Abstract
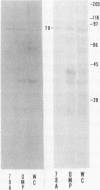
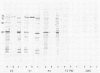
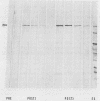
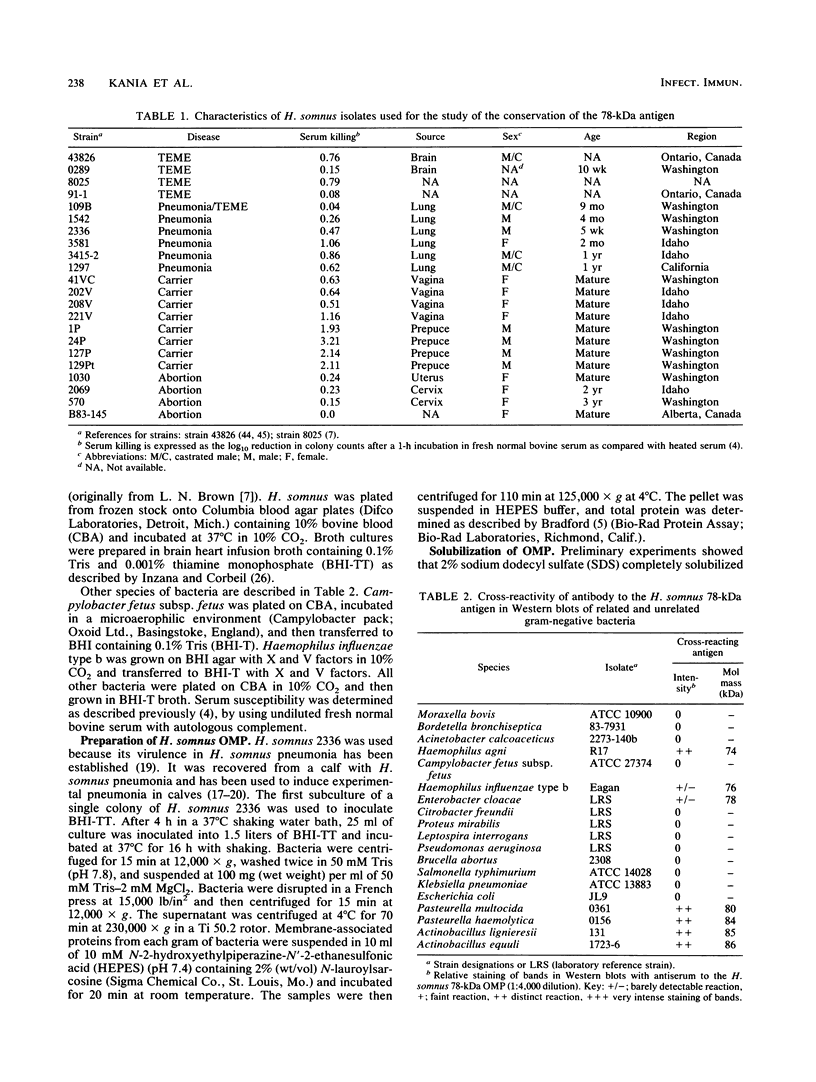
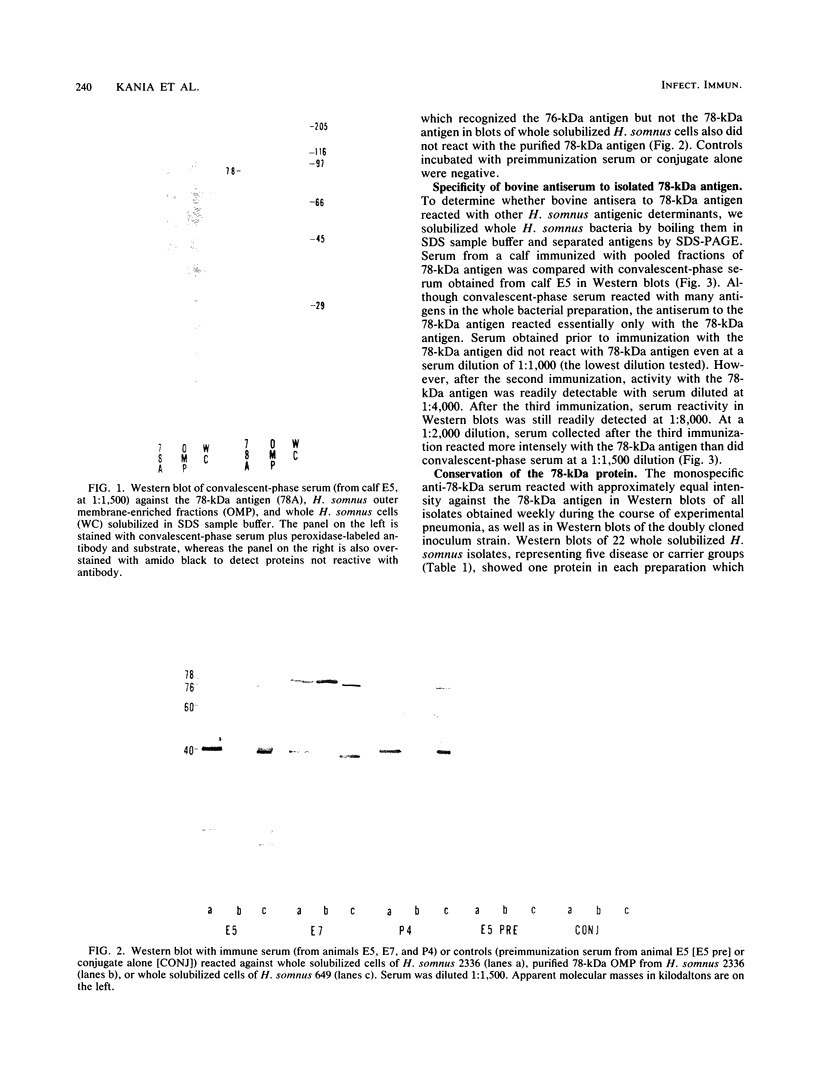
A 78-kilodalton (kDa) outer membrane protein (OMP) of Haemophilus somnus was one of the two antigens most consistently and most intensely immunoreactive in Western immunoblots of whole cells of H. somnus reacted with convalescent-phase serum obtained from cattle with experimental H. somnus pneumonia. This antigen was isolated by gel filtration chromatography of sodium dodecyl sulfate-solubilized OMP. Reactions of Western blots with bovine monospecific antiserum prepared against the 78-kDa antigen indicated that this 78-kDa OMP was present in each of 22 isolates of H. somnus obtained from cattle with pneumonia, thromboembolic meningoencephalitis, and abortion as well as from vaginal or preputial carriers. The 78-kDa OMP was also present in each isolate obtained weekly throughout the course of experimental H. somnus pneumonia in a calf. Monospecific antiserum to the 78-kDa OMP also reacted with proteins from closely related bacterial species in the family Pasteurellaceae but not with bacteria of 13 other genera. The 78-kDa OMP of H. somnus is of interest because it is surface accessible, highly conserved, immunogenic, cross-reactive with other members of the family Pasteurellaceae, and reactive with convalescent-phase serum which is passively protective against H. somnus pneumonia.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. J., Anderson T. D., Slife L. N., Stevenson G. W. Microscopic lesions associated with the isolation of Haemophilus somnus from pneumonic bovine lungs. Vet Pathol. 1985 Mar;22(2):131–136. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailie W. E., Anthony H. D., Weide K. D. Infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalomyelitis (sleeper syndrome) in feedlot cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1966 Jan 15;148(2):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J. Protection by serum antibodies in experimental nontypable Haemophilus influenzae otitis media. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):572–578. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.572-578.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau K. A., Ward A. C., Prieur D. J., Corbeil L. B. Serum susceptibility of bovine pasteurellas. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Apr;51(2):157–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur B. R., Larose Y., Tsang P., Hamel J., Ashton F., Ryan A. Protection against infection with Neisseria meningitidis group B serotype 2b by passive immunization with serotype-specific monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):510–516. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.510-516.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canto G. J., Biberstein E. L. Serological diversity in Haemophilus somnus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1009–1015. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1009-1015.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canto J., Biberstein E. L., Schulte T. A., Behymer D. Cross-reactivity of Haemophilus somnus antibody in agglutination and complement fixation tests and in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):500–506. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.500-506.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R. Pasteurellosis: Pasteurella multocida and Pasteurella hemolytica. Adv Vet Sci. 1967;11:321–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chladek D. W. Bovine abortion associated with Haemophilus somnus. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Jul;36(7):1041–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Gentry M. J., Fulton R. W. Immunologic response to Pasteurella haemolytica and resistance against experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis, induced by bacterins in oil adjuvants. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Feb;48(2):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Arthur J. E., Widders P. R., Smith J. W., Barbet A. F. Antigenic specificity of convalescent serum from cattle with haemophilus somnus-induced experimental abortion. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1381–1386. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1381-1386.