Abstract
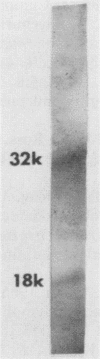
Lectin-binding proteins of chlamydiae were detected by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. All three Chlamydia species tested expressed two proteins when whole-elementary-body lysates were reacted with the biotinylated lectin Dolichos biflorus agglutinin. The protein with a molecular mass of 18 kilodaltons (kDa) responded strongly compared with a higher-molecular-mass protein that varied from 27 to 32 kDa with each chlamydia strain tested. Among six lectins tested, including concanavalin A, D. biflorus agglutinin, Ulex europaeus agglutinin, soybean agglutinin, peanut agglutinin, and wheat germ agglutinin, the latter was the only lectin that did not recognize any chlamydial protein. For each lectin that reacted against the elementary body of serovar L2 of Chlamydia trachomatis, the same two peptides, an 18-kDa peptide and a 32-kDa peptide, were revealed. These two polypeptides adhered to HeLa cell surface components. Binding of a lectin to the L2 reticulate body resulted in a reduced response at the 18-kDa peptide. The 18- and 32-kDa peptides were purified from L2 serovar elementary bodies by affinity chromatography. The two proteins isolated from a concanavalin A-agarose column maintained their lectin-binding capacities and elicited hemagglutinating properties against mouse erythrocytes. Periodate oxidation abolished the abilities of the peptides to adhere to any of the lectins tested. These results suggest that these lectin-binding proteins are glycoproteins that may be an essential factor for attachment of chlamydial organisms to host cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bose S. K., Smith G. B., Paul R. G. Influence of lectins, hexoses, and neuraminidase on the association of purified elementary bodies of Chlamydia trachomatis UW-31 with HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1060–1067. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1060-1067.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kuo C. C., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of Chlamydiae by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. I. Antigenic heterogeneity between C. trachomatis and C. psittaci. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):963–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOGOLAK F. M., ROSS M. R. The properties and chemical nature of the psittacosis virus hemagglutinin. Virology. 1955 Dec;1(5):474–496. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON F. B., QUAN A. L. OCCURENCE OF GLYCOGEN IN INCLUSIONS OF THE PSITTACOSIS-LYMPHOGRANULOMA VENEREUM-TRACHOMA AGENTS. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:186–196. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon B. B., Pena S. D. The surface glycoproteins of human skin fibroblasts detected after electrophoresis by the binding of peanut (Arachis hypogaea) agglutinin and Ricinus communis (castor-bean) agglutinin I. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 15;208(2):351–358. doi: 10.1042/bj2080351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLEMAN M. R., HAIG D. A., HELMOLD R. J. The indirect complement fixation hemagglutination and conglutinating complement absorption tests for viruses of the psittacosis-lymphogranuloma venereum group. J Immunol. 1951 Jan;66(1):115–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T. Identification and properties of chlamydial polypeptides that bind eucaryotic cell surface components. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.13-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijimoto-Ochiai S., Katagiri Y. U., Ochiai H. Analysis of N-linked oligosaccharide chains of glycoproteins on nitrocellulose sheets using lectin-peroxidase reagents. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 15;147(1):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Chi E. Y. Ultrastructural study of Chlamydia trachomatis surface antigens by immunogold staining with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1324–1328. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1324-1328.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Effect of polycations, polyanions and neuraminidase on the infectivity of trachoma-inclusin conjunctivitis and lymphogranuloma venereum organisms HeLa cells: sialic acid residues as possible receptors for trachoma-inclusion conjunction. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.74-79.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. J. Wheat germ agglutinin blockage of chlamydial attachment sites: antagonism by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):946–953. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.946-953.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis H., Sharon N. Lectins as molecules and as tools. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:35–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohringer R., Holden D. W. Protein blotting: detection of proteins with colloidal gold, and of glycoproteins and lectins with biotin-conjugated and enzyme probes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jan;144(1):118–127. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins: cell-agglutinating and sugar-specific proteins. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):949–959. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund G., Kihlström E. Attachment and internalization of a Chlamydia trachomatis lymphogranuloma venereum strain by McCoy cells: kinetics of infectivity and effect of lectins and carbohydrates. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):930–935. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.930-935.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund G., Kihlström E. Physicochemical surface properties of elementary bodies from different serotypes of chlamydia trachomatis and their interaction with mouse fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):893–899. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.893-899.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D., Hackstadt T. Chlamydial hemagglutinin identified as lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3826–3828. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3826-3828.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Meuser R. U. Chlamydia trachomatis elementary bodies possess proteins which bind to eucaryotic cell membranes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):602–607. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.602-607.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]