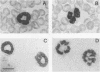
Abstract
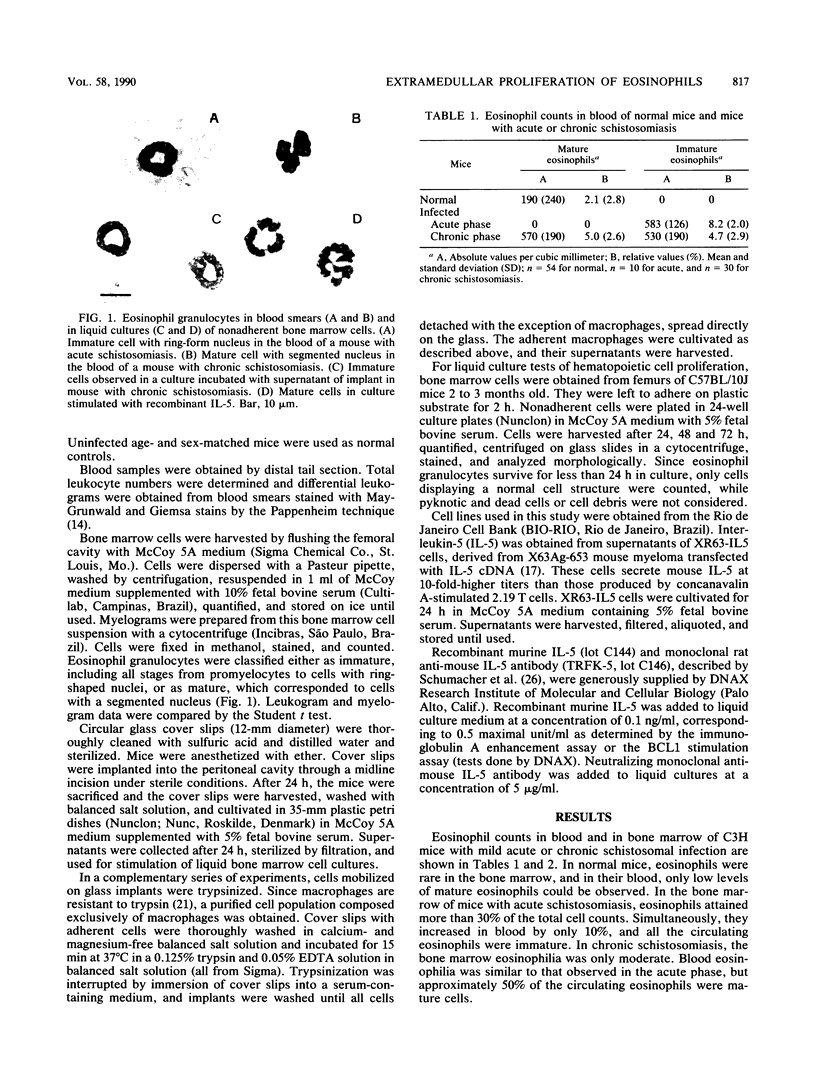
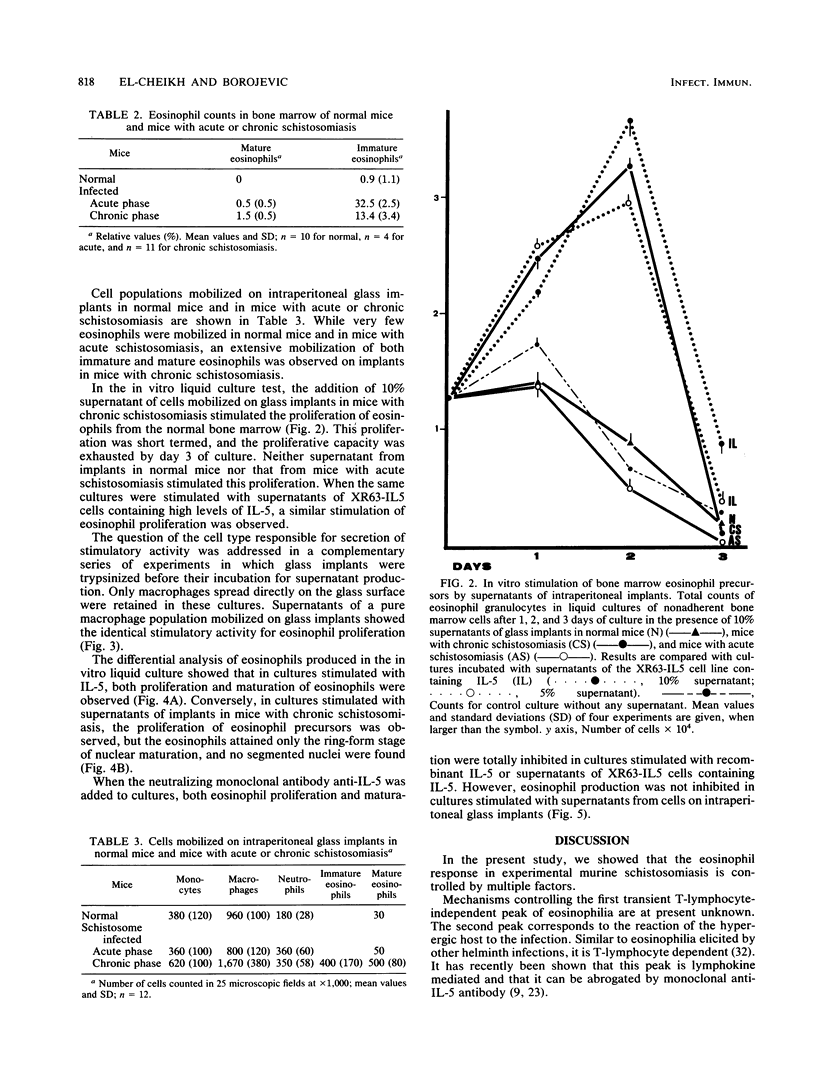
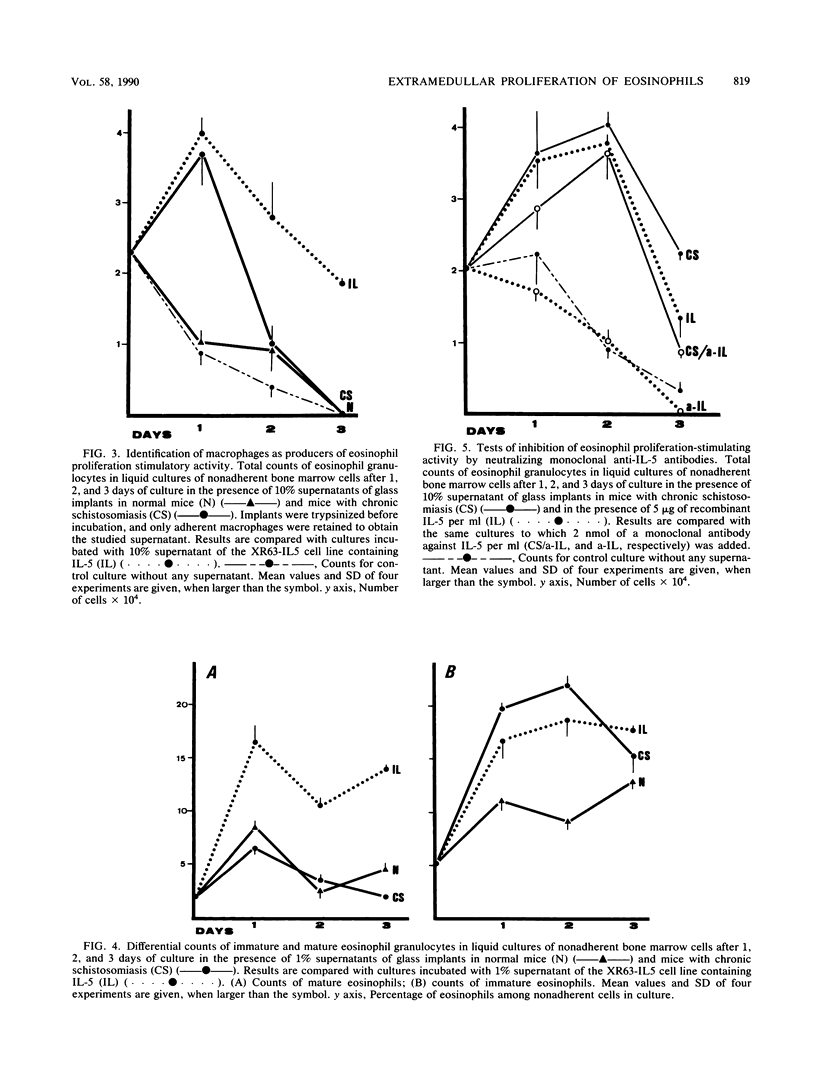
In chronic murine schistosomiasis mansoni, extramedullar myelopoiesis of eosinophils has been described, associated with tissue inflammatory infiltrates and periovular granulomas. It may be experimentally induced by intraperitoneal glass implants in mice with chronic schistosomiasis but not in normal mice or in mice with acute schistosomiasis. In vivo studies showed that this induction depended on macrophages adherent to the implants. In an in vitro test with bone marrow cells, we demonstrated that this eosinophil proliferation was mediated by a factor secreted by the mobilized macrophages. In contrast to murine interleukin-5 (IL-5), which induced both proliferation and differentiation of eosinophils, the studied monokine did not induce their maturation. A potent neutralizing monoclonal antibody for murine IL-5 did not abrogate the stimulatory activity of the monokine, indicating that it is a cytokine distinct from IL-5. These data, together with a quantitation of bone marrow, blood, and peripheral eosinophils, indicated that in chronic schistosomiasis, the systemic medullar supply of eosinophils is supplemented in tissues by their local proliferation, mediated by macrophages mobilized in local granulomatous and diffuse inflammatory reactions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basten A., Boyer M. H., Beeson P. B. Mechanism of eosinophilia. I. Factors affecting the eosinophil response of rats to Trichinella spiralis. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1271–1287. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borojevic R., Cury El-Cheikh M. C., Nicola M. H. Schistosoma mansoni: control of extramedullar eosinophil myelopoiesis in chronically infected mice by inflammatory macrophages. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Dec;62(3):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borojevic R., Nicola M. H., Santos da Silva C. Modulation of macrophage and polymorphonuclear granulocyte inflammatory reaction in experimental murine schistosomiasis mansoni. Cell Mol Biol. 1984;30(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borojevic R., Nicola M. H., Santos-da-Silva C., Grimaldi G., Jr Schistosoma mansoni: extramedullar eosinophil myelopoiesis induced by intraperitoneal glass implants in chronically infected mice. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Jun;59(3):290–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(85)90083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borojevic R., Pinto C. G., el-Cheikh M. C., Dutra H. S. Experimental murine schistosomiasis mansoni: hyperplasia of the mono-macrophage cell lineage and stimulation of myeloid proliferation by peripheral macrophages. