Abstract
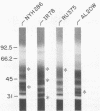
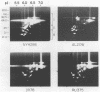
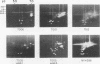
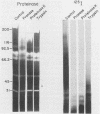
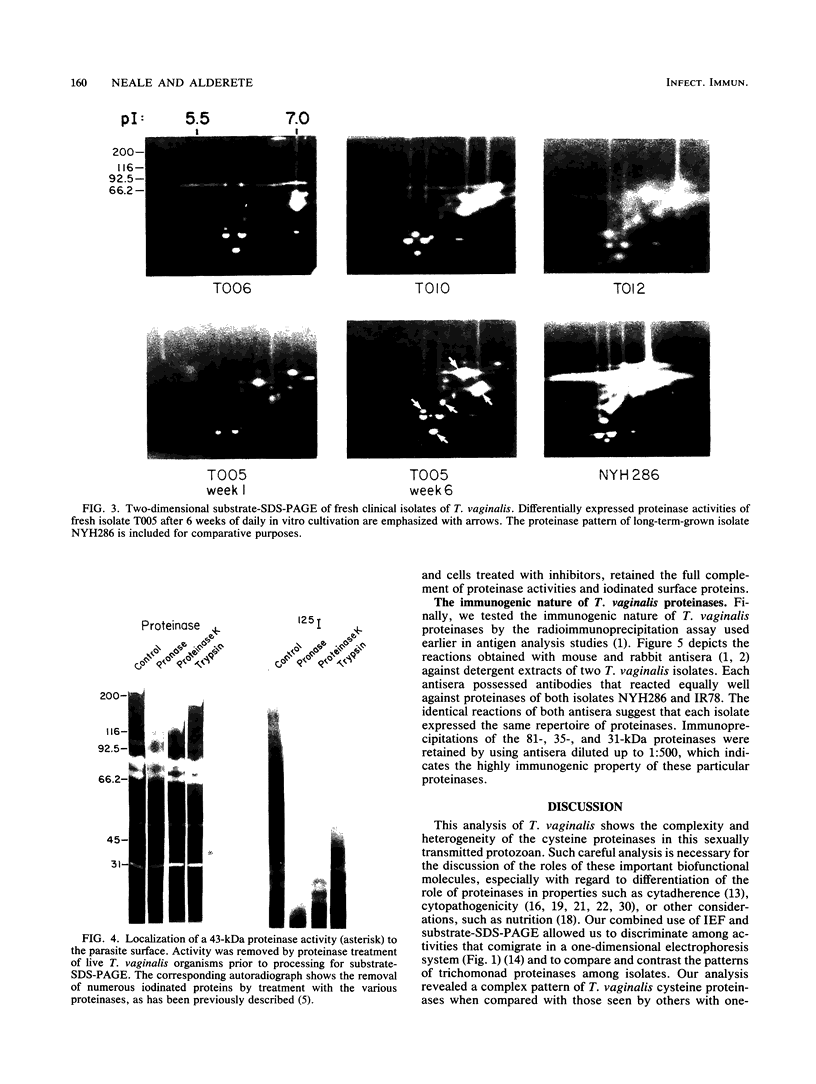
Isoelectric focusing and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) with acrylamide copolymerized with gelatin (substrate-SDS-PAGE) were combined to evaluate the proteinases of both long-term-grown and fresh isolates of Trichomonas vaginalis. This two-dimensional substrate-SDS-PAGE resolved as many as 23 distinct proteinase activities in several isolates, and proteinases had relative molecular masses between 23 and 110 kilodaltons (kDa). Isoelectric points (pI) of proteinases ranged from 5.7 to 7.0. Overall, the various representative proteinase profiles were similar among those of long-term-grown and fresh isolates, although heterogeneity existed among several cysteine proteinase activities. Pattern changes were detected in fresh isolates passaged over several weeks, showing the ability of proteinases to be differentially expressed and to undergo phase variation. The two-dimensional proteinase patterns were very reproducible for isolates analyzed over a certain period of time before expression of some proteinases varied. The heterogeneity and differential expression of certain proteinases were not coordinated with phenotypic variation of already characterized immunogens and adhesins. Data suggesting that a 43-kDa proteinase resided on the parasite surface were obtained on the basis of removal of activity following pronase or proteinase K treatment of live organisms. Finally, immunized experimental animals produced antibody to many T. vaginalis proteinases, which indicates the immunogenic nature of trichomonad proteinases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F. Antigen analysis of several pathogenic strains of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1041–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1041-1047.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Demes P., Gombosová A., Valent M., Yánoska A., Fabusová H., Kasmala L., Garza G. E., Metcalfe E. C. Phenotypes and protein-epitope phenotypic variation among fresh isolates of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1037–1041. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1037-1041.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Demeś P., Gombosova A., Valent M., Fabusová M., Jánoska A., Stefanovic J., Arroyo R. Specific parasitism of purified vaginal epithelial cells by Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2558–2562. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2558-2562.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for detecting antibody to Trichomonas vaginalis: use of whole cells and aqueous extract as antigen. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Jun;60(3):164–170. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.3.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G. E. Identification and properties of Trichomonas vaginalis proteins involved in cytadherence. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.28-33.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G. E. Soluble Trichomonas vaginalis antigens in cell-free culture supernatants. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Oct;13(2):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G. E. Specific nature of Trichomonas vaginalis parasitism of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):701–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.701-708.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G., Smith J., Spence M. Trichomonas vaginalis: electrophoretic analysis and heterogeneity among isolates due to high-molecular-weight trichomonad proteins. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Apr;61(2):244–251. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Kasmala L., Metcalfe E., Garza G. E. Phenotypic variation and diversity among Trichomonas vaginalis isolates and correlation of phenotype with trichomonal virulence determinants. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):285–293. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.285-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major glycoprotein immunogen mediates differential complement-independent lysis of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):697–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.697-699.