Abstract
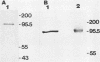
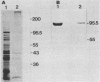
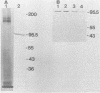
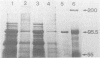
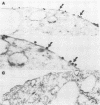
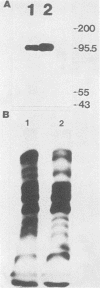
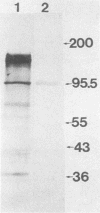
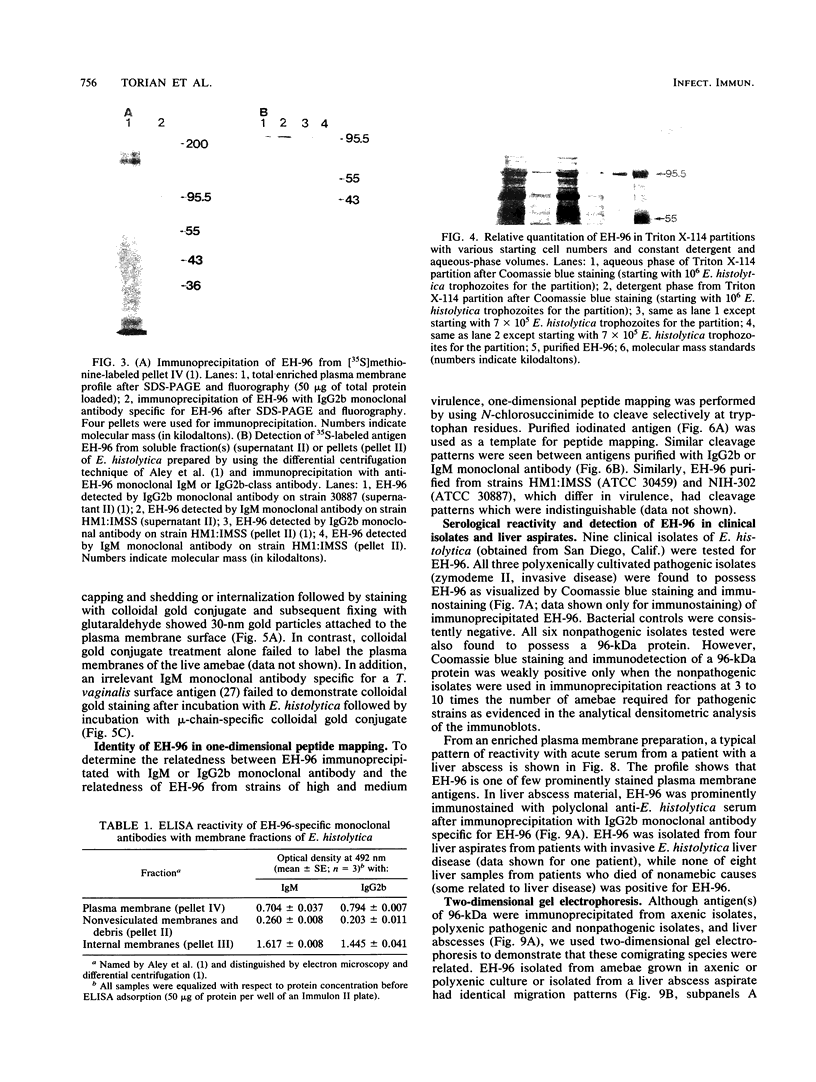
A surface antigen (EH-96) of Entamoeba histolytica was demonstrated to be a plasma membrane antigen by immunoprecipitation of metabolically 35S-labeled antigen from live trophozoites, Triton X-114 detergent extracts, and plasma membrane-enriched fractions prepared by concanavalin A membrane stabilization and differential centrifugation. In addition, the antigen was localized to the plasma membrane by electron microscopy with colloidal gold. Antigen from E. histolytica strains immunoprecipitated with specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) or IgG2b monoclonal antibody was identical by one-dimensional peptide mapping with N-chlorosuccinimide. Additionally, antigen from different axenically cultivated amebae was demonstrated to be identical by N-chlorosuccinimide peptide mapping, as were peptide maps of IgG and IgM monoclonal antibody-purified antigen. The 96-kilodalton (kDa) surface antigen was identified on four axenically cultivated pathogenic isolates and on three polyxenically cultivated pathogenic isolates (zymodeme II) of E. histolytica but was absent or present in lesser quantity on six nonpathogenic polyxenically cultivated isolates. The 96-kDa antigen was detected in liver abscess fluid from four patients with amebic abscesses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunoprecipitation. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis profiles of the 96-kDa antigen purified from abscess material or from polyxenically cultivated trophozoites demonstrated that the antigens were related to the 96-kDa antigen found in axenically cultivated organisms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aley S. B., Scott W. A., Cohn Z. A. Plasma membrane of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):391–404. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhave G. G., Wagle N. M., Joshi U. M. Detection of amoebic antigen by enzyme linked immuno-sorbent assay (ELISA). J Postgrad Med. 1985 Jul;31(3):146–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier J., Etges R. J., Bordier C. Identification and purification of membrane and soluble forms of the major surface protein of Leishmania promastigotes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15504–15509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderón J., Avila E. E. Antibody-induced caps in Entamoeba histolytica: isolation and electrophoretic analysis. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):927–932. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadasi H., Kessler E. Correlation of virulence and collagenolytic activity in Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):528–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.528-531.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel L. I., Giladi M., Huber M., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S. DNA probes specific for Entamoeba histolytica possessing pathogenic and nonpathogenic zymodemes. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):926–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.926-931.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
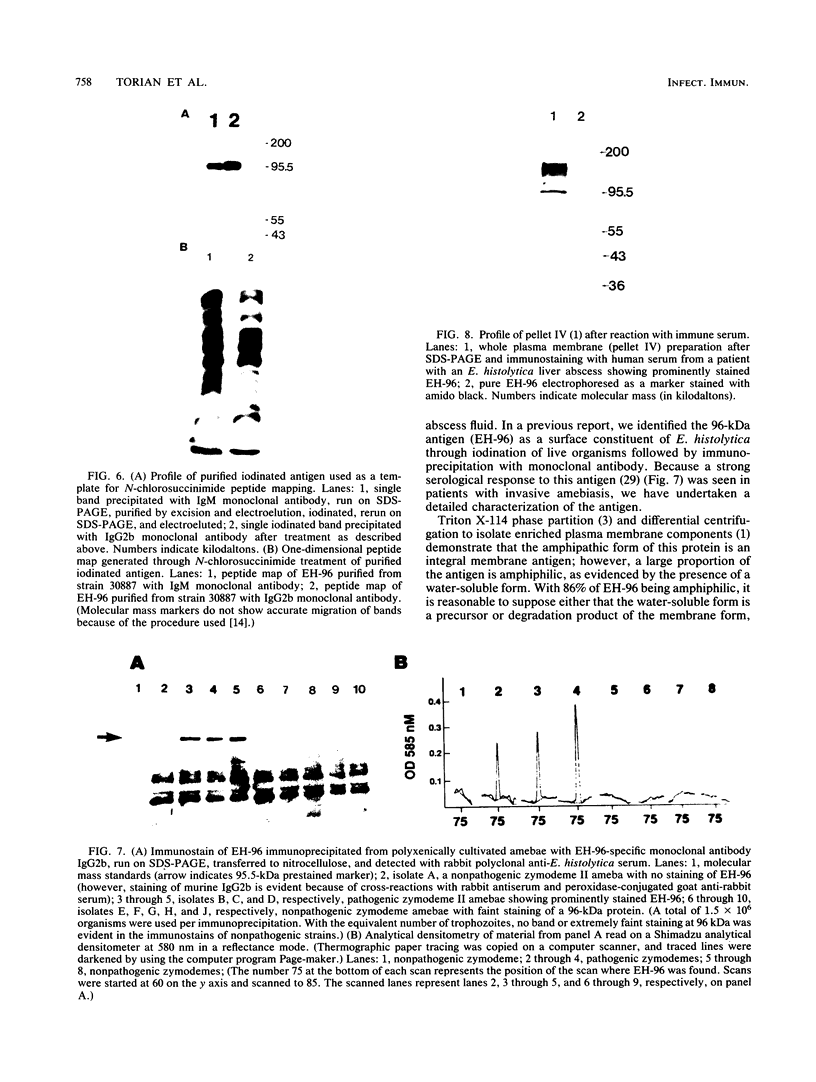
