Abstract
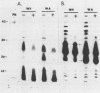
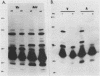
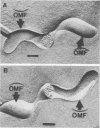
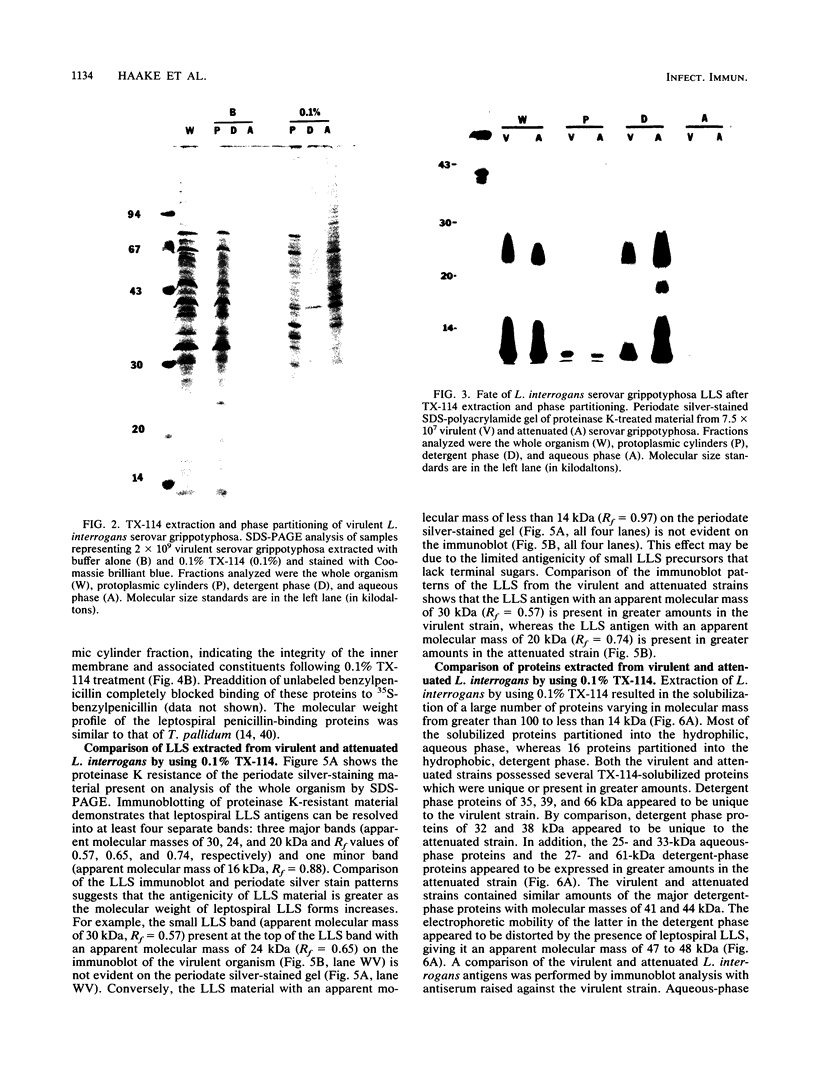
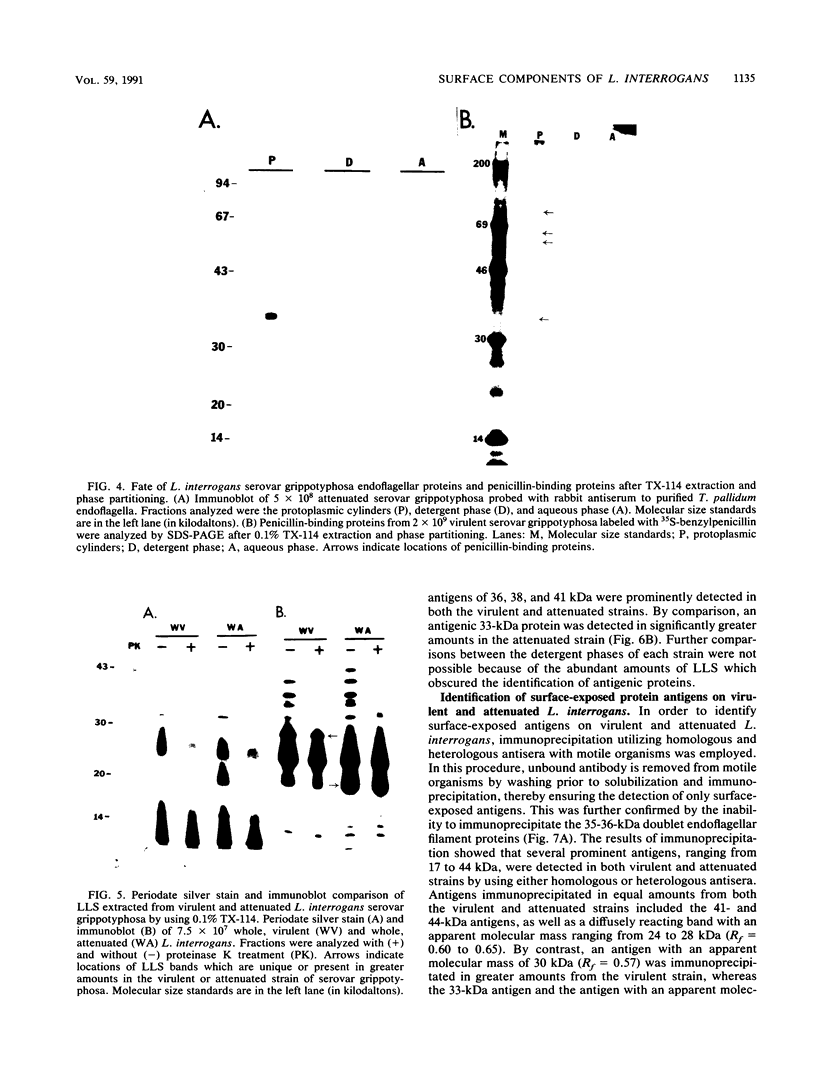
Surface components of virulent and attenuated Leptospira interrogans serovar grippotyphosa were compared by using Triton X-114 solubilization and phase partitioning, immunoprecipitation of intact organisms, and freeze-fracture electron microscopy. Removal of the leptospiral outer membrane by using 0.1% Triton X-114 was demonstrated by whole-mount electron microscopy and by essentially complete solubilization of a lipopolysaccharidelike substance (LLS) from the outer membrane. Triton X-114 (0.1%) did not solubilize subsurface proteins, such as endoflagellar filaments or penicillin-binding proteins, which are markers for the periplasmic space and inner membrane, respectively. Triton X-114 solubilized material from both the virulent and attenuated strains, which partitioned into the hydrophobic, detergent phase, contained LLS and major proteins of 41 and 44 kDa, which were also immunoprecipitable from intact organisms. The virulent strain contained greater amounts of an LLS component with an apparent molecular mass of 30 kDa (R(f) = 0.57), whereas the attenuated strain contained larger amounts of an LLS component with an apparent molecular mass of 20 kDa (R(f) = 0.74). Differences in protein components between virulent and attenuated organisms were also detected; whereas the 41- and 44-kDa proteins were immunoprecipitated in equal amounts from both the virulent and attenuated strains, a 33-kDa protein was immunoprecipitated in significantly greater amounts from the attenuated strain. Quantitation of outer membrane particle density by freeze-fracture electron microscopy showed that both strains had a low transmembrane outer membrane protein content compared with that of typical gram-negative bacteria. The virulent and attenuated strains had 443 and 990 particles (P less than 0.000001) per micron, respectively, in the concave outer membrane fracture face. These findings suggest that in vitro cultivation of L. interrogans is accompanied by quantitative and qualitative changes in both LLS and outer membrane-associated proteins.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Yanagawa R. Inhibition of leptospiral agglutination by the type-specific main antigens of leptospiras. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):466–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.466-467.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler B., Faine S. Serological cross-reactions of leptospiral lipopolysaccharide (F4) antigen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1979 Jul;244(2-3):291–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E. Role of fibronectin in the pathogenesis of syphilis. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9 (Suppl 4):S372–S385. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_4.s372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bey R. F., Johnson R. C. Humoral immune response of dogs vaccinated with leptospiral pentavalent outer envelope and whole culture vaccines. Am J Vet Res. 1978 May;39(5):831–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Walker E. M., Haake D. A., Champion C. I., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Complement activation limits the rate of in vitro treponemicidal activity and correlates with antibody-mediated aggregation of Treponema pallidum rare outer membrane protein. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1914–1921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt M. E., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Immunogenic integral membrane proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi are lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):983–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.983-991.