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1989;22(5):579–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borojevic R., Stocker S., Grimaud J. A. Hepatic eosinophil granulocytopoiesis in murine experimental Schistosomiasis mansoni. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Oct;62(5):480–489. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byram J. E., Imohiosen E. A., von Lichtenberg F. Tissue eosinophil proliferation and maturation in schistosome-infected mice and hamsters. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Mar;27(2 Pt 1):267–270. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. R., Chen B. D., Boros D. L. Macrophage progenitor cell and colony-stimulating factor production during granulomatous schistosomiasis mansoni in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2680–2685. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2680-2685.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Seymour B. W., Hudak S., Jackson J., Rennick D. Antibody to interleukin-5 inhibits helminth-induced eosinophilia in mice. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):308–310. doi: 10.1126/science.2787531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G. Immune responses to a soluble schistosomal egg antigen preparation during chronic primary infection with Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E. O., Warren K. S. Endogenous desensitization: changing host granulomatou response to schistosome eggs at different stages of infection with schistosoma mansoni. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):369–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. P., Buchanan R. D., Colley D. G. Schistosoma mansoni infection in mice depleted of thymus-dependent lymphocytes. I. Eosinophilia and immunologic responses to a schistosomal egg preparation. Am J Pathol. 1973 May;71(2):193–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaud J. A., Borojević R. Mésenchyme et parenchyme hépatique dans la bilharziose expérimentale à Schistosoma mansoni: métaplasie myéloide. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1972 Feb 7;274(6):897–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenzi H. L., Sobral A. C., Lenzi J. A. "In vivo" kinetics of eosinophils and mast cells in experimental murine schistosomiasis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1987;82 (Suppl 4):67–76. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02761987000800011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariano M., Spector W. G. The formation and properties of macrophage polykaryons (inflammatory giant cells). J Pathol. 