Abstract
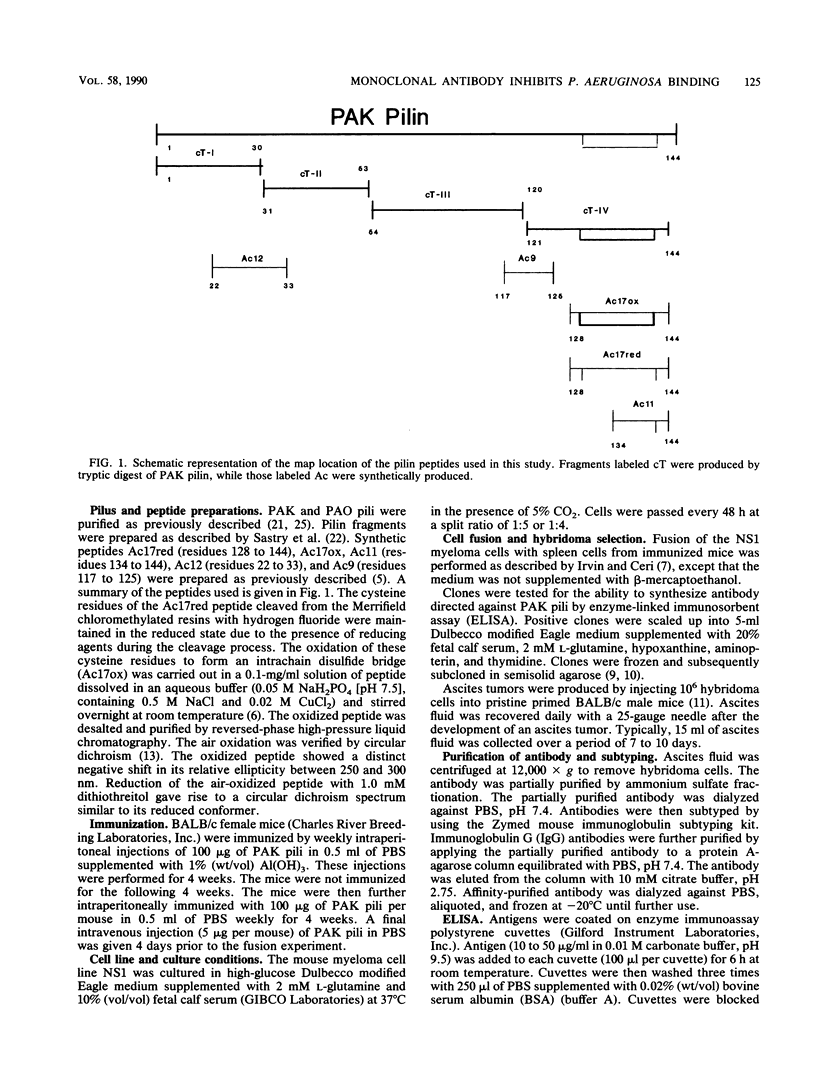
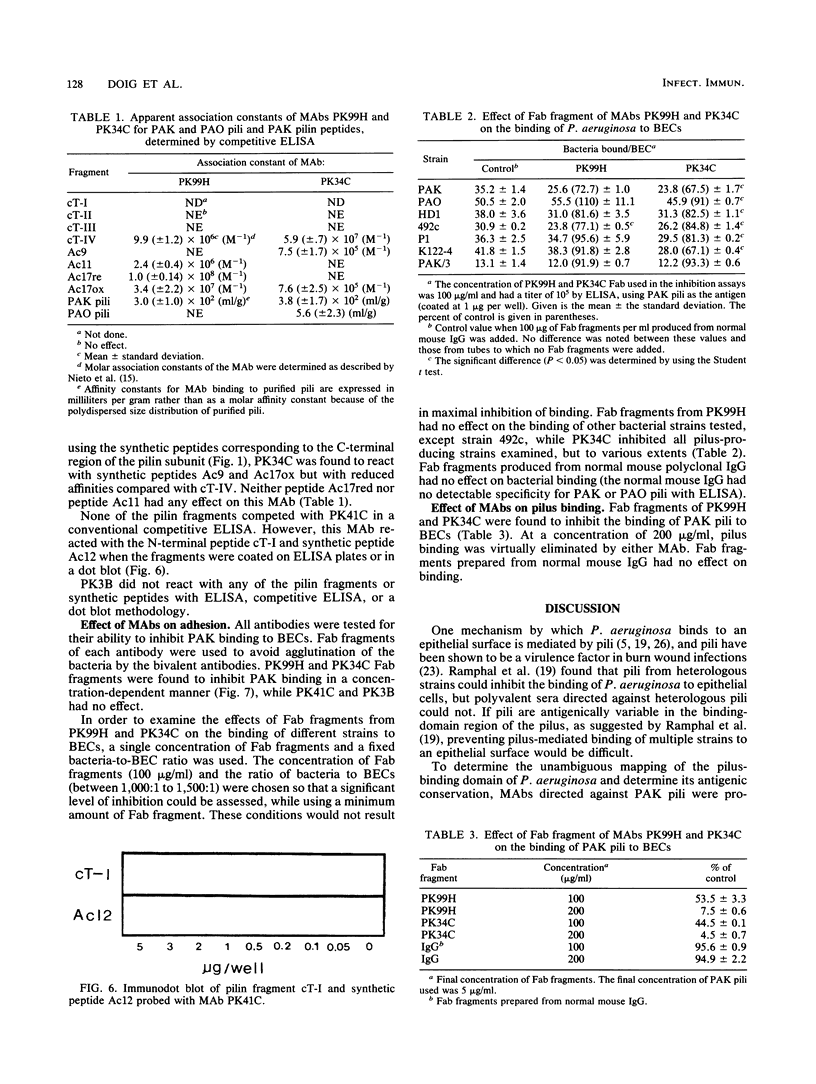
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilus is capable of mediating the binding of this strain to human respiratory epithelial cells. We have produced monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to the PAK pilus in order to elucidate the location of the binding domain of the pilus for human buccal epithelial cells (BECs). Four MAbs are described. MAbs PK41C and PK34C were found to react with P. aeruginosa pilins produced by a large number of strains. The epitope recognized by PK41C was determined to lie within the N-terminal region of the pilin and is likely constituted by amino acid residues 22 through 33. The epitope for PK34C was located in the C-terminal region of the pilin and was partially dependent on an intact intrachain disulfide bridge between cysteine residues 129 and 142. PK99H and PK3B were found to react specifically with PAK pilin. The epitope for PK99H was also localized in the C-terminal region of the pilin protein and appears to reside between amino acid residues 130 and 138. The epitope for PK3B was not localized by using the methods of this study, but it is likely dependent on the three-dimensional structure of the pilin. Fab fragments of PK99H inhibited adhesion of strains PAK and 492c to BECs, but the adherence of five other strains was not affected. Fab fragments of PK34C inhibited adhesion of all piliated strains examined. Fab fragments from both of these antibodies inhibited PAK pilus binding to BECs. Fab fragments of PK41C and PK3B had no effect on P. aeruginosa binding to BECs. These results confirm that the C-terminal region of the pilin has adhesin qualities and that a conserved epitope lies within this region.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley D. E. A function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO polar pili: twitching motility. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):146–154. doi: 10.1139/m80-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Pitt T. L. Pilus-dependence of four Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages with non-contractile tails. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Todd T., Sastry P. A., Lee K. K., Hodges R. S., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. Role of pili in adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human respiratory epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1641-1646.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges R. S., Saund A. K., Chong P. C., St-Pierre S. A., Reid R. E. Synthetic model for two-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coils. Design, synthesis, and characterization of an 86-residue analog of tropomyosin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1214–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Ceri H. Immunochemical examination of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycocalyx: a monoclonal antibody which recognizes L-guluronic acid residues of alginic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Mar;31(3):268–275. doi: 10.1139/m85-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Govan J. W., Fyfe J. A., Costerton J. W. Heterogeneity of antibiotic resistance in mucoid isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa obtained from cystic fibrosis patients: role of outer membrane proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1056–1063. