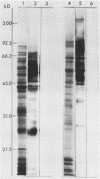
Abstract
An adaptation of the immunoblotting technique was used to investigate binding interactions between Trypanosoma cruzi and mammalian host cells at the molecular level. A specific binding interaction was observed between T. cruzi and two host cell membrane polypeptides with molecular masses of approximately 32 and 34 kilodaltons. This molecular interaction was observed with antigen extracts of T. cruzi and with live, infective trypomastigote stages of the parasite, suggesting that the observed phenomenon may have relevance to the initial attachment of the parasite to the host cell membrane before invasion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer E. A., Skutelsky E., Wilchek M. The avidin-biotin complex in affinity cytochemistry. Methods Enzymol. 1979;62:308–315. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)62235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti M. A., Piras M. M., Henríquez D., Piras R. The interaction of a Trypanosoma cruzi surface protein with Vero cells and its relationship with parasite adhesion. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jun;24(2):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M., Kalish D. I., Jacobson B. S., Branton D. Membrane isolation on polylysine-coated beads. Plasma membrane from HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Oct;75(1):119–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csete M., Lev B. I., Pereira M. E. An influenza virus model for Trypanosoma cruzi infection: interactive roles for neuraminidase and lectin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;117:153–165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70538-0_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak J. A., Crane M. S. Vertebrate cell cycle modulates infection by protozoan parasites. Science. 1981 Nov 27;214(4524):1034–1036. doi: 10.1126/science.7029713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak J. A. The natural heterogeneity of Trypanosoma cruzi: biological and medical implications. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(4):357–371. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Engvall E., A'Hearn E., Barnes D., Pierschbacher M., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment on replicas of SDS polyacrylamide gels reveals two adhesive plasma proteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):20–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriquez D., Piras R., Piras M. M. The effect of surface membrane modifications of fibroblastic cells on the entry process of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Apr;2(5-6):359–366. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson B. S. Imporved method for isolation of plasma membrane on cationic beads. Membranes from Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 14;600(3):769–780. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90479-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keirszenbaum F., Stiles B. Evidence supporting the existence of a host cell surface receptor for Trypanosoma cruzi. J Protozool. 1985 May;32(2):364–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R. E., Murnane J. E. Trypanosoma cruzi: immune destruction of parasitized mouse fibroblasts in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Feb;41(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meirelles M. N., Martinez-Palomo A., Souto-Padron T., De Souza W. Participation of concanavalin A binding sites in the interaction between Trypanosoma cruzi and macrophages. J Cell Sci. 1983 Jul;62:287–299. doi: 10.1242/jcs.62.1.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: mechanism of entry and intracellular fate in mammalian cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1402–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuna A., Ortega G., Gamarro F., Castanys S., Mascaro M. C. Some factors affecting the in vitro invasion of HeLa cells by Trypanosoma cruzi. Int J Parasitol. 1984 Jun;14(3):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(84)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouaissi M. A., Cornette J., Capron A. Identification and isolation of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigote cell surface protein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Jun;19(3):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piras M. M., Henriquez D., Piras R. The effect of proteolytic enzymes and protease inhibitors on the interaction Trypanosoma cruzi-fibroblasts. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Feb;14(2):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell M. R., Kuhn R. E. Measurement of cytolytic antibody in experimental Chagas' disease using a terminal radiolabelling procedure. J Parasitol. 1980 Jun;66(3):399–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pung O. J., Kuhn R. E. Experimental American leishmaniasis in the Brazilian squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus): lesions, hematology, cellular, and humoral immune responses. J Med Primatol. 1987;16(3):165–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D. The cell surface of Trypanosoma cruzi. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;117:75–92. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70538-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarleton R. L., Schafer R., Kuhn R. E. Effects of extracts of Trypanosoma cruzi on immune responses: induction of a nonspecific suppressor factor. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):978–986. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.978-986.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velge P., Ouaissi M. A., Cornette J., Afchain D., Capron A. Identification and isolation of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigote collagen-binding proteins: possible role in cell-parasite interaction. Parasitology. 1988 Oct;97(Pt 2):255–268. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000058467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenian A., Kierszenbaum F. Inhibition of macrophage-Trypanosoma cruzi interaction by concanavalin A and differential binding of bloodstream and culture forms to the macrophage surface. J Parasitol. 1982 Jun;68(3):408–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingales B., Colli W. Trypanosoma cruzi: interaction with host cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;117:129–152. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70538-0_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]