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Chikami G., Yarnall M., Smith J., Guiney D. G. Cloning and expression of genes encoding Haemophilus somnus antigens. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2736–2742. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2736-2742.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Schurig G. G., Bier P. J., Winter A. J. Bovine veneral vibriosis: antigenic variation of the bacterium during infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.240-244.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Widders P. R., Gogolewski R., Arthur J., Inzana T. J., Ward A. C. Haemophilus somnus: Bovine Reproductive and Respiratory Disease. Can Vet J. 1986 Feb;27(2):90–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Kania S. A., Inzana T. J., Widders P. R., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Protective ability and specificity of convalescent serum from calves with Haemophilus somnus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1403–1411. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1403-1411.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Kania S. A., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Protective ability of antibodies against 78- and 40-kilodalton outer membrane antigens of Haemophilus somnus. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2307–2316. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2307-2316.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Leathers C. W., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Experimental Haemophilus somnus pneumonia in calves and immunoperoxidase localization of bacteria. Vet Pathol. 1987 May;24(3):250–256. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Schaefer D. C., Wasson S. K., Corbeil R. R., Corbeil L. B. Pulmonary persistence of Haemophilus somnus in the presence of specific antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1767–1774. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1767-1774.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagblom P., Segal E., Billyard E., So M. Intragenic recombination leads to pilus antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):156–158. doi: 10.1038/315156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindennach I., Henning U. The major proteins of the Excherichia coli outer cell envelope membrane. Preparative isolation of all major membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Stephens L. R., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Thorsen J. Prevalence and distribution of Haemophilus somnus in the male bovine reproductive tract. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):791–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Corbeil L. B. Development of a defined medium for Haemophilus somnus isolated from cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Mar;48(3):366–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY P. C., BIBERSTEIN E. L., HOWARTH J. A., FRAZIER L. M., DUNGWORTH D. L. Infectious meningo-encephalitis in cattle, caused by a haemophilus-like organism. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Mar;21:403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. A minor high-molecular-weight outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b is a protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):253–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.253-259.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh H. V., Pedersen K. B., Blom E. Haemophilus somnus in semen from Danish bulls. Vet Rec. 1983 May 7;112(19):460–460. doi: 10.1136/vr.112.19.460-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R. Protection of infant rats from Haemophilus influenzae type b infection by antiserum to purified outer membrane protein a. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2612–2618. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2612-2618.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Acres S., Janzen E., Willson P., Allen B. A field trial of preshipment vaccination of calves. Can Vet J. 1984 Mar;25(3):145–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Musoke A. J. Biologic activities of bovine IgG subclasses. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;137:359–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. B., Lein D. H., McEntee K. E., Hall C. E., Shin S. Haemophilus somnus infection of the reproductive tract of cattle: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jun 15;182(12):1390–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nansen P. Selective immunoglobulin deficiency in cattle and susceptibility to infection. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D. G., Shreeve J., Bradley R. The experimental infection of calves with a British strain of Haemophilus somnus. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Jan;26(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfaçon D., Higgins R. Epidemiology of Haemophilus somnus infection in dairy cattle in Quebec. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Oct;47(4):456–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfaçon D., Higgins R., Mittal K. R., L'Archevêque G. Haemophilus somnus: a comparison among three serological tests and a serological survey in beef and dairy cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Jul;47(3):304–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R. S., Sparling P. F., Cannon J. G. Variation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae protein II among isolates from an outbreak caused by a single gonococcal strain. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):250–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.250-252.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Vaccination of calves with leukotoxic culture supernatant from Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jan;52(1):30–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Barnum D. A. Morphological, biochemical, antigenic, and cytochemical relationships among Haemophilus somnus, Haemophilus agni, Haemophilus haemoglobinophilus, Histophilus ovis, and Actinobacillus seminis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):728–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.728-737.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B. Ultrastructure of Haemophilus somnus, causative agent of bovine infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Sep;42(9):1638–1640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Humoral immunity in experimental thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle caused by Haemophilus somnus. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Mar;42(3):468–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Isolation of Haemophilus somnus antigens and their use as vaccines for prevention of bovine thromboembolic meningoencephalitis. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Feb;45(2):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. L. Evaluation of attenuated, live staphylococcal mastitis vaccine in lactating heifers. J Dairy Sci. 1984 Nov;67(11):2608–2613. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(84)81620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. L. Immunologically-specific resistance to infection with particular reference to staphylococcal mastitis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;137:579–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. L. Serological response of sheep to live and killed Staphylococcus aureus vaccines. Vaccine. 1987 Dec;5(4):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Dorrance L. A., Yarnall M., Corbeil L. B. Immunoglobulin-binding activity among pathogenic and carrier isolates of Haemophilus somnus. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):639–642. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.639-642.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Dowling S. C., Gogolewski R. P., Smith J. W., Corbeil L. B. Isotypic antibody responses in cattle infected with Haemophilus somnus. Res Vet Sci. 1989 Mar;46(2):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Paisley L. G., Gogolewski R. P., Evermann J. F., Smith J. W., Corbeil L. B. Experimental abortion and the systemic immune response to "Haemophilus somnus" in cattle. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):555–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.555-560.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak K., Diaz J. L., Jackson D., Heckels J. E. Antigenic variation during infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae: detection of antibodies to surface proteins in sera of patients with gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):166–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dreumel A. A., Kierstead M. Abortion associated with Hemophilus somnus infection in a bovine fetus. Can Vet J. 1975 Dec;16(12):367–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]