1974 May;113(1):1–19. doi: 10.1002/path.1711130102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. L., Grove D. I., Warren K. S. The Schistosoma mansoni egg granuloma: quantitation of cell populations. J Pathol. 1977 Jan;121(1):41–50. doi: 10.1002/path.1711210107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. M., DiConza J. J., Gold J. A., Reid W. A. Schistosomiasis in the congenitally athymic (nude) mouse. I. Thymic dependency of eosinophilia, granuloma formation, and host morbidity. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):594–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular and cellular biology of eosinophil differentiation factor (interleukin-5) and its effects on human and mouse B cells. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schriber R. A., Zucker-Fraklin D. Induction of blood eosinophilia by pulmonary embolization of antigen-coated particles: the relationship to cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1348–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher J. H., O'Garra A., Shrader B., van Kimmenade A., Bond M. W., Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. The characterization of four monoclonal antibodies specific for mouse IL-5 and development of mouse and human IL-5 enzyme-linked immunosorbent. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1576–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein D. S., Dessein A. J., Elsas P. P., Fontaine B., David J. R. Characterization of a factor from the U937 cell line that enhances the toxicity of human eosinophils to Schistosoma mansoni larvae. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):3042–3050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadecker M. J., Wright J. A. Distribution and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes in granulomas elicited by eggs of Schistosoma mansoni. Am J Pathol. 1984 Aug;116(2):245–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Mermod J. J., Vassalli P. Phagocytosis and inflammatory stimuli induce GM-CSF mRNA in macrophages through posttranscriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON LICHTENBERG STUDIES ON GRANULOMA FORMATION. III. ANTIGEN SEQUESTRATION AND DESTRUCTION IN THE SCHISTOSOME PSEUDOTUBERCLE. Am J Pathol. 1964 Jul;45:75–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Goetzl E. J. The regulatory and effector roles of eosinophils. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:339–371. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva L. C., Mourão P. A., Borojevic R. Patterns of sulfated glycosaminoglycan synthesis and accumulation in hepatic granulomas induced by schistosomal infection. Exp Mol Pathol. 1989 Jun;50(3):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(89)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]