- Lischwe M. A., Ochs D. A new method for partial peptide mapping using N-chlorosuccinimide/urea and peptide silver staining in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):453–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan R. C., Ganguly N. K. Amoebic antigen in immunodiagnosis and prognosis of amoebic liver abscess. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(3):300–302. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Chapman M. D., Snodgrass T., Mann B. J., Broman J., Ravdin J. I. Subunit structure of the galactose and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3007–3012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Joyce M. P., Broman J., Smith R. D., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Recognition of the galactose- or N-acetylgalactosamine-binding lectin of Entamoeba histolytica by human immune sera. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2327–2331. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2327-2331.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Smith R. D., Schlesinger P. H., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Isolation of the galactose-binding lectin that mediates the in vitro adherence of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1238–1244. doi: 10.1172/JCI113198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Croft B. Y., Guerrant R. L. Cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):377–390. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Murphy C. F., Salata R. A., Guerrant R. L., Hewlett E. L. N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. I. Partial purification and relation to amoebic virulence in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):804–815. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. L. The laboratory diagnosis of human parasitic amoebae. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales-Encina J. L., Meza I., López-De-León A., Talamás-Rohana P., Rojkind M. Isolation of a 220-kilodalton protein with lectin properties from a virulent strain of Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Grene J. D. The differentiation of invasive and non-invasive Entamoeba histolytica by isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(5):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Neal R. A. A comparative study of Entamoeba histolytica (NIH :200, HK9, etc.), "E. histolytica-like" and other morphologically identical amoebae using isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan W. D., Chiodini P. L., Spice W. M., Moody A. H., Ackers J. P. Immunological differentiation of pathogenic and non-pathogenic isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. Lancet. 1988 Mar 12;1(8585):561–563. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Horstmann R. D., Knobloch J., Arnold H. H. Genomic DNA differences between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5118–5122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torian B. E., Connelly R. J., Barnes R. C., Kenny G. E. Antigenic heterogeneity in the 115,000 Mr major surface antigen of Trichomonas vaginalis. J Protozool. 1988 May;35(2):273–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1988.tb04343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torian B. E., Lukehart S. A., Stamm W. E. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify, characterize, and purify a 96,000-dalton surface antigen of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):334–343. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torian B. E., Reed S. L., Flores B. M., Plorde J., Stamm W. E. Serologic response to the 96,000-Da surface antigen of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):794–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Harven E., Soligo D. Scanning electron microscopy of cell surface antigens labeled with colloidal gold. Am J Anat. 1986 Feb-Mar;175(2-3):277–287. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001750212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]