Pai C. H. Inhibition of human neutrophil chemiluminescence by plasmid-mediated outer membrane proteins of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.145-151.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Carter P. B. Isolation and functional characteristics of adherent phagocytic cells from mouse Peyer's patches. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):769–774. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price S. B., Straley S. C. lcrH, a gene necessary for virulence of Yersinia pestis and for the normal response of Y. pestis to ATP and calcium. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1491–1498. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1491-1498.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers B., Mims C. A. Interaction of influenza virus with mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):751–757. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.751-757.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Forsberg A., Rimpiläinen M., Bergman T., Wolf-Watz H. The cytotoxic protein YopE of Yersinia obstructs the primary host defence. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):657–667. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet M., Richard S., Berche P. Electron microscopic evidence for in vivo extracellular localization of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis harboring the pYV plasmid. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):841–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.841-845.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M. Expression of antigens encoded by the virulence plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica under different growth conditions. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.183-190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Cibull M. L. Differential clearance and host-pathogen interactions of YopE- and YopK- YopL- Yersinia pestis in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1200–1210. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1200-1210.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Harmon P. A. Growth in mouse peritoneal macrophages of Yersinia pestis lacking established virulence determinants. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):649–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.649-654.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Harmon P. A. Yersinia pestis grows within phagolysosomes in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.655-659.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tertti R., Eerola E., Lehtonen O. P., Ståhlberg T. H., Viander M., Toivanen A. Virulence-plasmid is associated with the inhibition of opsonization in Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 May;68(2):266–274. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. In vivo comparison of avirulent Vwa- and Pgm- or Pstr phenotypes of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):895–900. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.895-900.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. Roles of V antigen in promoting virulence and immunity in yersiniae. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2226–2230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Nakajima R., Brubaker R. R. Roles of V antigen in promoting virulence in Yersiniae. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter E., Brade V. Influence of surface modulations by enzymes and monoclonal antibodies on alternative complement pathway activation by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1984–1989. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1984-1989.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]