Abstract
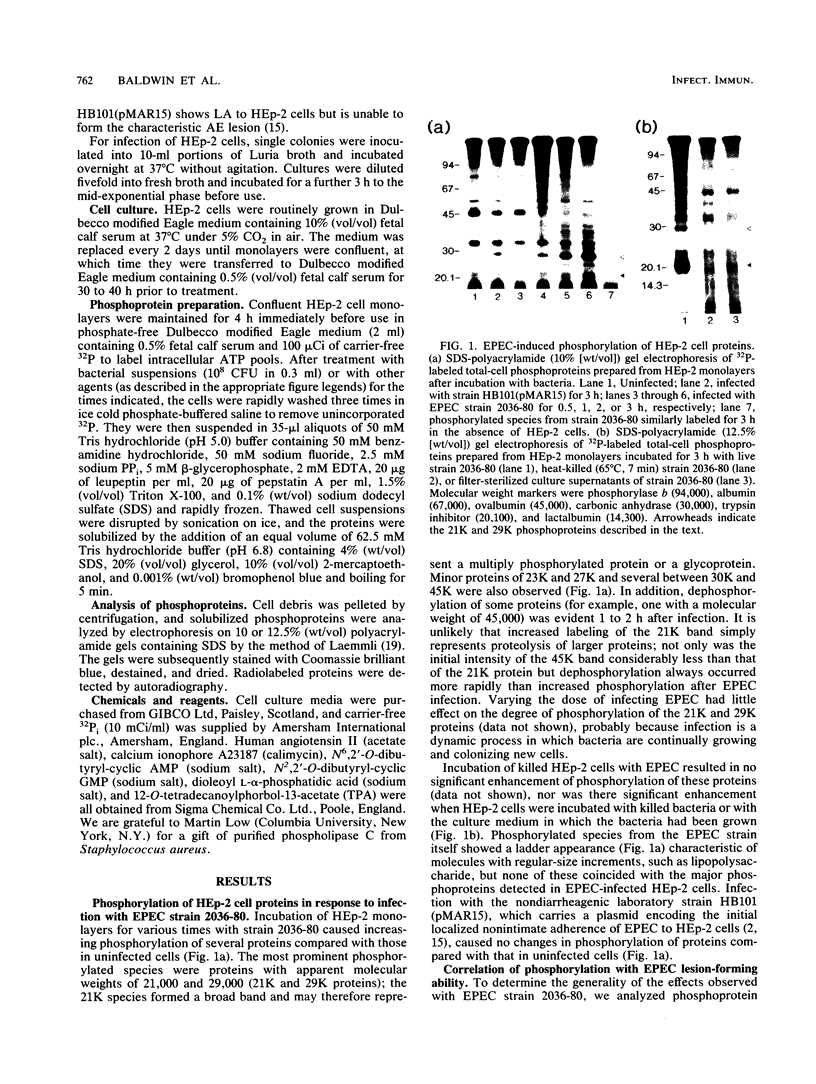
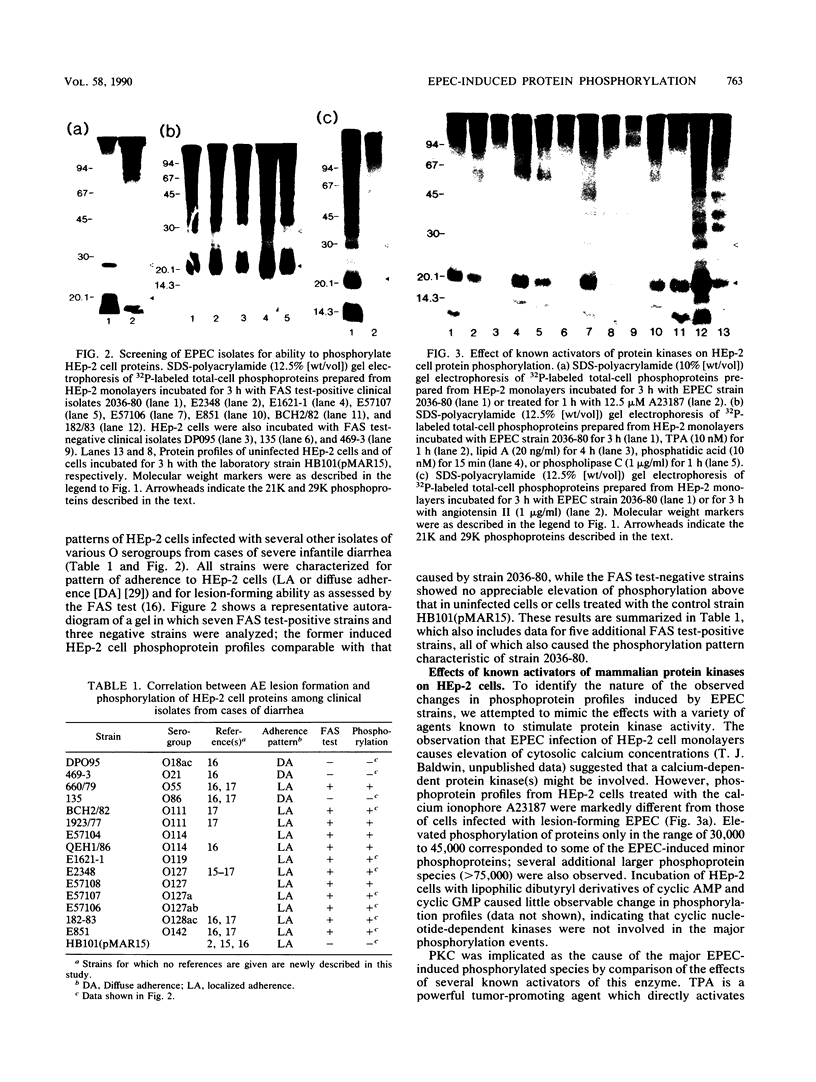
Infection of HEp-2 monolayers with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli 2036-80 (O119) stimulated phosphorylation of several target cell proteins, the most prominent of which had apparent molecular weights of 21,000 and 29,000. Proteins of the same size were phosphorylated in response to known activators of the calcium-phospholipid-dependent protein kinase C. Screening of clinical isolates of various O serogroups revealed that all strains able to form the characteristic attaching and effacing lesion of enteropathogenic E. coli showed elevated phosphorylation of 21,000- and 29,000-dalton protein species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldini M. M., Nataro J. P., Kaper J. B. Localization of a determinant for HEp-2 adherence by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.334-336.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate accumulation in hormone-treated hepatocytes via a phospholipase D mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15309–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran R. J., Schworer C. M., Hashimoto Y., Fong Y. L., Rich D. P., Smith M. K., Soderling T. R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):313–325. doi: 10.1042/bj2580313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C. A., Aitken A., Takayama K., Qureshi N. Substitution of phosphatidylserine by lipid A in the activation of purified rabbit brain protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 29;218(2):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Mechanisms of action of calcium-mobilizing agonists: some variations on a young theme. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2670–2676. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.11.2456243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Mechanisms of action of cholera and Escherichia coli enterotoxins. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):189–196. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fondacaro J. D., Henderson L. S. Evidence for protein kinase C as a regulator of intestinal electrolyte transport. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):G422–G426. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.3.G422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goligorsky M. S., Menton D. N., Hruska K. A. Parathyroid hormone-induced changes of the brush border topography and cytoskeleton in cultured renal proximal tubular cells. J Membr Biol. 1986;92(2):151–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01870704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., McNeish A. S. Role of plasmid-encoded adherence factors in adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):78–85. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.78-85.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal enterocytes and cultured human intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.69-77.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Baron L. S., Buysse J. Genetic determinants of virulence in Shigella and dysenteric strains of Escherichia coli: their involvement in the pathogenesis of dysentery. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:71–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. Virulence factors of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1988 May;26(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., Sotman S. Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan L. C., Aitken A., Heath J., Foulkes J. G. Embryonal carcinoma-derived growth factor activates protein kinase C in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):921–926. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Bansal V. S., Inhorn R. C., Ross T. S., Lips D. L. Inositol phosphates: synthesis and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3051–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manalan A. S., Klee C. B. Calmodulin. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;18:227–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. T., Burgess D. R. Partial reconstruction of the microvillus core bundle: characterization of villin as a Ca++-dependent, actin-bundling/depolymerizing protein. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):648–656. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila P., Häyry P., Renkonen R. Protein kinase C is crucial in signal transduction during IFN-gamma induction in endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):362–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Kruijer W., Tilly B. C., Verlaan I., Bierman A. J., de Laat S. W. Growth factor-like action of phosphatidic acid. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):171–173. doi: 10.1038/323171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Tertoolen L. G., de Laat S. W. Phorbol ester and diacylglycerol mimic growth factors in raising cytoplasmic pH. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):371–374. doi: 10.1038/312371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Scaletsky I. C., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M., Trabulsi L. R. Plasmid-mediated factors conferring diffuse and localized adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):378–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.378-383.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Michetti M., Sparatore B., Salamino F., Sacco O., Horecker B. L. Phosphorylation and proteolytic modification of specific cytoskeletal proteins in human neutrophils stimulated by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3604–3608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Kaibuchi K., Kawahara Y., Fukuzaki H., Takai Y. Induction of protein kinase C activation and Ca2+ mobilization by fibroblast growth factor in Swiss 3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiel J. E., Hamilton T. A., Adams D. O. LPS induces altered phosphate labeling of proteins in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3012–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., Lackie J. M., Haston W. S., Islam L. N. Effects of phorbol esters on shape and locomotion of human blood lymphocytes. J Cell Sci. 1988 Aug;90(Pt 4):645–655. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann A., Gehr P., Keller H. U. Diacylglycerol-induced shape changes, movements and altered F-actin distribution in human neutrophils. J Cell Sci. 1988 Aug;90(Pt 4):657–666. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.4.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge H. R., Lohmann S. M. Mechanisms by which cyclic nucleotides and other intracellular mediators regulate secretion. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;112:116–138. doi: 10.1002/9780470720936.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