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Gerhard W., Croce C. M. Production of antibodies against influenza virus by somatic cell hybrids between mouse myeloma and primed spleen cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2985–2988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsoukas J. M., Scanlon M. N., Moore G. J. A cyclic angiotensin antagonist: [1,8-cysteine]angiotensin II. J Med Chem. 1984 Mar;27(3):404–406. doi: 10.1021/jm00369a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEachran D. W., Irvin R. T. Adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human buccal epithelial cells: evidence for two classes of receptors. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Jun;31(6):563–569. doi: 10.1139/m85-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto A., Gaya A., Jansa M., Moreno C., Vives J. Direct measurement of antibody affinity distribution by hapten-inhibition enzyme immunoassay. Mol Immunol. 1984 Jun;21(6):537–543. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Sastry P. A., Volpel K., Loh B. A., Speert D. P. Fimbriae (pili): molecular basis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa adherence. Clin Invest Med. 1986;9(2):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasloske B. L., Finlay B. B., Paranchych W. Cloning and sequencing of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilin gene. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):408–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80821-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasloske B. L., Sastry P. A., Finlay B. B., Paranchych W. Two unusual pilin sequences from different isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3738–3741. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3738-3741.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Sadoff J. C., Pyle M., Silipigni J. D. Role of pili in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to injured tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.38-40.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M., Nicotra M. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid strain. Its significance in adult chest diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):833–836. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Finlay B. B., Pasloske B. L., Paranchych W., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B. Comparative studies of the amino acid and nucleotide sequences of pilin derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK and PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):571–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.571-577.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B., Paranchych W. Studies on the primary structure and antigenic determinants of pilin isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa K. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;63(4):284–291. doi: 10.1139/o85-042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Okinaga K., Saito H. Role of pili in the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infection. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(2):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Sastry P. A., Hodges R. S., Paranchych W. Mapping of the antigenic determinants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK polar pili. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):113–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.113-121.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]