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Brandt M. E., Erwin A. L., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Major integral membrane protein immunogens of Treponema pallidum are proteolipids. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2872–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2872-2877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Radolf J. D., Hsu P. L., Sell S., Norgard M. V. Genetic and physicochemical characterization of the recombinant DNA-derived 47-kilodalton surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.71-78.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinco M., Banfi E., Giani M., Gundelach M. L., Galanos C. Chemical and biological properties of a phenol-water extract from Leptospira interrogans. Evidence for the absence of lipopolysaccharide. Infection. 1988 Jul-Aug;16(4):238–241. doi: 10.1007/BF01650761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinco M., Banfi E., Panfili E. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharide banding patterns in Leptospira spp. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Apr;132(4):1135–1138. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-4-1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinco M., Banfi E., Panfili E. Leptospiral lipopolysaccharide presence in the outer envelope: electrophoretic evidence and immunological specificity. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;269(3):277–283. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Identification of Treponema pallidum penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5298–5300. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5298-5300.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. M., Walker E. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Selective release of the Treponema pallidum outer membrane and associated polypeptides with Triton X-114. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5789–5796. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5789-5796.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty J. P., Adler B., Rood J. I., Billington S. J., Faine S. Expression of two conserved leptospiral antigens in Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Feb;28(2):143–149. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-2-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everard C. O., Fraser-Chanpong G. M., Everard J. D. The incidence of severe leptospirosis in Trinidad. Trop Geogr Med. 1987 Apr;39(2):126–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faine S., Adler B., Palit A. Chemical, serological and biological properties of a serotype-specific polysaccharide antigen in Leptospira. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1974 Apr;52(2):311–319. doi: 10.1038/icb.1974.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H. Detection of antibody-accessible proteins on the cell surface of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):950–953. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.950-953.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata K., Ono E., Yanagawa R. Comparative studies of strains Ictero No. I and RGA as the type strain of Leptospira interrogans: agglutinin absorption test, protein and antigen profiles, and enzyme activities. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(8):817–832. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isogai E., Isogai H., Ito N. Decreased lipopolysaccharide content and enhanced susceptibility of leptospiras to serum leptospiricidal action and phagocytosis after treatment with diphenylamine. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Nov;262(4):438–447. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost B. H., Adler B., Faine S. Experimental immunisation of hamsters with lipopolysaccharide antigens of Leptospira interrogans. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):115–120. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost B. H., Adler B., Faine S. Reaction of monoclonal antibodies with species specific determinants in Leptospira interrogans outer envelope. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Sep;27(1):51–57. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost B. H., Adler B., Vinh T., Faine S. A monoclonal antibody reacting with a determinant on leptospiral lipopolysaccharide protects guinea pigs against leptospirosis. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Nov;22(3):269–275. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-3-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Naiki M., Yanagawa R. Isolation of the antigen-active components from leptospiral serovar-specific lipopolysaccharide antigen by mild acid hydrolysis. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1982 Jun;44(3):473–478. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.44.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelson J. S., Adler B., Chapman A. J., Faine S. Identification of leptospiral flagellar antigens by gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. J Med Microbiol. 1988 May;26(1):47–53. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A., Singer S. J. Anomalous interaction of the acetylcholine receptor protein with the nonionic detergent Triton X-114. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):958–962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzawa T., Nakamura R., Shimizu T., Iwamoto Y., Morita T., Yanagihara Y. Immunological characteristics of the glycolipid antigen of Leptospira interrogans serovar lai. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2502–2506. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2502-2506.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niikura M., Ono E., Yanagawa R. Molecular comparison of antigens and proteins of virulent and avirulent clones of Leptospira interrogans serovar copenhageni, strain Shibaura. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Oct;266(3-4):453–462. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Edwards P. L., Thiermann A. B., Bassford P. J., Jr, Stamm L. V. Identification and characterization of the protein antigens of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):492–497. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.492-497.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Cockayne A., Bailey M. J. The outer membrane of Treponema pallidum: biological significance and biochemical properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2349–2357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Chamberlain N. R., Clausell A., Norgard M. V. Identification and localization of integral membrane proteins of virulent Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by phase partitioning with the nonionic detergent triton X-114. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):490–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.490-498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Moomaw C., Slaughter C. A., Norgard M. V. Penicillin-binding proteins and peptidoglycan of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1248–1254. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1248-1254.