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Neale K. A. Relatedness of structures of a major immunogen in Trichomonas vaginalis isolates. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1849–1853. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1849-1853.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Suprun-Brown L., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major surface glycoprotein immunogen differentiates isolates and subpopulations of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.70-75.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo R., Alderete J. F. Trichomonas vaginalis surface proteinase activity is necessary for parasite adherence to epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):2991–2997. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.2991-2997.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs G. H., North M. J. An analysis of the proteinases of Trichomonas vaginalis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Parasitology. 1983 Feb;86(Pt 1):1–6. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000057103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND L. S. The establishment of various trichomonads of animals and man in axenic cultures. J Parasitol. 1957 Aug;43(4):488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber G. E., Lemchuk-Favel L. T., Bowie W. R. Isolation of a cell-detaching factor of Trichomonas vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1548–1553. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1548-1553.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heussen C., Dowdle E. B. Electrophoretic analysis of plasminogen activators in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate and copolymerized substrates. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigberg B. M., Livingston M. C., Frost J. K. Pathogenicity of fresh isolates of Trichomonas vaginalis: "the mouse assay" versus clinical and pathologic findings. Acta Cytol. 1966 Sep-Oct;10(5):353–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Holmes K. K., Spence M. R., Rein M. F., McCormack W. M., Tam M. R. Geographic variation among isolates of Trichomonas vaginalis: demonstration of antigenic heterogeneity by using monoclonal antibodies and the indirect immunofluorescence technique. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):979–984. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Poisson M. A., Rein M. F. Beta-hemolytic activity of Trichomonas vaginalis correlates with virulence. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1291–1295. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1291-1295.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulda J., Honigberg B. M., Frost J. K., Hollander D. H. Pathogenicity of Trichomonas vaginalis. a clinical and biologic study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Nov 15;108(6):908–918. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(70)90333-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood B. C., North M. J., Coombs G. H. The release of hydrolases from Trichomonas vaginalis and Tritrichomonas foetus. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Aug;30(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood B. C., North M. J., Coombs G. H. Trichomonas vaginalis, Tritrichomonas foetus, and Trichomitus batrachorum: comparative proteolytic activity. Exp Parasitol. 1984 Dec;58(3):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(84)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood B. C., North M. J., Scott K. I., Bremner A. F., Coombs G. H. The use of a highly sensitive electrophoretic method to compare the proteinases of trichomonads. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 May;24(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North M. J. Comparative biochemistry of the proteinases of eucaryotic microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Sep;46(3):308–340. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.3.308-340.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pindak F. F., Gardner W. A., Jr, Mora de Pindak M. Growth and cytopathogenicity of Trichomonas vaginalis in tissue cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):672–678. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.672-678.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]