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V., Schulz W. W. Outer membrane ultrastructure explains the limited antigenicity of virulent Treponema pallidum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2051–2055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segers R. P., van der Drift A., de Nijs A., Corcione P., van der Zeijst B. A., Gaastra W. Molecular analysis of a sphingomyelinase C gene from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2177–2185. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2177-2185.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Matsusaka E., Nagakura N., Takayanagi K., Masuzawa T., Iwamoto Y., Morita T., Mifuchi I., Yanagihara Y. Chemical properties of lipopolysaccharide-like substance (LLS) extracted from Leptospira interrogans serovar canicola strain Moulton. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(8):717–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Matsusaka E., Takayanagi K., Masuzawa T., Iwamoto Y., Morita T., Mifuchi I., Yanagihara Y. Biological activities of lipopolysaccharide-like substance (LLS) extracted from Leptospira interrogans serovar canicola strain Moulton. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(8):727–735. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimono E., Sugiyama K., Yanagawa R. Specificity of serovar-specific main antigens of leptospiras shown by the inhibition of leptospiral microscopic agglutination. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1979 Dec;41(6):623–628. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.41.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Hodinka R. L., Wyrick P. B., Bassford P. J., Jr Changes in the cell surface properties of Treponema pallidum that occur during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2255–2261. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2255-2261.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Molecular characterization of the pathogen-specific, 34-kilodalton membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3314–3323. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3314-3323.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B. Leptospirosis: current developments and trends. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Mar 15;184(6):722–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Putative Treponema pallidum cytadhesins share a common functional domain. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):833–835. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.833-835.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins and the antibacterial effectiveness of beta-lactam antibiotics. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;8 (Suppl 3):S260–S278. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_3.s260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres J., Yanagawa R., Ono E. Inhibition of Leptospiricidal reaction by the type-specific main antigen of Leptospira. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981;250(1-2):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinh T., Adler B., Faine S. Ultrastructure and chemical composition of lipopolysaccharide extracted from Leptospira interrogans serovar copenhageni. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jan;132(1):103–109. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. M., Zampighi G. A., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Demonstration of rare protein in the outer membrane of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by freeze-fracture analysis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5005–5011. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5005-5011.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeigler J. A., VanEseltine W. P. Isolation and chemical characterization of outer envelope of Leptospira pomona. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jul;21(7):1102–1112. doi: 10.1139/m75-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]